Part 3 images Flashcards
(40 cards)
What mechanism does this occur from?

hyperextension mechanism
What is the diagnosis? What makes you think so?

posterior arch fracture of C1
there is a thin vertical line going through the posterior arch of atlas
Findings and diagnosis?

Findings: bilateral lateral mass offset
diagnosis: Jefferson’s fx
What is the diagnosis? What disease is this most commonly seen in?

atlantoaxial instability
RA
What is the diagnosis?

Type II odontoid fracture (high dens fracture)
What is the diagnosis?

low dens fracture (Type III odontoid fracture)
Findings? Diagnosis?

broken Harris’ ring
hangman’s fracture
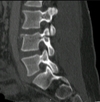
findings? diagnosis?

decreased anterior body height, sclerosis of superior endplate
compression fracture at L1
Old or new fracture?

new
most significant diagnosis?
findings?

burst fracture
vertebral body “exploded” into several fragments
findings? diagnosis?

bowtie sign
unilateral facet dislocation
findings? diagnosis?

perched facets
incomplete bilateral facet dislocation
Findings? Diagnosis?

interlocking facets, bilateral facet dislocation
Findings? Diagnosis?

triangular fragment at the anterior inferior body, facets dislocated
flexion teardrop fracture
Findings? Diagnosis?

triangular fragments in the anterior inferior part of the body, NO facet dislocations
extension teardrop fracture
Findings? Diagnosis?

fracture of the spinous process of C6
Clay Shoveler’s fracture
Diagnosis?

Spinous fracture at C4
Diagnosis?

Laminar fracture
Diagnosis?

Pillar fracture at C6
Findings? Diagnosis?

increased interspinous space between C7 and T1
whiplash injury
Findings?
Diagnosis?

decreased vertical height of L1 anterior body
compression fracture of L1
Findings? Diagnosis?

Dowager’s hump due to multiple compression fractures
Compression fractures most likely due to osteoporosis
Findings? Diagnosis?

Decreased anterior and posterior height at L3, posterior body convexity
burst fracture of L3
Findings? Diagnosis?

increased radiolucency of the pedicles on the AP, decreased body height anteriorly and posteriorly
pathological fracture most likely due to osteoporosis, multiple myeloma or lytic mets