Life Cycles Flashcards
(32 cards)
LH acts on…to produce FSH acts on…to produce (in males)
- LH –> Leydig cells to produce Testosterone, StAR, SCP
- FSH –> Sertoli cells to produce Androgen Binding Protein (ABP), Aromatase (convert androgen to estrogen), increase spermatogenesis, increase inhibin

first sign of puberty in boys and girls and at what age?
Boys: testicular enlargement (>3ml) age 9-14
Girls: breast bud development age 8-13 in caucasian girls
*African Americans and Hispanic girls start puberty on average 1 year earlier*
McCune-Albright syndrome
due to mutation affecting G-protein signaling. Presents with unilateral café-au-lait spots, polyostotic
fibrous dysplasia,precocious puberty, multiple endocrine abnormalities. Lethal if mutation occurs before fertilization (affecting all cells), but survivable in patients with mosaicism
Tx: girls can be treated with aromatase inhibitor to block conversion of androgens to estrogen.
boys: treated with ketoconazole or combo of androgen blocker and aromatase inhibitor

Branchial (pharyngeal) apparatus
Branchial clefts: derived from ectoderm (also called grooves)
Branchial arches: derived from mesoderm (muscles, arteries), and neural crest (bones, cartilage)
Branchial pouches: derived from endoderm
CAP covers outside to inside
Clefts=ectoderm
Arches=mesoderm + neural crest
Pouches= endoderm
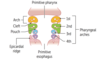
Branchial cleft derivatives
1st: external auditory meatus
2nd-4th: temporary cervical sinus (obliterated by proliferation of 2nd arch mesenchyme)
What is the result of Mullerian agenesis?
presents as primary amenorrhea (due to lack of uterine development, because mullerian develops into uterus, fallopian tubes, upper 2/3 of vagina (columnar epithelium))
-have fully developed secondary sexual characteristics (like functional ovatres)
Mesonephric ducts also known as….
Paramesonephric ducts also known as…
mesonephric=wolffian
paramesonephric= mullerian
-incomplete fusion of the paramesonephric ducts results in bicornuate uterus (uterus has two horns with communicating ducts
Picture shows partial failure of fusion of paramesonephric ducts

mesonephric duct becomes…in males
male internal structures (except prostate)
- Seminal Vesicle
- Epididymus
- Ejactulatory Duct
- Ductus Deferens
SEED
pathway of sperm during ejactulation
SEVEN UP
S: seminiferous tubules
E: epididymus
V: Vas deferens
E: ejaculatory ducts
N: NOTHING
U: urethra
P: penis
In females, FSH acts on… and LH acts on…
FSH–> Granulosa cells to convert androgens to estrogens via aromatase
LH –> Theca cells to convert cholesterol to androgens via desmolase
Actions of progesterone (9)
- stimulation endometrial glandular secretions
- maintain pregnancy
- decrease myometrial excitability
- produce cervical mucus to inhibit sperm entry
- increase body temp
- inhibit gonadotropins (LH, FSH)
- uterine smooth muscle relaxation (prevent contraction)
- decrease estrogen receptor expression
- prevent endometrial hyperplasia
phases of miosis that egg is suspended in
Primary oocyte begin meiosis 1 during fetal life and complete miosis 1 just prior to ovulation
Meiosis I is arrested in prOphase 1 for years until Ovulation (10 oocyte)
Meiosis II is arrested in metaphase II until fertilization (20 oocyte) “an egg MET a sperm”

Mittelschmerz
transient mid-cycle ovulatory pain (Middle Hurts); classically associated with peritoneal irritation (follicular swelling/rupture, fallopian tube contraction)
-can mimic appendicitis

Menorrhea Terms
- Dysmenorrhea
- Oligomenorrhea
- Polymenorrhea
- Metrorrhagia
- Menorrhagia
- Menometrorrhagia
- Dysmenorrhea: pain with menses, often associated with endrometriosis
- Oligomenorrhea: > 35 day cycle
- Polymenorrhea: <21 day cycle
- Metrorrhagia: Frequent or irregular menstruation
- Menorrhagia: Heavy menstrual bleeding >80ml blood loss or >7 days of menses
Menometrorrhagia: Heavy, irregular menstruation
hCG fun facts (source, function)
Source is syncytiotrophoblast of placenta
- maintain corpus luteum (and thus progesterone) for first 8-10 weeks by acting like LH
- Used to detect pregnancy (appears in urine 2 weeks, appears in blood 1 week)
- Identical alpha subunits to LH, FSH, TSH (unique Beta subunit, what test)
Klinefelter syndrome
male 47, XXY
Testicular atrophy, eunuchoid body shape, tall, long extremities, gynecomastia, female hair distribution.
- Presence of inactivated X-chromosome (Barr Body)
- Dysgenesis of seminiferous tubules –> decresed inhibin B –> increased FSH
- Abnormal leydig cell function –> decreased testosterone and Increased LH –> increased estrogen

struma ovarii
cystic ovarian mass in combination with signs of excessive thyroid hormone
- a thyroid hormone secreting teratoma
- manifests as unilateral, cystic, pelvic masses with concomminant hyperthyroid sx
What hormone is responsible for development of external male genetalia (prenatally)
DHT (prenatally)
Later it is involved in development of secondary sexual characteristics such as hair distribution, increased statue, increased sweat gland secretion. Also causes an increase in the size of the prostate and epididymus
A positive transillumination test of the testes suggests…
A cystic mass, a testicular hydrocele is the most common cause of painless scrotal enlargement
orchitis and what are the cuases
testicular inflammation
- usually caued by viral infection (rubella, mumps) or bacterial infection
- pain, tenderness and erythema are common sx
hydrocele
fluid collection in the space between the visceral and parietal layer of the tunica vaginalis of the scrotum

Pseudomyxoma peritonei
intraperitoneal accumulation of mucinous material from ovarian or appendiceal tumor.
wehre do sperm achieve motility and what is the lining of this structure
Spermatogenesis takes place in the seminal vesicle.
Some maturation does occur in the epididymus with enhancement of motility.
The epididymus is lined with pseudostratified columnar epithelium with stereocilia




