Behavioral Sciences 1: Biology and Behavior Flashcards
(87 cards)
neuropsychology
the study of the connection between the nervous system and behavior
often focuses on the functions of various brain regions
Franz Gall
early psychologist
theorized that behavior, intellect, personality may be linked to brain anatomy - phrenology
false thought that development –> brain growth –> physical bulge
Pierre Flourens
studied the functions of the major sections of the brain through extirpation/ablation on rabbits and pigeons (removing parts and watching what happens)
learned that specific parts of the brain had specific functions
William James
father of American psychology
studied how the mind functioned in adapting to environment
helped form functionalism - how mental processes help individuals adapt to environments
John Dewey
helped form functionalism - how mental processes help individuals adapt to environments
studied the organism as a whole and not with discrete parts as it reacts to environment
Paul Broca
demonstrated that specific functional impairments can be linked to specific brain lesions
Hermann von Helmholtz
first person to measure the speed of a nerve impulse
transitioned psych into a natural science
Sir Charles Sherrington
first inferred the existence of synapses
organization of nervous system

parasympathetic nervous system effects
- acetylcholine
- constricts pupil
- stimulates saliva
- slow heartbeat
- stimulates peristalsis
- stimulates bile release
- contracts bladder
sympathetic nervous system effects
- adrenaline/noradrenaline
- dilates pupil
- inhibits saliva
- relaxes bronchi
- accelerates heartbeat
- inhibits peristalsis
- stimulates glucose production and release
- inhibits bladder contraction
- stimulates orgasm
three subdivisions of the brain
hindbrain, midbrain, forebrain
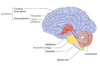
hindbrain
consists of the cerebellum, medulla oblongata, reticular formation
more primitive structure, has vital functions for survival
also called rhombencephalon divides during development to form myelencephalon (medulla) and metencephalon (pons and cerebellum)
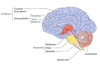
medulla oblongata

lower brain structure
breathing
heart rate
blood pressure
pons

lies above the medulla
sensory/motor pathways between cortex and medulla
cerebellum
above pons
maintain posture and balance
coordinates body movements

reticular formation
the portion that passes through medulla and pons and stops near midbrain
functions in arousal, alertness, attention

brainstem
consists of the midbrain and hindbrain
midbrain
mesencephalon
region of brain that receives sensory/motor information from the rest of the body
associated with involuntary sensorimotor reflex responses
have prominent nuclei

superior colliculus
nuclei in the midbrain that receives visual sensory input
inferior colliculus
nuclei in the midbrain that receives auditory input
has a role in reflexive reactions to loud noises
forebrain
proencephalon
divides to form telencephalon (cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, limbic) and diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, posterior pituitary, pineal glands)
associated with complex perpetual, cognitive, behavioral processes
greatest influence over human behavior, not needed for survival
number of pain receptors in the brain
none!
thalamus

relay center for all sensory input for smell, transmits to cerebral cortex












