Ch 7: Bone Tissue Flashcards
Exam 2 Review (100 cards)
The study of bone is known as
Osteology
Bone is both a _______ and an _______.
tissue, organ
The skeletal system is composed of
- bones
- cartilages
- ligaments
Ligaments connect
bone to bone
Tendons attach
muscle to bone
What are the 6 functions (w/ brief description) of the skeleton?
- Support - hold up body, support muscles
- Protection - brain, spinal cord, heart, lungs
- Movement - limb movements, breathing, action of muscle on bone
- Electrolyte balance - calcium (nerve production, muscle contraction) and phosphate ions (bone modeling and remodeling)
- Acid-base balance - buffers blood against excessive pH changes
- Blood formation - red bone marrow is the chief producer of blood cells
Bone what type of tissue?
osseous
Individual bones consist of…
- bone tissue
- bone marrow
- cartilage
- adipose tissue
- nervous tissue
- fibrous connective tissue
What are the four general types of bones?
- flat
- long
- short
- irregular
Characteristics of flat bones:
- protect soft organs
- curved, but wide and thin
- ex. sternum
Characteristics of long bones
- longer than wide
- rigid lvers acted upon by muscles
- ex. femur or humerus
Characteristics of short bones:
- equal in length and width
- glide across one another in multiple directions
- ex. tarsal bone
Characteristics of irregular bones
- elaborate shapes that do not fit into other categories
- ex. tarsals, carpals, sacrum
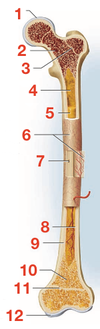
Define bone feature:
Compact bone
dense outer shell of long bone
Define bone feature:
diaphysis
shaft cylinder of compact bone
Define bone feature:
medullary cavity
space in the diaphysis of long bone that contains bone marrow
Define bone feature:
epiphyses
enlarged ends of long bone which are strengthened for joint, ligament and tendone attachments
Characteristics of spongy bone:
- spongelike appearance
- spaces are filled with red bone marrow
- few osteons
- provides strength with minimal weight
Define bone feature:
articular cartilage
- layer of hyaline cartilage that covers the joint surface where only bone meets another
- allows joint to move more freely and relatively friction free
Define bone feature:
nutrient foramina
minute holes in the bones surface that allow blood vessels to penetrate
Define bone feature:
periosteum
External sheath that covers bone except where there is articular cartilage
What are the two layers of periosteum and their general function?
- outer fibrous layer - attach to tendons
- innter osteogenic layer - bone forming cells important for growth and healing of fractures (stem cells are in this layer)
Define bone feature and general function:
endosteum
- thin layer of reticular tissue lining marrow cavity
- has cells that dissolve osseous tissue and others that deposit it
Define bone feature and general function:
epiphyseal plate
- Area of hyaline cartilage that separates the marrow spaces of the epiphysis and diaphysis.
- enables growth in length of bone