Microbiology-Bacterial Vaginosis Flashcards
(32 cards)
Inflammation of the vaginal epithelium
Vaginitis
Inflammation of the endocervix + mucopurulent discharge
Cervicitis
Vaginal irritation, pruritis and odor w/o PMN response
Vaginosis, due to disruption of normal flora
Typical agent involved in vaginal yeast infections
Candida albicans
Vaginal inflammation associated with STDs
Trichomonas
Most common etiology of vaginitis
Bacterial vaginosis 40-50% of cases
A woman presents with lower abdominal pain, a feeling of fullness and vaginal pruritis. Physical exam shows red vaginal walls and labia with a thin, grayish/white odorous discharge. What are significant risks will she be at risk for if this condition is not resolved?
Preterm delivery, postpartum infection, post-surgical infection, increased risk of STDs, PID and salpingitis.
A woman presents with lower abdominal pain, a feeling of fullness and vaginal pruritis. Physical exam shows red vaginal walls and labia with a thin, grayish/white odorous discharge. What could be causing her condition?
Loss of lactobacilli + proliferation of anaerobes like mobiluncus or gardnerella vaginalis happens with bacterial vaginosis. This can be a consequence in changes in hormone status (low estrogen = loss of lactobacilli), presence of semen (alkalinizes vagina) and abx/douching that alters normal flora.
What bacteria are present in these different gram stains?

Note the large, pleomorphic gram-positive rods indicating lactobacilli. These are present in healthy normal vaginal flora.
How does lactobacilli repress growth of chlamydia and gonorrhea?
Bacteriosins are antibiotic secretions from lactobacilli.
Normal vaginal pH
< 4.5. This is the range when lactobacilli thrive, they die when pH > 5.
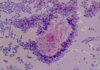
A woman presents with lower abdominal pain, a feeling of fullness and vaginal pruritis. Physical exam shows red vaginal walls and labia with a thin, grayish/white odorous discharge. 10% KOH whiff test was + for amine (fishy) smell. Vaginal pH > 5. Gram stain is shown below. What is your diagnosis?
Note the clue cells (epithelial cells covered with gram + rods: gardnerella vaginalis). This is an indication of bacterial vaginosis.
A woman presents with lower abdominal pain, a feeling of fullness and vaginal pruritis. Physical exam shows red vaginal walls and labia with a thin, grayish/white odorous discharge. Vaginal pH > 5. Culture is shown below. What is your diagnosis?
Note the beta-hemolytic pattern on human blood agar with colonies susceptible to metronidazole disk. This is typical of gardnerella vaginalis.
A woman presents with lower abdominal pain, a feeling of fullness and vaginal pruritis. Physical exam shows red vaginal walls and labia with a thin, grayish/white odorous discharge. 10% KOH whiff test was + for amine (fishy) smell. Vaginal pH > 5. How do you treat her?

Bacterial vaginosis is treated with metronidazole gel or pills. Note that metronidazole is specific for treating anaerobes.
Side effect of metronidazole
Liver toxicity when used with alcohol
Effect of treating the male urethra for gardnerella vaginalis in preventing bacterial vaginosis
Ineffective
Why don’t we recommend probiotics for bacterial vaginosis?
Species are not present in probiotics that colonize a healthy vagina. This may work because normal flora in the vagina come from the GI tract.
What oral condition is associated with bacterial vaginosis?
Periodontal disease
A woman presents with vulvo-vaginal itching and burning on urination. Physical exam reveals a thick, white, cottage cheese-like discharge. What are risk factors for her condition?
Antibiotic therapy, change in hormone status (menarche), diabetes mellitus and immunodeficiency are risks for Candida vaginitis.
Why can yeast infections occur with normal flora?
They love a low pH environment created by the normal flora.
A woman presents with vulvo-vaginal itching and burning on urination. Physical exam reveals a thick, white, cottage cheese-like discharge. What would you expect to see on lab tests?
Candida is a yeast infection and shows budding yeast or hyphae.

Treatment for yeast infection in women who are diabetic, pregnant or HIV?
Oral fluconazole. They will have trouble clearing a systemic infection with the normal “azole” topical OTC creams.
What bacteria is this and where does it colonize?

Trichomonas vaginalis. This bacteria is an aerotolerant anaerobe that utilizes the vagina as a reservoir.
Why do we rarely hear about trichomoniasis as an STD?
Although prominent, it is usually asymptomatic


