Respiratory Pathology Flashcards
(132 cards)
Condition
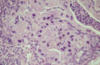
Inclusion Body Rhinitis
Condition

Interstitial Emphysema
T/F: In cats, pnumonias are more common than upper respiratory infections.
False
Possible etiologies for Equine Viral Rhinopneumonitis
EHV -1
EHV -4
Viruses that cause pneumonia in Cattle
Bovine Herpesvirus -1
Par-Influenza Virus - 3
Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus - BRSV
Etiology of Porcine Enzootic Pneumonia
Mycoplasma hyponeumoniae
Cattle: Disease that causes chronic necrotizing bronchopneumonia. Histologic appearance shows caseous necrosis.
Mycoplasma bovis Pneumonia
Disease in sheep that is similar to Shipping Fever in cattle?
Ovine Penumonic Mannheimosis
Condition
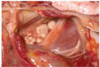
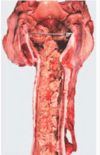
Guttural Pouch Empyema
Etiology of Verminous Bronchitis/Pneumonia in Swine
Metastrongylus spp
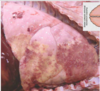
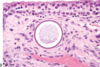
Condition

Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma
Condition
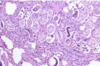
Aelurostrongylus abstrusus infection
Syndrome caused by type I hypersensitivity in cows sensitized by their own milk casein and lactalbumin
Milk Allergy
Condition

Glasser’s Disease
Condition

Shipping Fever
Cattle: Disease occurs several days to weeks after shipment. Causes fibrinous bronchopneumonia and marbling of pulmonary parenchyma. Histologic appearance shows coagulative necrosis.
Pneumonic Mannheimosis - Shipping Fever
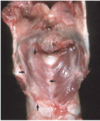
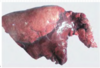
Highly contagious and often fatal respiratory disease of pigs 2-5 months of age characterized by fibrinous bronchopneumonia on the dorsal area of the caudal lung lobe.
Porcine Contagious Pleuropneumonia
Etiology of Porcine Contagious Pleuropneumonia
Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae
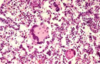
Respiratory disease of equids that causes transient broncho-interstitial pnumonia. Histological appearance shows foamy eosinophilic proteinaceous material within alveoli
Equine Adenovirus
___________________________
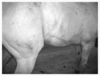
Common complication in Arabian foals with SCID
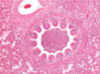
What are these called?
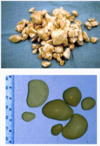
Chondroids
Type of necrosis seen on histology associated with Pneumonic Mannheimiosis

Coagulative Necrosis
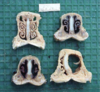
Condition and Etiology

Stranges
Streptococcus equi
Condition

Fibrinous Rhinitis
Etiology of Respiratory Hisophilosis in cattle
Histophilus somni