Ch 5 Flashcards
(171 cards)
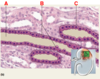
* What type of cut is: A

Longitudinal section
* What type of cut is: B

Cross section
* What type of cut is: C
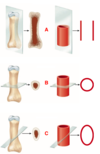
Oblique section
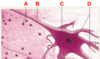
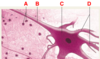
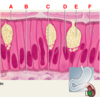
Classes of epithelium
ID: A
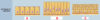
Simple
Classes of epithelium
ID: B
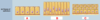
Pseudostratified columnar
Classes of epithelium
ID: C
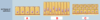
Stratified
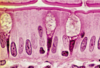
Basic Components of Epithelium
ID: A
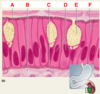
Microvilli (brush border)
Basic Components of Epithelium
ID: B

Connective tissue
Basic Components of Epithelium
ID: C

Basement membrane
Basic Components of Epithelium
ID: D

Nuclei
Basic Components of Epithelium
ID: E

Goblet cell
Basic Components of Epithelium
ID: F
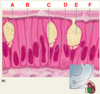
Columnar cells
What type of tissue is this?

Aerolar
What type of tissue is this?
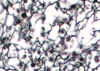
Reticular
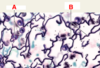
ID: A

Ground Substance
ID: B

Elastic fibers
ID: C

Collagenous fibers
ID: D

Fibroblasts
ID: A
Leukocytes
ID: B
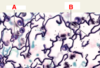
Reticular fibers
What type of tissue is this?

Dense Irregular Connective
What type of tissue is this?

Dence Regular Connective
What type of tissue is this?

Bone
ID: A

Lacunae