Hematopoietic System Pathology Flashcards
(126 cards)
Morphological diagnosis

Acute multifocal necrotizing hepatitis and splenitis
Splenomegaly caused by

Amyloidosis
Indications for examining bone marrow
Unexplained cytopenia
Maturation defects or morphologic abnormalities in blood cells
Potential myelo/lympho-proliferative disease
Potential malignancies
Condition

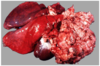
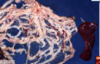
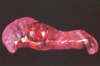
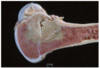
Splenic Hemangioma
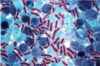
Etiology of Strangles
Streptococcus equi subsp equi
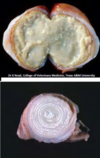
Condition
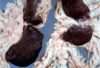
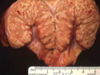
Multiple “Spleens”
Autosomal recessive bone marrow disorder that disrupts the sequence of steps leading to the migration of leukocytes into sites of inflammation leading to bone marrow hyperplasia
Bovine Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency Syndrome - BLAD
Differential diagnosis for hyperplastic splenitis
Aleutian Disease
Equine Infectious Anemia
Differential diagnosis for splenic thrombosis/ infarction
Classicial Swine Fever (Hog Cholera)
Lymphosarcoma
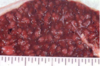
Splenic nodules with a blood consistency can be
Hematomas
Incompletely contracted areas of spleen
Acute splenic infarcts
Vascular neoplasms
Bloody spleen can be generally caused by
Congestion
Acute Hyperemia
Acute Hemolytic Anemia
Disease in pigs that causes diffuse granulomatous lymphadenitis
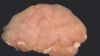
Postweaning Multisystemic Wasting Disease
Morphological Diagnosis

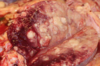
Necrotizing splenitis
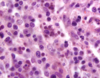
Malignant bone marrow neoplasm of histiocytic origin.
Histocytic Sarcoma
Disease in which carbon particles are retained in macrophages, medulla of lymph node appears black.
Anthracosis
________________________________
Common finding in animals living in polluted urban areas
Disease of the spleen that causes necrotizing splenitis characterized by white-grey milliary foci scarttered throughout the splenic parenchyma.
Tularemia - Rabbit Fever
Condition

Histiocytic Sarcoma
Hemal Nodes
Prominant in ruminants, small, dark red similar architecture
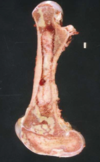
Bone Marrow Hypoplasia/ Atrophy may be the result of
Myelophthisis
Abnormality of hematopoietic cells
Etiology of Cytauxzoonosis
Cytauxzoon felis
Disease

Multiple Myeloma
Condition
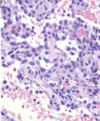
Splenic hemangiosarcoma
Etiology
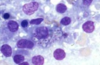
Histoplasma capsulatum
Disease that causes granulomatous lymphadenitis characterized by B and T lymphoid depletion and “botryoid” intracytoplasmic inclusions in macrophages.
Post Weaning Multisystemic Wasting Disease - PMWD