Dermatitis and Eczema Flashcards
(28 cards)
If a patient has atopic eczema, it will be more likely that they will have another atopic condition
True or false?
True
Which term describes a non-specific or isolated type of eczema that has sudden onset, failure of oedema to escape and formation of vesicles?
Pompholyx dermatitis

Which anti-arrhythmic drug can cause photosensitivity?
Amiodarone
What is stasis dermatitis?
Dermatitis caused by poor venous return and due to the resulting increased hydrostatic pressure, extravation of red blood cells occurs
What does lichen simplex dermatitis involve?
Spongiotic dermatitis and external trauma

What does drug related dermatitis involve?
Spongiotic dermatitis and eosinophils
Which types of dermatitis solely involve spongiotic dermatitis?
- Contact irritant
- Contact allergic
- Atopic
- Photosensitive
What is spongiotic dermatitis?
A group of disorders that share intercellular oedema of the epidermis associated with exocytosis of lymphocytes and a papillary dermal perivascular infiltrate
What causes crusting around atopic dermatitis?
S. aureus infection
Which type of dermatitis is associated with yellow greasy scale most commonly on the head, face and neck region?
Seborrheic dermatitis
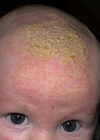
What are the diagnostic criteria for a diagnosis of eczema?
Itching
Plus 3 of:
- Age of onset < 2 years
- Generally dry skin
- History of flexural rash
- Personal history of atopy
- Visible flexural rash
Which dermatological condition is very similar to psoriasis, but lacks raised plaques?
Discoid eczema

Eczema around the neck and eyes is characteristic in which age group?
Infants

All types of dermatitis are spongiotic
True or false?
True
How is the acute phase of eczema described?
Papulovesicular erythematous lesions with oedema (due to spongiosis), oozing, scaling and crusting
How is the chronic phase of eczema described?
Lichenification, elevated plaques and increased scaling
For which reason does weeping occur with severe eczema?
Spongiosis becomes so severe, small vesicles develop and collect into blisters
Why do children with eczema exhibit neurocognitive impairment?
Eczema (constant itching) causes lack of sleep and lower cognitive ability during the day
What percentage of school children suffer from atopic dermatitis at some stage?
25%
What is the pathology of contact allergic dermatitis?
- Langerhans cells in the epidermis process antigen
- Antigen is displayed to TH cells in the dermis
- Sensitised T cell migrate to the lymphatics and then to regional nodes where antigen is amplified
What is the first immune cell an allergen will encounter in the epidermis?
Langerhans cell

What is the most common cause for contact irritant dermatitis?
Soap and detergent
Other causes include:
- Garlic
- Nickel
- Silver
Which term describes the persistence of nuclei in the keratin layer?
Parakeratosis
What is the main cause for the development of eczema?
Mutation in the filaggrin gene