Heme/Onc Flashcards
1
Q
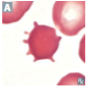
A
- Acanthocyte (“spur cell”)
- Liver disease, abetalipoproteinemia (states of cholesterol dysregulation)
2
Q

A
- Basophilic stippling
- Lead poisoning, sideroblastic anemias, myelodysplastic syndrome
3
Q

A
- Dacrocyte (“teardrop cell”)
- Bone marrow infiltration
4
Q

A
- Degmacyte (“bite cell”)
- G6PD deficiency
5
Q
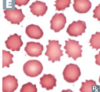
A
- Echinocyte (“burr cell”)
- End-stage renal disease, liver disease, pyruvate kinase deficiency
- Different from acanthocyte: projections more uniform and smaller
6
Q

A
- Elliptocyte
- Hereditary elliptocytosis, usually asymptomatic
- caused by mutation in genes encoding RBC membrane proteins (eg, spectrin)
7
Q

A
- Macro-ovalocyte
- Megaloblastic anemia (also hypersegmented PMNs)
8
Q

A
- Ringed sideroblast
- Sideroblastic anemia; Excess iron in mitochondria
9
Q

A
- Schistocyte
- Microangiopathic hemolytic anemias, including DIC, TTP/ HUS, HELLP syndrome, mechanical hemolysis (eg, heart valve prosthesis)
10
Q

A
- Sicklecell
- Sickling occurs with dehydration, deoxygenation, and at high altitude
11
Q

A
- Spherocyte
- Hereditary spherocytosis, drug- and infection-induced hemolytic anemia
12
Q

A
- Target cell
- HbC disease, Asplenia, Liver disease, Thalassemia (HALT the target)
13
Q

A
- Heinz bodies
- Seen in G6PD de ciency.
14
Q

A
- Howell-Jolly bodies; Basophilic nuclear remnants found in RBCs
- Seen in patients with functional hyposplenia or asplenia
15
Q
A
16
Q
A
17
Q
A
18
Q
A
19
Q
A
20
Q
Anti-coag factors produced by endothelium
A
PGI2 and NO
21
Q
Ristocetin
A
Activates vWF to bind GpIb
Failure of aggregation in vW disease and Bernard-Soulier
22
Q
α-thalassemia
A
- 4 deleted: no α-globin; Excess γ-globin forms γ4 (Hb Barts): hydrops fetalis
- 3 allele deletion: very little α-globin. Excess β-globin forms β4 (HbH)
- 2 allele deletion: less clinically severe anemia
- 1 allele deletion: no anemia (clinically silent)
23
Q
β-thalassemia minor
A
β chain is underproduced; Usually asymptomatic.
Diagnosis confirmed by HbA2 (> 3.5%) on electrophoresis
24
Q
β-thalassemia major
A
β chain is absent severe microcytic, hypochromic anemia with target cells and increased anisopoikilocytosis
Marrow expansion, B19 infxn
25
Lead poisoning
* inhibits ferrochelatase and ALA dehydratase
* decr heme and incr protoporphyrin
Symptoms of LEAD poisoning:
* Lead Lines on gingivae (Burton lines) and on metaphyses of long bones D on x-ray.
* Encephalopathy and Erythrocyte basophilic stippling
* Abdominal colic and sideroblastic Anemia
* Drops—wrist and foot drop
26
Treatment for lead poinsoning
Dimercaprol and EDTA are 1st line of treatment
Succimer used for chelation for kids
27
Sideroblastic anemia causes
X-linked defect in ALA synthase gene)
myelodysplastic syndromes
reversible: (alcohol is most common; also lead, vitamin B6 de ciency, copper de ciency, isoniazid)
28
Siderblastic anemia lab findings
Incr iron, decr TIBC, incr ferritin
Ringed siderblasts
Basophilic stippling
29
Treatment for sideroblastic anemia
pyridoxine (B6, cofactor for ALA synthase).
30
Folate deficiency
Malnutrition, malabsorption, drugs
Incr homocystein; nml methylmalonic acid
31
Vit B12 deficiency
Vegetarian, Crohn, tapeworm
Incr homocystein and methylmalonic acid
SHilling test +
32
Orotic aciduria
Inability to convert orotic acid to UMP
(de novo pyrimidine synthesis) d/t defect in UMP synthase
failure to thrive, developmental delay, and megaloblastic anemia refractory to folate and B12
33
Diamond-Blackfan anemia
Rapid-onset anemia within 1st year of life due to intrinsic defect in erythroid progenitor cells.
34
Hereditary spherocytosis
Extravascular hemolysis; defect in RBC membrane protins (ankyrin)
Small, round RBCs with less surface area and no central pallor ( MCHC)
+osmotic fagility test
35
G6PD defeciency
Decr glutathione: increased susecptibility to oxidative stress
Blood smear shows RBCs with Heinz bodies and bite cells
36
Pyruvate kinase defeciency
Decreased ATP -\> rigid RBCs
Increased 2,3 BPG -\> decr Hg affinity for O2
37
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
Increased complement destruction of RBC; impaired synthesis of GPI anchor for decay-accelerating factor
38
Warm hemolytic anemia
IgG, seen in SLE and CLL
39
Cold hemolytic anemia
IgM
CLL, mycoplasma, IM
40
Acute intermittent porphyria
Decr Porphobilinogen deaminase; Porphobilinogen, ALA accumulate
41
Porphyria cutanea tarda
Uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase deficiency
Uroporphyrin (tea- colored urine) builds up
42
Iron poisoning
Cell death due to peroxidation of membrane lipids
43
t(8;14)
Burkitt lymphoma (c-myc activation)
44
t(9;22)
Philadelphia
(BCR-ABL hybrid)
45
t(11;14)
Mantle cell lymphoma (cyclin D1 activation)
46
t(14;18)
Follicular lymphoma (BCL-2 activation)
47
t(15;17)
APL (M3 type of AML)
48
Busulfan
Cross-links DNA
Treat CML
SE: myelosuppression, pulmonary fibrosis, hyperpigmentation
49
Bevacizumab
MCA against VEGF; Inhibits angiogenesis
Treats Solid tumors
SE: Hemorrhage, blood clots, and impaired wound healing.
50
Erlotinib
EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Non-small cell lung carcinoma.
Rash.
51
Cetuximab
Monoclonal antibody against EGFR.
Stage IV colorectal cancer (wild-type KRAS), head and neck cancer.
Rash, elevated LFTs, diarrhea.
52
Imatinib
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor of BCR-ABL (Philadelphia chromosome fusion gene in CML) and c-kit (common in GI stromal tumors).
CML, GI stromal tumors (GIST)
Fluid retention.
53
Rituximab
Monoclonal antibody against CD20, which is found on most B-cell neoplasms.
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, CLL, ITP, rheumatoid arthritis.
Incr risk of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
54
Bortezomib, carfillzomib
Proteasome inhibitors, induce arrest at G2-M phase and apoptosis. Multiple myeloma, mantle cell lymphoma.
Peripheral neuropathy, herpes zoster reactivation.
55
Tamoxifen, raloxifene
Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs)—r- antagonists in breast and agonists in bone: Block binding of estrogen to ER ⊕ cells.
Breast cancer (tamoxifen only) and prevention
Raloxifene prevents osteoporosis.
Tamoxifen—partial agonist in endometrium: incr risk of endometrial cancer; “hot ashes.” Raloxifene—no risk of endometrial carcinoma (so you can relax!):estrogen receptor antagonist in endometrial tissue.
Both risk of thromboembolic events (eg, DVT, PE).
56
Trastuzumab (Herceptin)
Monoclonal antibody against HER-2 (c-erbB2), a tyrosine kinase receptor: inhibition of HER2-initiated cellular signaling and antibody- dependent cytotoxicity.
HER-2 ⊕ breast cancer and gastric cancer (tras2zumab). Cardiotoxicity.
“Heartceptin” damages the heart.
57
Vemurafenib
Small molecule inhibitor of BRAF oncogene ⊕ melanoma. VEmuRAF-enib is for V600E- mutated BRAF inhibition.
Metastatic melanoma.
58
Rasburicase
Recombinant uricase that catalyzes metabolism of uric acid to allantoin
Prevention and treatment of tumor lysis syndrome.
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73


