Biology 3: Embryogenesis Development Flashcards
(44 cards)
Ampulla
widest part of the fallopian tube

Cortical reaction
a release of calcium ions
these calcium ions depolarize the membrane of the ovum
Two purposes of the calcium ions depolarizing the membrane:
prevents the fertilization of the ovum by multiple cells
increased calcium concentration increases the metabolic rate of the new zygote
Indeterminate cleavage
results in cells that when isolated can still develop into complete organisms
Determinate cleavage
results in cells with fates that are already determined
Morula
solid mass of cells

Blastula
hollow ball of cells with a fluid-filled inner cavity - (blastocoel)

Trophoblast cells
surround the blastocoel and give rise to the chorion and later the placenta

Chorion
extra-embryonic membrane that develops into the placenta
interface between maternal blood and the embryo

Chorionic villi
microscopic fingerlike projections that penetrate the endometrium
Yolk Sac
site of early blood cell development before the development of placenta

Allantois
involved in early fluid exchange between the embryo and the yolk sac
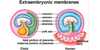
Amnion
thin, tough membrane filled with amniotic fluid
acts as a shock absorber
outer membrane is formed by the chorion

Induction
ability of one group of cells to influence the fate of other nearby cells
Neural crest cells
migrate outward to form the peripheral nervous system
Teratogens
substances that interfere with development, causing defects or even death of the developing embryo
genetics of an individual embryo interferes with the formation of these
Determination
irreversible commitment of a cell to having a particular function in the future
can occur through unbalanced distribution of mRNAs and protein in mitosis
can occur through secretion of morphogens from nearby cells
Morphogens
chemicals that cause nearby cells to follow a particular developmental pathway
Totipotent
include embryonic stem cells
can ultimately differentiate into any cell types, either in the fetus or placental structures
present in the blastula
Pluripotent
can differentiate into any cell type in fetal structures
cannot differentiate into cell types in placental structures
brought about by gastrulation
Multipotent
can differentiate into multiple types of cells within a particular group
ex. hematopoietic stem cells
Juxtacrine
a cell communicating by directly stimulating receptors of the adjacent cell
Growth factors
peptides that promote differentiation and mitosis
Senescence
biological aging as a result of disrupted metabolism, accumulated changes in molecular and cellular structure









