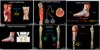
Gluteal and Posterior Thigh and Leg Flashcards
(14 cards)
Surface anatomy of gluteal region
- Location?
- Common site for what? Where is the safe zone for this?
Surface anatomy of gluteal region
- Gluteal region lies posterior to pelvis from the level of the iliac crests (L4) to the gluteal fold, which marks the inferior border of the gluteus maximus
- Gluteal region is a common site for intramuscular injections
- In order to avoid the sciatic nerve, the superior lateral quadrant is considered a safe zone for injection
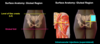
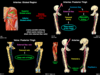
Superficial gluteal muscles
- What are the four superficial muscles?
Gluteus maximus
- Insertion?
- Action?
- Innervation?
Superficial gluteal muscles
- Gluteus maximus
- Gluteus medius and minimus
- Tensor fasciae latae
Gluteus maximus
- Insertion:
- Iliotibial tract
- Gluteal tuberosity of femur
- Action:
- Extend hip
- Laterally rotate hip
- Ex. rising from sitting position and climbing stairs
- Innervation:
- Inferior gluteal nerve (L5-S2)

Gluteal medius and minimus
- Deep to?
- Insertion?
- Action?
- Innervation?
- What is the Trendelenburg test?
Gluteal medius and minimus
- Deep to gluteus maximus
- Insertion:
- Greater trochanter of femur
- Action:
- Abduct hip joint
- Medially rotate hip joint
- Keep pelvis level when contralateral leg is raised
- Innervation:
- Superior gluteal nerve (L4-S1)
-
Trendelenburg test
- If superior gluteal nerve is injured, when a person is asked to stand on that limb, the pelvis tilts towards the unsupported side (positive)
- Injury to this nerve on the right will cause pelvis to tilt on the left side

Tensor fasciae latae
- Origin?
- Insertion?
- Action?
- Innervation?
Tensor fasciae latae
- Origin: ASIS
- Insertion: iliotibial tract
- Action:
- Tense the fascia lata, thus improving efficiency of other thigh muscles and assisting venous return
- Weakly flex hip joint
- Medially rotate hip joint
- Innervation: superior gluteal nerve (L4-S1)

Deep gluteal muscles
- What are they?
- Origin?
- Insertion?
- Action?
- Innervation?
- Side note: what muscle also does the same actions as the deep gluteal muscles?
Deep gluteal muscles
- Origin: pelvic girdle
- Insertion: proximal femur
- Action:
- Laterally rotate hip joint
- Stabilize hip joint
- Innervation: small motor branches of the sacral plexus
- Muscles:
-
Piriformis
- Superior gluteal vessels and nerves emerge superior to it
- Inferior gluteal vessels and nerves emerge inferior to it
- Remember: piriformis creates posterior wall of pelvis
- Obturator internus
- Superior and inferior gemelli
- Quadratus femoris
-
Piriformis
- Note: Obturator externus (part of medial compartment of thigh and innervated by the obturator nerve) also laterally rotates and stabilizes hip joint

Sciatic nerve
- Exits where?
- Courses?
- Consists of what two nerves?
- Where do these nerves usually separate?
- In 12% of people they separate where?
- What is piriformis syndrome?
Sciatic nerve
- Exits greater sciatic foramen inferior to piriformis
- Courses deep to gluteus maximus but does NOT innervate gluteal muscles
- Consists of two nerves:
- Tibial nerve (medial)
- Common fibular nerve (lateral)
- Tibial and common fibular nerves usually separate in the distal thigh (just proximal to the popliteal fossa)
- However, this can vary - in 12% of people the two nerves separate as they leave the pelvis with the common fibular nerve passing through the piriformis
-
Piriformis syndrome
- Excessive use of the deep gluteal muscles (e.g. rock climbers, figure skaters, cyclists, etc) can lead to hypertrophy of piriformis muscle, which can compress the sciatic nerve
- Those 12% with a proximal split of the nerve can have the common fibular nerve compressed as well as it passes through the piriformis

Posterior compartment of the thigh
- What are the muscles?
Hamstrings
- Origin?
- Action?
- Innervation?
- What are the three hamstring muscles? Insertion points?
Posterior compartment of the thigh
- Hamstrings
- Semitendinosus
- Semimembranosus
- Long head of biceps femoris
- Short head of biceps femoris
Hamstrings
- Origin: ischial tuberosity
- Action:
- Extend hip joint
- Flex knee joint
- (crosses hip and knee joints)
- Innervation: tibial nerve (L5-S2) (part of sciatic nerve)
-
Semitendinosus
- Medial
- Insertion: proximal tibia
-
Semimembranous
- Medial, deep to semitendinosus
- Insertion: proximal tibia
-
Long head of biceps femoris
- Lateral
- Insertion: proximal fibula

Short head of biceps femoris
- Part of hamstrings?
- Origin?
- Insertion?
- Innervation?
- Action?
Pes anserinus
- What three tendons form this?
- Also called?
- Irritation of the bursa can cause what where?
Short head of biceps femoris
- NOT a hamstring muscle
- Origin: linea aspera of femur
- Insertion: proximal fibula (via shared tendon with long head)
- Innervation: common fibular nerve (part of sciatic nerve)
- Action: flex knee joint (crosses knee joint)
Pes anserinus
- Tendons of semitendinosus, gracilis, and sartorius fuse distally to insert on the medial aspect of the proximal tibia, forming the pes anserinus AKA “goose’s foot”
- Irritaton of the bursa underlying the pes anserinus (pes anserinus bursitis) can cause pain on the medial aspect of the knee
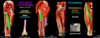
Lateral compartment of leg
- Composed of what two muscles?
- Action?
- Innervation?
- Insertion of each muscle?
- What is foot drop?
Lateral compartment of leg
- Muscles:
- Fibularis (peroneus) longus - superficial
- Fibularis (peroneus) brevis - deep
- Action:
- Evert foot
- Weakly plantarflex ankle joint (stand on toes)
- Innervation: superficial fibular nerve (L5-S2)
- Branch of common fibular nerve
- Innervates the muscles of the lateral compartment of the leg
- Innervates the skin of the anterior lateral leg and most of the dorsal foot
Fibularis (peroneus) longus
- Insertion: tendon passes posterior to the lateral malleous, crosses the sole of the foot, and inserts on the base of the first metatarsal and medial cuneiform
Fibularis (peroneus) brevis
- Insertion: tendon passes posterior to the lateral malleolus to insert on the tuberosity of the fifth metatarsal
Foot drop
- If the common fibular nerve is injured where it wraps around the neck of the fibula, the muscles in the anterior and lateral compartments of the leg and dorsal foot will be affected
- The patient will present with foot drop, which is caused by a loss of dorsiflexion and toe extension
- The foot may also be inverted, as eversion is also affected
- One invertor will be affected (tibialis anterior is innervated by the deep fibular nerve), BUT one invertor will still be intact (tibialis posterior is innervated by the tibial nerve)
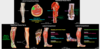
Posterior compartment of the leg
- Muscles?
- Action?
- Innervation?
- Branch of?
- Travels between?
- Innervates?
Posterior compartment of the leg
- Muscles:
- Superficial group
- Triceps surae
- Gastrocnemius
- Soleus
- Plantaris
- Triceps surae
- Deep group
- Popliteus
- Flexor digitorum longus
- Flexor hallucis longus
- Tibialis posterior
- Superficial group
- Action:
- Plantarflex ankle joint
- Flex toes
- Innervation: tibial nerve (L4-S3)
- Medial branch of sciatic nerve
- Travels between the superficial and deep muscle groups of the posterior compartment of the leg
- Innervates the muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg
- Innervates the skin on the posterior lateral aspect of the leg and lateral foot (via the sural nerve, which also receives contribution from the common fibular nerve)

Superficial group (of the posterior compartment of the leg)
- Insertion?
- What is the calcaneal tendon reflex?
- What three muscles compose the superficial group of the posterior compartment of the leg?
- Actions?
- What is triceps surae composed of? Which muscle is superficial / deep?
Superficial group (of the posterior compartment of the leg)
- Insertion: calcaneal tuberosity via calcaneal (Achilles) tendon
-
Calcaneal tendon reflex
- Tests the tibial nerve and the S1-S2 spinal levels
- It primarily tests the S1 spinal level
- Lesion at S1 level will result in a virtually absent calcaneal reflex
-
Gastrocnemius
- Gastrocnemius + soleus = triceps surae
- Medial and lateral head
- Most superficial
- Actions:
- Flex knee joint (crosses knee joint)
- Plantarflex ankle joint
-
Soleus
- Deep to gastrocnemius
- Action: plantarflex ankle joint
-
Plantaris
- Small muscle belly with long, thin tendon
- Actions:
- Weakly flex knee joint (crosses knee joint)
- Plantarflex ankle joint
- Absent in 5-10% of people
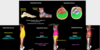
Deep group (of the posterior compartment of the leg)
- What four muscles compose the deep group of the posterior compartment of the leg?
- Insertions? Actions?
- What muscle rotates the femur on the tibia?
- Flexor retinaculum holds what four tendons in place where?
- What is Tom, Dick, and Harry?
Deep group (of the posterior compartment of the leg)
-
Popliteus
- Action: unlocks the knee from extended position
- When knee is extended in standing position, popliteus rotates the femur laterally 5% on the tibia, unlocking the knee so that flexion can occur
-
Flexor digitorum longus (FDL)
- Insertion: tendon travels posterior to medial malleolus of tibia in tarsal tunnel, and divides into four tendons to insert on the distal phalanges 2-5
- Actions:
- Flex digits 2-5 (MTP, PIP, and DIP joints)
- Plantarflex ankle joint
-
Flexor hallucis longus (FHL)
- Insertion: tendon travels posterior to medial malleolus of tibial in tarsal tunnel and inserts on distal phalax of hallux (big toe)
- Actions:
- Flex hallux (MTP and IP joints)
- Weakly plantarflex ankle joint
-
Tibialis posterior
- Insertion: tendon travels posterior to medial malleolus of tibia in tarsal tunnel and inserts priomarily on the navicular tuberosity
- Actions:
- Plantarflex ankle joint
- Invert foot
Tarsal tunnel
- Tendons of the flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus, and tibialis posterior are held in place in the tarsal tunnel by the flexor retinaculum, which forms the roof of the tarsal tunnel
- Tom, Dick ANd, Harry
- Summarizes relative position (anterior, middle, and posterior) of the tendons of the tibialis posterio__r (Tom), flexor digitorum longus (Dick), and flexor hallucis longus (Harry) as they travel posterior to the medial malleolus in the tarsal tunnel
- The posterior tibial artery/vein and tibial nerve (ANd) are between the tendons of the FDL and FHL
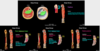
Vasculature
What arteries supply:
- Gluteal region
- Posterior thigh
- Posterior and lateral leg
Vasculature
-
Gluteal region
- Gluteal arteries arise from the internal iliac artery
- Superior gluteal artery - exits greater sciatic foramen superior to piriformis
- Inferior gluteal artery - exits greater sciatic foramen inferior to piriformis
- Superior and inferior gluteal veins accompany the arteries and are tributaries of the internal iliac vein
-
Posterior thigh
- Perforating branches from the deep artery of the thigh (primary course) and the obturator artery
- Deep vein of the thigh
-
Posterior and lateral leg
- Femoral artery passes through adductor hiatus and becomes the popliteal artery
Branches of the popliteal artery
- What are the three branches of the popliteal artery?
- Where do the geniular branches form anastomoses?
- What does the anterior tibial artery pass through and supply?
- What does the posterior tibial artery travel with, supply, and give off to? What do these arteries give off to or supply? Where does posterior tibial artery travel to in the tarsal tunnel, between what, and deep to what?
- Where can you palpate posterior tibial pulse?
- Veins of the posterior and lateral leg?
Branches of the popliteal artery
-
Geniular branches
- Genu = knee
- Form anastomoses around the knee joint
-
Anterior tibial artery
- Passes through gap in superior part of the interosseous membrane
- Supplies the anterior lateral leg and dorsal foot
-
Posterior tibial artery
- Travels with tibial nerve, between superficial and deep muscle groups
- Supplies posterior leg
- Gives off to fibular artery, which supplies posterior lateral leg (including lateral compartment)
- Around the ankle, the posterior tibial artery give off medial malleolar and calcaneal branches while the fibular artery gives off lateral malleolar and calcaneal branches (form anastomoses around ankle joint)
- Posterior tibial artery travels posterior to medial malleolus in the tarsal tunnel, between tendons of FDL and FHL (Tom, Dick, and Harry) and deep to flexor retinaculum (can palpate posterior tibial pulse here)
- Deep veins of the posterior and lateral leg parallel the arteries and share the same names
- Recall that the popliteal vein also receives blood from the small saphenous vein (draining superficial tissues)