L46: Female Reproductive Anatomy Flashcards
(63 cards)
What structures (as a whole) does the female reproductive system consists of? (5)
Vulva
Vagina
Uterus
Uterine tubes
Ovaries
What are ovaries?
Female gonads that are responsible for oogenesis and steroidogenesis
What does ovulation induce? (3)
- Stigma tear 2. Oocyte completes meoisis 1 3. Ovulation occurs
In the CL of the ovaries, granulosa cells are called?
Granulosa lutein cells
In the CL of ovaries, theca cells are called?
Theca lutein cells
If there is no implantation, the CL degenerates and undergoes___?
Luteolysis
If implantation occurs H from the trophoblast signals the endometrium not to relase____ so that the CL does not undergo ____
PGFa2; Luteolysis
In most mammals, CL maintains_____
entire pregnancy
PGFa2 induces _____ and CL dies due to _____
loss of blood vessles; ischemia
2 cells = 2 ______
Gonadotropins
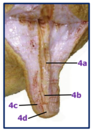
What is unique about the wall of circular muscle of the myometrium of the uterus?
Thick
The mucosa of the peritoneum has what type of cells in the UTERUS?
Columnar epithelium
What cells make up ectocervix?
strat squa nonkert epit
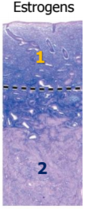
What type of cells are present in the mucosa of the vagina?
Strat sqa epit
In a lactating animal, what is there less of and what is there more of?
Less stroma, more developed parenchyma
In a nonlactating animal, what is ther emore of what is there less of?
More storma, less developed parenchyma
Estrogen is associated with?
Ductal growth
Progesterone is asssociated with?
Acinar growth
Prolactin is associated with?
Milk production
What are the secretions of mammary gland?
- Colostrum 2. Milk
What is produced first after giving birth? Milk or colostrum?
Colostrum- produced shortly after birth
Features of colustrum vs milk
Colostrum: protein-rich, IgA antibodies Milk: lipid droplets, proteins, IgA
Structures/ cell of mammarly gland?
Simple column epit with smoot hmuscle cells
3 hormones associated with mammary gland?
Prolactin, progest, estrogen