Lab Exam Flashcards
(127 cards)
Morphological Diagnosis

Catharal enteritis
Lesions caused by thiamine deficiency in carnivores are typically found in what area of the brain?
Caudal colliculi
Morphological diagnosis
Multifocal ulceration and gastric hyperplasia
Gross Morphological Diagnosis

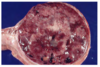
Adrenocortical Hyperplasia
Morphological Diagnosis

Suppurative pneumonia
Gross Morphological Diagnosis

Nodular Thyroid Hyperplasia
Two areas of the brain that are affected in Nigropallidal encephalomalacia
Globus Pallidus
Substantia nigra
Morphological Diagnosis

Inguinal hernia incarceration
Morphological Diagnosis

Coronary artherosclerosis
Morphological Diagnosis

Multifocal to coalescing necrotizing (ulcerative) gastritis
Morphological Diagnosis

Lymphocytic Thyroiditis
Morphologic Diagnosis

Hepatic Cirrhosis
Condition

Hepatosis Dietetica of Swine - Massive Hepatic Necrosis
Gross Morphological Diagnosis

Parathyroid Hyperplasia
Morphological Diagnosis

Enlarged lymph nodes with diffuse dark brown to black pigmentation
Condition

Fatty Liver Syndrome
What complication can arise from this lesion?

Bronchopneumonia
Morphological Diagnosis
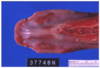
Ulcerative stomatitis
Morphological Diagnosis

Reticulum Lymphosarcoma
Morphologial Diagnosis

Fibrino-hemorrhagic and necrotizing pneumonia
Disease

Chronic Nephritis
Morphological Diganosis

Chronic Hepatic Congestion
Morphological Diagnosis

Pyogranulomatous Pneumonia
Etiology

Pasturella