Neuropathology Flashcards
(33 cards)
Name three infectious agents which affect the grey matter of the brain.
(x7 in total)
- Rabies - Lyssavirus
- Pseudorabies - suid Herpes virus 1
- Teschen disease - Picornaviridae
- Borna disease - Bornavirus
- West Nile Encephalitis - Flavivirus
- Louping ill - Flavivirus
- Listeriosis - Listeria monocytogenes
What is shown here?
Describe.
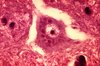
Negri bodies
Eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies
What is shown here?
What cells make up the structure?

Glial nodule
Made up of microglia (macrophage-like) - activated rod cells - surrounding necrotic tissue
What histological features are associated with pseudorabies?
- Non-suppurative
- Meningopolioencephalitis
- Glial nodules
- Neurophagia
- Neuronal nodules
What is shown here?
Describe the lesion.

Neurophagic nodule
Microglia surrounding neurone
What clinical presentation is associated with pseudorabies?
Pruritis
Violet scratching
Automutilation
Swine polioencephalitis is also known as..
Teschen disease
Viral polioencephalitis is characterised by what type of inflammation?
NON-SUPPURATIVE
What histological features are associated with Techen disease?
- Non-suppurative
- Polioencephalitis
- Neuronal necrosis
- Glial nodules
- Neurophagia
Neuronal death/ damage is characterised by what histological features?
Reversible: Chromatolysis (enlarged cytoplasmic volume and nucleus pushed to the periphery) - oxidative stress
Irreversible: Vacuolation and red hypoxic neurones (hypereosinophilic) - excitotoxicity and oxidative stress
This viral disease is selective for the grey matter of hippocampus, cerebral cortex and brainstem.
What histological features are associated with this disease?
Bornavirus
- Non-suppurative
- Polioencephalomyelitis
- Neuronal degeneration
- Neuronophagia
West nile encephalitis is characterised by what histological changes?
- Non-suppurative
- Polioencephalomyelitis
Also affects grey matter of the thoraco-lumbar spinal cord
This flavivirus caused disease targets purkinje cells and causes gliosis and leptomeningitis.
Louping ill
This bacteria causes encephalitis via retrograde axonal transport to the brain before causing multifocal microabscessation of the grey matter.
Listeria monocytogenes
Name three infectious agents which affect the white matter of the brain.
- Canine distemper virus - morbilivirus
- Post-vaccinal distemper
- Maedi-visna - lentivirus
What histological changes are associated with Maedi Visna virus?
- Granulomatous leukoencephalitis
- Lymphoplasmacytic infiltration
- Cavitation and malacia
- Choroiditis and meningitis
What histological changes are associated with Canine distemper virus?
Remember two phases.
Demyelinating leukoencephalitis
- Acute: pale and demyelinated
- Chronic: non-suppurative w/ cavitation
- Post-vaccinal: 2 weeks post vaccination
Name the four parasitic causes of polioencephalitis.
- Toxoplasma gondii
- Neospora caninum
- Sarcocystis neurona/ tenella
- Taenia multiceps
What is GID?
What pathological changes does it cause?
Coerneurosis caused by Taenia multiceps
Brain fluid filled cysts
How does the pathology of T. gondii differ between young and old animals?
Young: non-suppurative polioencephalitis and gliosis
Old: necrotising and granulomatous encephalitis
Equine protozoal encephalomyelitis is caused by what pathological agent?
What histological signs are observed?
Sarcocystis neurona
Necrotising myelitis
Name two causes of infectious meningitis.
- H. somni - sleeper syndrome
- GME - granulomatous meningoencephalitis
This virus causes spinal cord inflammation (myelitis) and petechial/ ecchymoid haemorrhage of white and grey matter.
Equine herpes virus 1
Name three viral causes of vasculitis.
- Classical swine fever: Pestivirus
- Rubarths disease: Canine adenovirus 1
- Malignant catarrhal fever: Ovine herpes virus 1



