Cardio/Neuro Flashcards
(16 cards)
Astrocyte (3 functions, marker, embryology)
Maintain BBB, Metabolize K, Provide reserve of glycogen buffer
Marker: GFAP
Embryology: Neuroectoderm

Drugs that predispose to long QT and thus to Torsades de Pointes
(ABCDE)
Very anti going into Torsades
ABCD
AntiArrhythmics (class IA, III)
AntiBiotics (e.g., macrolides)
Anti“C”ychotics (e.g., haloperidol)
AntiDepressants (e.g., TCAs)
AntiEmetics (e.g., ondansetron)
Serotonin Syndrome (what causes it, sx, tx)
Caused by any drug that increases 5HT
MAO inhibitors, SNRIs, TCAs
Sx: hyperthermia, confusion, myoclonus, cardiovascular instability, flushing, diarrhea, seizures.
Treatment: cyproheptadine (5-HT2 receptor antagonist).
Broca aphasia
nonfluent expressive aphasia with good comprehension
Broca=broken Boca
Broca area is located in inferior frontal gyrus of frontal lobe

Familial hypercholesterolemia
Elevated LDL due to defective or absent LDL receptor. Leads to severe atherosclerotic disease early in life, corneal arcus, tendon xanthomas (classically in the Achilles tendon).

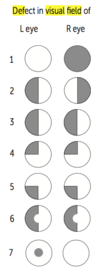
Visual Field Defects

- Right anopia
- Bitemporal hemianopia (pituitary lesion, chiasm)
- Left homonymous hemianopia
- Left upper quadrantic anopia (right temporal lesion, MCA)
- Left lower quadrantic anopia (right parietal lesion, MCA)
- Left hemianopia with macular sparing (PCA infarct), macula bilateral projection to occiput
- Central scotoma (macular degeneration)
GPCR associated with:
A1
A2
B1,B2,B3
M1
M2
M3
D1
D2
H1
H2
V1
V2
QISSS and QIQ till you’re SIQ of SQS
“KISS and KICK till you’re SICK of SEX”
A1: Gq
A2: Gi
B1,B2,B3: Gs
M1: Gq
M2: Gi
M3: Gq
D1: Gs
D2: Gi
H1: Gq
H2: Gs
V1: Gq
V2: Gs
Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome
Most common type of ventricular pre- excitation syndrome. Abnormal fast accessory conduction pathway from atria to ventricle (bundle of Kent) bypasses the rate-slowing
AV node ventricles begin to partially depolarize earlier characteristic delta wave with widened QRS complex and shortened PR interval on ECG. May result in reentry circuit supraventricular tachycardia

Coarctation of the aorta is seen in what pts
- Associated with bicuspid aortic valve, other heart defects, and Turner syndrome
- Hypertension in upper extremities and weak, delayed pulse in lower extremities (brachial-femoral delay). With age, collateral arteries erode ribs (notched appearance on CXR).

Meduloblastoma
- Most common primary brain tumor in children
- Highly malignant cerebellar tumor. A form of primitive neuroectodermal tumor. Can compress 4th ventricle, causing hydrocephalus. Can send “drop metastases” to spinal cord.
Increased ICP, cerebellar ataxia and nystagmus are all sx
Homer-Wright rosettes. Solid (gross), small blue cells

Tardive Dyskinesia
-stereotypic oral- facial movements as a result of long-term antipsychotic use.
Seen with older, high potency antipsychotics…which are: Haloperidol, trifluoperazine, fluphenazine, thioridazine, chlorpromazine (haloperidol + “-azines”).
What is this called? Found in normal aging adults in heart, colon, liver, kidney, eye, and other organs

-Lipofuscion
“wear and tear” pigment associated with normal aging
-Formed by oxidation and polymerization of autophagocytosed organellar membranes
Funcitons of following pathways/nucleus:
Locus Coeruleus
Mesolimbic/Mesocortical
Nigrostriatal Pathway
Paramedian Pontine Reticular Formation
Raphe Nucleus
Locus Coeruleus: site of norepinephrine synthesis
Mesolimbic/Mesocortical: major DA pathway associated with schizophrenia. Mesocortical is associated with negative sx (blunting of affect, anhedonia). Mesolimbic is associated with positive sx (hallucinations, dilusions, disorganized thought)
Nigrostriatal Pathway: DA pathway associated with Parkinsons
Paramedian Pontine Reticular Formation (PPRF): gaze center responsbile for rapid eye movement associated with REM
Raphe Nucleus: major source of 5HT in brain
Receptors that act via Gq pathway
(those Gq models could use some candy)
H1
Alpha-1
V1
M1
M3
HAVe-1 M&M
Receptors that act via Gi pathway
MAD GI JO=2 letters
M2
Alpha-2
D2
MAD-2’s


