Section 1: Chapter 2 Secondary Dominants And Borrowed Chords Flashcards
(32 cards)
Secondary dominants give the effect of which progression?
V-I
The compositional method used to give a momentary tonic sound to a chord is called:
Tonicization
What is the term used to describe a harmony with chromatic alterations?
Chromaticism
The chord quality of a secondary dominant will always be:
Dominant/ Maj min7
A secondary leading tone chord is constructed on which interval below its target chord?
Minor 2nd
The technique that uses chords borrowed from a parallel key is known as:
Mode Mixture
When the tonic chord is borrowed from the Major and is used in place of the I, it is called a ___________:
Picardy 3rd
What are secondary dominants?
A secondary dominant is a triad or dominant seventh chord built upon the dominant of supertonic (ii), mediant (iii, III), subdominant (iv, IV), dominant (V), submediant (vi, VI), and subtonic (VII) of the prevailing key.
What is used for harmonic analysis for secodary dominants?
use two Roman numerals separated by a slash.
The top Roman numeral will reflect the function and the quality of the chord; the bottom numeral will reflect the secondary chord relation. For example, a V7/ii, would literally translate to the dominant seventh of the supertonic (ii) minor. A more common interpretation would be the “Five seven of two.”
What are characteristics of secondary dominants in Major?

- Secondary dominants will have at least one pitch that is foreign to the key.
- The most common form of a secondary dominant is the V/V or the V7/V.
- Secondary dominants will only be used to precede a Major or minor qualitychord.
- The use of the V/IV is a possibility; however, it is not the best option becauseV/IV is identical to tonic (I) of the key.
- Composers will add a 7th to the secondary dominant of the IV (V7/IV) in order togive greater clarity to tonicization.
What are characteristics of secondary dominants in the Minor mode?
The same concepts apply in minor as they do in Major with a few additions.
- The V/III and V7/III are respectively identical to the VII and VII7 but are still an option as a secondary dominant.
- The V/III and V7/III are not chromatically altered, but are still an option for a secondary dominant.
- The V/VI is normally analyzed as the III vice a secondary dominant.

How is a V/ii, V7/ii used in an harmonic structure?
Any inversion except 2nd
How is a V/iii, V7/iii used in a harmonic structure?
Any inversion except 2nd
How is a V/III, V7/III used in a harmonic structure?
any inversion
How is a V/iv, V7/iv used in a harmonic structure?
any inversion
How is a V7/IV used in a harmonic structure?
any inversion
How is a V/V, V7/V used in a harmonic structure?
Major: Any inversion
Minor: Any inversion except 2nd
How is a V/vi, V7/vi used in a harmonic structure?
Any inversion
How is a V/VI, V7/VI used in a harmonic structure?
Any inversions
2nd inversion – only used in a descending line
How is a V/VII, V7/VII used in a harmonic structure?
Any inversion 2nd
Are seventh chords available for tonicization its secondary dominant?
Primary and secondary triads that are available for tonicization by a secondary dominant, may occur with its dominant 7th tone.
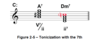
What is the voice movement of a secondary dominant?
Secondary dominants are typically treated the same as regular V7 or V chords, specifically, with regards to voice leading. Leading tones will resolve up and the 7ths will resolve down. If a secondary dominant 7th is resolving to another 7th chord, the leading tone may move down chromatically.

What are the principles for secondary leading tone chords?
- If the triad being tonicized is minor, use the fully diminished 7th secondaryleading tone chords (viio7/).
- If the triad being tonicized is Major, use the viio7/ or viiø7/.
- The viio7 is more widely used.
- Secondary leading tones move in the same manner as secondary dominants.
•Take caution not to double the 7th in resolving the viio7/V or the vii ø7/V.
Is there an exception to the secondary leading tone chord?
there is no secondary leading tone chord for the V chord in the vii ø7. This is an exception to the statement, “any chord or triad that can be tonicized by a secondary dominant may be tonicized by a secondary leading tone.”


