Physiology-Recurrent Pregnancy Loss Flashcards
(24 cards)
What defines recurrent pregnancy loss?
2+ consecutive miscarriages
Undisputed reasons for pregnancy loss
Genetic (most miscarry in 1st trimester), anatomic, immunologic
What chromosomal abnormalities most often occur that result in pregnancy loss?
90% are trisomy and monosomy. 10% include translocations, inversions and mosaicism.
Which chromosomes are at higher risk for Robertsonian translocations?
Acrocentric chromosomes 12, 14, 15, 21 and 22.
Products of conception
Karyotypic analysis of miscarried fetal tissue after D&C.
What can be done for a genetic cause of recurrent pregnancy loss?
Genetic counseling, early fetal testing (chorionic villus sampling), IVF/ICSI or donor gametes can be used.
Anatomic causes of recurrent pregnancy loss
Congenital (septate, unicornuate, bicornuate, didelphys uterus), fibroids and intrauterine adhesions (Asherman syndrome after D&C).
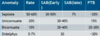
How can you treat patients with congenital uterine malformations?
Hysteroscopic septum resection for septate uterus. There is no surgery benefit in didelphys, bicornuate or unicornuate uterus.
What type of fibroids affect pregnancy the most?
Submucosal and intracavitary. Subserosal and intramural typically do not affect pregnancy outcomes unless > 5cm.
Treatment for Asherman syndrome
Hysteroscopic adhesiolysis. Post-op live birth rate is 50-90%
When is the fetus at highest risk for injury in a mother with lupus?
2nd to 3rd trimester. Other risk factors include active disease at conception, onset of SLE during pregnancy and renal disease.
What immunologic condition has a high risk for pre-eclampsia?
SLE
Sometimes found in women without SLE. What is the diagnostic criteria for this condition?
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. Must have 1 positive from each category.

Treatment for women with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome that are trying to get pregnant.
Aspirin + Heparin. LMWH (lovenox). Immunosuppressants (IVIG, prednisone not used prophylactically).
What clotting factors are increased in pregnancy?
V, VII, VIII, X, fibrinogen and PAI-1. Many of these are procoagulants.
What clotting factors are decreased in pregnancy?
Protein S and resistance to activated Protein C is increased. These are anticoagulants.
When should you test a patient for thrombophilia? What do you test for? How do you treat?
History of clots or FH of clots. Test for factor V Leiden, prothrombin, MTHFR, AT-III and proteins C/S. You can prophylactically treat with aspirin or heparin if the patient has a history or FH of clots.
Why do we treat women with elevated TSH levels with levothyroxine?
Hypothyroidism has an increased risk for miscarriage and cretinism.
Treatment for women with history of diabetes that are pregnant
Metformin
Why is hyperprolactinemia a risk factor for recurrent pregnancy loss? Treatment for women with hyperprolactinemia who want to get pregnant?
High levels of prolactin impair folliculogenesis and oocyte maturation. It can also cause a short luteal phase. You can suppress prolactin levels with DA agonists (cabergoline or bromocriptine).
What things do you want to check if you suspect recurrent pregnancy loss due to luteal phase defect? How do you treat?
TSH and prolactin levels. Treat with ovulation induction (clomid).
When would you put a pregnant patient on antibiotics to reduce chance of miscarriage?
Cervicitis and bacterial vaginosis (increases miscarriage risk 5x)
Environmental risks for miscarriage
Smoking, alcohol (> 2 drinks/day doubles risk) caffeine (< 300mg/day)
50% of women have recurrent pregnancy loss due to what?
No identifiable cause. 70-75% will ultimately have a successful pregnancy.


