Revision Lecture Flashcards
(20 cards)
List the key features of rheumatoid arthritis
- Morning stiffness in and around joints
- Symmetrical polyarthritis typically involving the small joints of the hand and/or wrists
- Subcutaneous nodules
- Rheumatoid factor
- Joint erosions on radiographs
Define rheumatoid factor.
Antibodies that recognize the Fc portion of IgG as their target antigen
typically IgM antibodies i.e. IgM anti-IgG antibody !
What substance makes synovial fluid viscous?
Hyaluronic acid = a non-sulphated glycosaminoglycan
Define Reactive Arthritis
Sterile inflammatory synovitis following an infection whose extra-articular manifestations may include:
Key features
- Enthesopathy
- Skin inflammation (circinate balanitis, keratoderma blennorrhagicum)
- Eye inflammation (conjunctivitis)
List two infections associated with Reactive Arthritis.
Urogenital infections
- E.g. Chlamydia trachomatis
Enterogenic infections
- E.g. Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter infections
- Reactive arthritis may be first manifestation of HIV or hepatitis C infection*
Define and give two examples of an enthesopathy.
Inflammation where a ligament, tendon, fascia or capsule insert into bone.
Examples include:
- Achilles tendonitis (painful heel) - inflammation at insertion of Achilles tendon into calcaneum
- Plantar fasciitis (painful feet) - inflammation at insertion of plantar fascia
- Dactylitis (swollen digits) - inflammation at insertion of capsule and ligaments in digits
- Spondylitis (spinal inflammation) in Ankylosing Spondylitis - inflammation where the outer part (annulus fibrosis) of the inter-vertebral disc inserts into the vertebral body
Rheumatoid vs reactive arthritis, complete the table..


In a single statement summarise the key pathological finding in osteoarthritis.
Irreversible loss of articular cartilage

Define (i) proteoglycan and (ii) glycosaminoglycan and give one example of each.
- glycoproteins containing sulphated glycosaminoglycan chains e.g.
* Aggrecan - repeating polymers of disaccharides e.g.
- Chondroitin sulphate
- disaccharides are: glucuronic acid and N-acetyl galactosamine
- Keratan sulphate
- disaccharides are: galactose and N-acetyl glucosamine
- Hyaluronic acid (= hyaluronate)
- disaccharides are: glucuronic acid and N-acetyl glucosamine
What is the major (i) collagen and (ii) proteoglycan found in articular cartilage?
(i)Type II collagen
(aide memoire – two T’s in articular cartilage = type two collagen, Bone has one in it so = type one collagen)
(i)Aggrecan

Radiographic changes in Rheumatoid Arthritis vs. Osteoarthritis.
Complete the table with YES or NO +/- comments.


List the major HLA association for each of the following diseases.
Ankylosing Spondylitis & Reactive Arthritis HLA-B27
SLE HLA-DR3
Rheumatoid arthritis HLA-DR4
Summarise the composition of bone
Bone is comprised of protein matrix (osteoid) and mineral (hydroxyapatite)
Osteoclasts resorb bone, osteoblasts form bone
Define Osteoporosis
Predisposition to skeletal fractures resulting from reduction in regional or total bone mass

Define Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia literally means ‘soft bones’ and is defined as impaired mineralisation in mature bones. Rickets is impaired mineralisation in immature bones
Most frequently due to inadequate extracellular fluid concentration of phosphate and/or calcium
Causes include:
- Vitamin D deficiency (can measure vitamin D level so easy to determine)
- Abnormal vitamin D metabolism e.g. liver or kidney disease
- Hypophosphataemia (may be due to renal phosphate loss which can be determined by measuring urinary phosphate levels)
Associated with:
- Low or normal serum calcium
- Low phosphate
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism i.e. high PTH and high serum alkaline phosphatase
Define Paget’s disease.
Disorder of bone remodelling of unknown cause where there is increased bone resorption followed by increased bone formation. This results in disorganised mosaic pattern of woven and lamellar bone
- Bone chemistry shows high alkaline phosphatase
- Paget’s is associated with increased cortical bone thickness on radiographs
The abnormal bone causes:
- Pain
- Bone deformity and sometimes fracture
Describe some biochemical changes in metabolic bone disease.

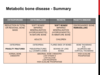

What is renal osteodystrophy?
Collective name for musculoskeletal disorders in chronic renal failure
They include:
- Secondary and tertiary hyperparathyroidism
- Osteomalacia
- Soft tissue and vascular calcification


