CH510 - Structure of d-metal coordination entities Flashcards
(51 cards)
What is a complex?
A structure composed of a central metal ion\atom (M), surrounded by a group of ligands (L).
Identify the relationship between the two Cl- ligands

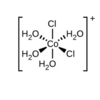
Cis
Identify the relationship between the two Cl- ligands

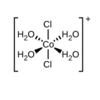
Trans
What is a ligand?
An ion or a molecule that can exist on its own. In coordination chemistry, it bonds to a central metal ion\atom through a coordinative covalent bond.
What is a coordinate compound?
A neutral complex or an ionic compound in which at least one of the ions (cation or anion) are a complex (a coordination entity).
e.g [Ni(CO)4], [Co(NH3)6]Cl3
How are coordination entities (complex) related to lewis acid\bases?
The metal ion\atom is a lewis acid while the ligands are lewis bases.
Thus complex stability is also affected by HSAB theory.
What is a donor atom in coordination entities?
The atom on ligands (lewis bases) which bonds to the central metal atoms.
e.g. N atom on NH3
What is an acceptor atom in coordination entities?
The central metal atom\ion which acts as a lewis acid.
Coordination compounds can be formed from ________ metal groups in the periodic table of elements, but are mostly formed from ________.
any one of the
d-block transition metals
What is an inner sphere complex?
A coordination entity in which ligands are bonded directly to the central metal atom\ion.
e.g. [Mn(OH2)5SO4]
What is an outer sphere complex?
A compound formed by weak electrostatic interaction between a cataionic coordination entity and solvent molecules or anionic ligand molecules.
e.g. {[Mn(OH2)6]2+ (SO4)2-}
What is the primary coordination sphere?
The “sphere” formed by inner-sphere ligands.
e.g. the octahedral structure around Mn2+ [Mn(OH2)6]2+
What is a coordination number?
The number of ligands which form the primary coordination sphere.
e.g. [Mn(OH2)6]2+ has C.N=6.
Define the term:
Monodentate ligands
Ligands which bond to a single site of attachment while donating one pair of electrons.
Define the term:
Polydentate ligands
Ligands which bond to more than one site of attachment.
Bidentate, tridentate ligands are specific cases of polydentate ligands.
Define the term:
Ambidentate ligands
Ligands with more than one different potential donor atom.
e.g. NO2-, NCS-
Define the term:
Chelate
A coordination entity in which
a ligand binds to more than one site and forms a ring that includes the metal atom
Chelates are formed by ________ ligands.
Polydentate
e.g. (en), (ox) ligands
Normal chelating ligands will attach to the metal only at two ________ coordination sites, in a ________ fashion.
adjacent
cis
A chelate formed from a chain of tetrahedral structures on an octahedral complex, creates a ________ membered ring since it preserves the ________ structure on the ligand and a ________ bite angle.
Td structures - as in a chain of methylene groups.
Five
Tetrahedral
90 degrees
Bite angle - the L-M-L angle
Bonds within the coordination sphere are usually ________.
(more stable, less stable)
More stable
Bonds within the coordination sphere usually require ________ heat or ________ time to break .
additional heat
additional time
They are stabler than outer-sphere bonds.
Changes within the ________ sphere of a coordination entity can change the color of its solution.
As the color of an aqueous solution of a coordination entity.
inner
Define the term:
Linkage Isomerism
Isomers formed when the same ligand links through
different atoms.
A complex with Nitrito-κO ligands vs a complex with Nitrito-κN ligands




