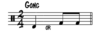Section 3: Chapter 6 Orchestration Flashcards
(97 cards)
_____________________ is the practice of assigning instruments to musical lines
Orchestration/Scoring
T/F Understanding the functionality of each instrument in an ensemble is necessary to apply proper orchestration.
True
When scoring for woodwinds, what function may the section be used for? A. Melodic lines B. Echoing figures C. Fast and difficult lines D. Color and contrast E. All of the above
A. Melodic lines B. Echoing figures C. Fast and difficult lines D. Color and contrast
Homophonic is directly translated to _______________, while Polyphonic is directly translated as ________________.
Same sound, many sounds
T/F It is best to orchestrate instrument combination within the most comfortable range of the horn.
True
Four techniques to homophonic voicings are _____________, _____________, _______________, and __________________.
Superimposed, Interlocked, Enclosed, Overlapped
T/F A limitation to a pure unison doubling between two instruments is their individual ranges.
True
Examples of polyphonic writing include, A. Solos B. Canons C. Fugues D. Both B and C E. None of the above
Cans and fugues
Percussion instruments can be divided into 2 families, __________________ and _____________________ percussion.
Definite Pitch, Indefinite Pitch
Indefinite pitch percussion is scored using a ____________ clef on ____ line staff or ______________ line.
Neutral, 5, Rhythm
__________________ percussion produces a pitch which can be recognized
Definite Pitch
T/F Vocalists rely on the ear to hear and perform a pitch. One way to help internalize the pitch for a vocalists is through establishing tonality via a harmonic cadence.
True
Does the woodwind family produce homogenous or heterogenous sounds?
It has a heterogeneous sound due to its inclusion of non-reeds, single reeds, and double reeds.
How do you determine which instrument or tone color is best suited for a particular theme?
musical taste, experience, and personal preference come into play.
What is the practical range of a piccolo?
The piccolo has a practical range that spans from D4 to C7.
What are the characteristics of the various ranges of the piccolo?
The low registers of the piccolo will produce a breathier, hollow tone that becomes brighter and clearer as the pitches increase. At the top of its register the piccolo can have a brilliant, piercing timbre that can cut through the rest of the ensemble.

What is the practical range for a flute?
The flute is a non-transposing instrument with a practical range that spans from C4 to C7.
How does the flute differ from the piccolo?
the flute differs in that its character is exceedingly appropriate when melodic lines require a warm, dark, and rich sound.

What is the practical range of an oboe?
The oboe is a non-transposing instrument with a practical range that spans from B3 to F6.
What are characteristics of an oboe
- At its lower pitches the oboe has a reedy, uncentered tone
- Capable of being heard through an ensemble
- It will often blend well with the flute, clarinet and muted trumpet.

What is the practical range of a bassoon?
The bassoon is a non-transposing instrument with a practical range that spans from B♭1 to B♭4.
What are characteristics of the bassoon?
- a reedy, uncontrolled timbre in its lower range and a brighter, clearer tonality within its mid- to upper register.
- a reedy sound that blends well with the tenor saxophone, and any member of the low brass section.

What is the practical range of a clarinet?
The B♭clarinet is a transposing instrument, sounding a Major 2nd lower than written. Its written practical range spans from E3 to G6, giving it the largest range in the woodwind family.
What are characteristics of the clarinet?
- In its lower register the clarinet will produce a warm, full tone that becomes brighter within the instruments higher pitches.
- At the top of its range, the clarinet will produce a much thinner and piercing characteristic.