ID Flashcards
(29 cards)
Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors (general groups, 5)
- PCN
- Cephalosporins
- Carbapenems
- Monobactams: Aztreonam
- Vancomycin
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors (general groups, 7)
- Aminoglycosides: Tobramycin, Gentamycin
- Tetracyclines: Docycycline, Minocycline
- Macrolides: Erythromycin, Azithromycin, Clarithromycin
- Lincomycins: Clindamycin
- Synthetic agents: Chloramphenicol
- Streptogramins: Quinupristin/Dalforpristin
- Oxazolidinones: Linezolid
Inhibitors of Folic Acid synthesis (2)
- Sulfonamide (analogs of PABA that competitively inhibit enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase) 2. Trimethoprim (inhibit dihydrofolate reductase) *NOT as sulfonamide*

Inhibit DNA Topoisomerase (1)
- Floroquinolones: Ciprofloxacin, Moxifloxicin, Levofloxacin
Abx that damage DNA (1)
- Metronidazole

Abx that inhibit mRNA synthesis (1)
- Rifampin (use with vancomycin in coag negative Staph infections)
use for prophylaxis for exposed pts to Neisseria Meningococci and Haemophilus Infleunza

mumps
paramyxovirus that causes mumps (uncommon due to effectiveness of MMR vaccine)
Symptoms: Parotitis, Orchitis (in ammation of testes), and aseptic Meningitis. Can cause sterility (especially after puberty).

Fishy smell from vagina
Gardnerella vaginalis
-pleomorphic, gram-variable rod involved in bacterial vaginosis. Presents as a gray vaginal discharge with a shy smell; nonpainful (vs. vaginitis). Associated with sexual activity, but not sexually transmitted. Bacterial vaginosis is also characterized by overgrowth of certain anaerobic bacteria in vagina. Clue cells, or vaginal epithelial cells covered with Gardnerella bacteria (“stippled” appearance along outer margins)

HSV1 and HSV2

Enveloped, Double Stranded Linear DNA virus. Dx by intranuclear inclusion bodies. Seen on Tzanck smear (multinucleated giant cells). Dew drops on rose petal (vesicles on erythematous base)
HSV1: cause of gingivostomatitis, keratoconjunctivitis, and herpes labialis. Can get herpetic whitlow on finger (usually a dentist). Most common cause of temporal lobe encephalitis (presents as AMS, seizures, aphasia). latent in trigeminal nerve
HSV2: cause of herpes genitalis, neonatal herpes. Associated with painful inguinal lymphadenopathy. Latent in sacral ganglia. Viral meningitis more common with HSV2
Ebstein-Barr Virus (HHV-4)

- Spread through respiratory secretions, saliva “kissing disease” (common in teens and young adults)
- Mononucleosis: fever hepatosplenomegaly (AVOID contact sports due to risk of splenic rupture)
- Associated with lymphoma (Endemic or African Burkitt Lymphoma) as well as Hodgkins Lymphoma (mixed cellularity type), nasopharyngeal carcinoma (Asian pts), and oral hairy leukoplakia (white plaque on tongue)
- Infects B cells through binding CD21 on B-cells
Dx: Monospot test: heterophile antibodies detected by agglutination. If treated PCN for strep, show maculopapular rash
Cytomegalovirus (HHV-5)

- DS linear virus, member of the herpes family
- Transmitted via congenital transfusion, sexual contact, saliva, urine, transplant
- Latent in mononuclear immune cells
- Number one cause of mental retardation due to viral illness, also number one cause of virus induced hearing loss
- Seen in HIV/AIDS immunocompromised pts when CD4<50
Tx: Gangyclovir or Foscarnet when have UL97 mutation
-Mononucleosis with -Monospot**
Varicella Zoster Virus (HHV-3)
- Herpes family virus, enveloped DS and linear
- Childhood is Chickenpox
- Transmitted resiratory droplets. Dew-drop on rose petal (like HSV)
- Adult presentation is pneumonia and encephalitis (can happen in kids too but more rare)
- Varicells vaccine now: live-attenuated
tx: acyclovir
Virus remains dormant in DRG. Reactivated with stress, age, and immunocompromised =Shingles. Follows dermatomal distribution. NOT cross midline. Pain can last after rash goes away =post-herpetic neuralgia
Zoster virus >60 adults. Live-attenuated. Can give to AIDS pts >200
tx: Valcyclovir and Famcyclovir
Human Herpes Virus 6 =Roseola

-DS DNA virus, primary host is human. Herpes virus family
-Infects CD4 cells
=Exanthum subitum
High fever (4 days) often >104, can cause seizures followed by maculopapular rash that spares face immediately
-Affects children 6mo-2 years
Tx: cool pt and supportive
-HHV-7 is a less common cause of Roseola
Rubella vs Roseola vs Rubeola
Rubella: German (3 day) measles. Blueberry muffin appearance, starts on face and spreads to extremities
Rubeola: ordinary measles. 3 C’s of measles: Cough
Coryza Conjunctivitis. “O for Ordinary”
Roseola: HHV6. High fever 4 days followed by rash sparing face

HHV8

- Member of herpes family, DS DNA, linear, enveloped
- Causes Kaposi Sarcoma (neoplasm of endothelial cells)
- Transmission via sexual contact
- Associated with AIDS and immunosuppression
- Etrythemtous lesions on extremities that are violacious in colors. Violet color. Causes proliferation of vasculature. Causes dysregulation of VEGF
- Can affect hard palate of mouth or GI tract as well as extremities
- Found in adults in Africa and old Russian men
tx: antiretroviral therapy or decrease immunosuppression
DDX: bartonelia (cat scratch fever), need to differentiate microscopically
Live Attenuated Vaccines
Smallpox
Yellow fever
Rotavirus
Chickenpox (VZV)
Sabin polio virus
MMR
Influenza (intranasal)
Mnemonic: Live! One night only! See small yellow rotating chickens get vaccinated with Sabin and MMR! It’s incredible!
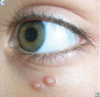
Molluscum contagiosum
flesh colored papule with central umbilication. Usually self-limiting. +/- itching
-Part of the poxvirus family (DS, enveloped, and linear, largest DNA virus), same family as SMALLPOX
subacute sclerosing panencephalitis
- Seen in late stages of Rubeola (measles) infection
- Usually presents 7-10 years AFTER measles infection
4 stages
1. Initial stage presents with dementia and personality changes. Lasts up to 1 year
- severe myoclonus, lasts 3-12 months
3/4. Worsening dementia, decotricate rigidity and eventual fatality
*Look for this answer in question stems where child was NOT vaccinated**
Most common cause of meningitis in children <6 months old?
Group B strep
GBS mothers pass to child through vaginal canal. Should be screened and treated for GBS prior to infection

Which two bugs have the mechanism where their exotoxin inactivates Elongation Factor 2?
- Corynebacterium Diptheriae (Diptheria toxin)
- Pseudamonas Aeurinosa (Exotoxin A)
Bacterial Conjugation
-Bacterial DNA is transferred directly from one bacterium to another

Hep C virus belongs to what family of viruses and what are 4 other examples?
-Flavivirus (enveloped, SS, Linear, RNA virus, icosahedral).
Other Flavirivuses include:
Yellow Fever
Dengue
St. Louis Encephalitis
West Nile Virus
Rhabdovirus

Virus responsible for Rabies. SS - sense RNA virus that is typically bullet shapped and forms Negri bodies (cytoplasmic inclusions commonly found in Puekinje cells of cerebellum and hippocampal neurons)
- If infected need to give 1. killed vaccine and 2. passive immunizations (preformed Ab) BEFORE sx arise. Incubation period is weeks to months depending on how distal bite was.
- Travel to CNS by retrograde up axons on DRG –> brain 1-3mm/day. Infects post synaptic motor endplate (binds ACh receptors)
- BATS most common in US
- malaise –> agitation, photophobia, hydrophobia, hypersalivation –> paralysis, coma –> death






