Lymphatic System Flashcards
(44 cards)
Functions of the Lymphatic System
- fluid recovery (2-4 L/day, prevents edema)
- immunity (lymph and blood monitored for pathogens and cancer cells)
- lipid absorption (via lacteals in small intestine)
6 Types of Lymphatic Cells
T Lymphocytes - develop in thymus
B Lymphocytes - develop in red bone marrow, produce antibodies
Macrophages - develop from monocytes, phagocytotic
Natural Killer Cells (NK cells) - large lymphocytes that attack and lyse bacteria, foreign tissue, infected host cells
Dendritic Cells - branched cells in skin, antigen presenters
Reticular Cells - branched cells in stroma of lymphatic organs
Lymphatic Fluid
- what is it?
- how is it produced?
AKA Lymph
- produced by filtration of plasma through capillaries
Pathway of Lymph Flow
- towards the heart
- begins in dead-ended lymphatic capillaries where blood capillaries are (except: brain, teeth, bones, marrow)
What is this structure?
Where is it found and where does it lead?

lymphatic capillaries
- smallest lymph vessel (larger than blood capillaries)
- permeable to lymph fluid and proteins via its valve-like overlapping endothelial cells
- dead-end at blood capillary beds and drain into lymph collecting vessels
- absent in cornea, bone marrow, CNS
What lymphatic structures do lymphatic capillaries drain into?
What is their structure like?
lymphatic collecting vessels
- contain valves to molve lymph towards heart
- have the same three tunics as blood vessels, but thinner walls and lower pressure
- have lymph nodes along length to filer lymph
- lie along with veins in superficial tissues and arteries in deeper tissues
The convergence of several lymphatic collecting vessels
lymphatic trunk
the five major lymphatic trunks
- Lumbar Trunk
- Intestinal Trunk
- Bronchomediastinal Trunk
- Subclavian Trunk
- Jugular Trunk
Paired lymphatic trunks branching off of the inferior end of the thoracic duct
Lumbar Trunks (left and right)
- carry lymph from lower limb, pelvic region and anterior abdominal wall
Single lymphatic trunk branching off of inferior thoracic duct
Intestinal Trunk
- drains lymph from stomach, intestines and other digestive organs
part C

bronchomediastinal trunks (left and right)
- carries lymph from thoracic viscera
- usually open into junction of internal jugular and subclavian veins
- sometimes join right lymphatic duct and thoracic duct
part B

subclavian trunks (left and right)
- lymph from upper limbs, inferior neck and superior thoracic wall
- open either into junction of internal jugular and subclavian veins or into jugular trunk and thoracic duct
part A

Jugular Trunks
- drains lymph from head and neck
- right side joins the venous angle (right internal jugular and subclavian veins)
- left side joins thoracic duct
Where do the lymphatic trunks drain?
- into the lymphatic ducts
- two major ducts: thoracic duct and right lymphatic duct

cisterna chyli
- dilated sac at inferior end of thoracic duct
- receives lymph from intestinal and lumbar trunks
- contains lots of chyle, fat-rich intestinal lacteal lymph

Thoracic Duct
- joins junction of left subclavian and internal jugular veins (the venous angle)
- drains left side of face, most of left thorax and lower body
top left question-marked structure:

right lymphatic duct
- joins right venous angle
- drains right side of head and upper body
- only present in 20% of people
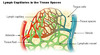
what is this collection of blue structures?

cervical lymph nodes
what is this grouping of green and blue structures?

axillary lymph nodes
what is this grouping of green structures?

inguinal lymph nodes
Lymphoid Tissue
- what kind of tissue is it?
- what cells are found in it?
- where is it found?
- reticular connective tissue dominated by lymphocytes (T, B cells and macrophages)
- it is found primarily in two places:
- MALT (mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue) - mucous membranes of digestive, respiratory, urinary and reproductive tracts
- all lymphoid organs except thymus
lymphatic capillaries that absord dietary fats within the villi of the small intestine
lacteal
Lymphoid Nodules
- where are they found?
- how are they different from lymphoid organs?
- describe their structure
- name examples
AKA lymphoid follicles
- scattered clusters within lymphoid tissue
- they lack a fibrous capsule
- they are made of densely packed lymphocytes with a (usually lighter-staining) central zone of dividing cells (the germinal center)
Ex: tonsils and peyer’s patches
Tonsils
- what are they?
- where are they?
- what do they do?
- large lymphatic nodules
- located in the pharynx and on the palate and tongue
- they trap bacteria and foreign pathogens entering the mouth and nose


















