DIT review - Micro 10 Flashcards
Transmission and presentation of Naegleria fowleri
- Transmission:
- Swimming in freshwater lakes – associated with water sports
- Enters via cribriform plate
- Presentation:
- Rapidly fatal meningoencephalitiis
- Nuchal rigidity and fever + AMS
- Rapidly fatal meningoencephalitiis
Diagnosis and treatment of Naegleria
- Diagnosis:
- Lumbar puncture – Amoebas in spinal fluid
- Treatment:
- Amphotericin B
Transmission and presentation of Trypanosoma cruzii
- Transmission:
- Reduviid bug (“kissing big”) feces deposited in bite, then induced by scratching
- Predominantly in South America
- Presentation:
- Chagas disease:
- Dilated cardiomyopathy, megacolon, megaesophagus
- Chagas disease:
Diagnosis and treatment of trypanosoma cruzii
- Diagnosis:
- Trypomastigote in blood smear
- Treatment:
- Nifurtimox (knee-high fur mocassins)
Transmission and presentation of babesia
- Transmission:
- Ixodes tick
- Often coinfected with Lyme disease
- Predominantly in Northeast US
- Presentation:
- Fever, hemolytic anemia, jaundice
- Higher risk in sickle cell disease
Diagnosis and treatment of babesia
- Diagnosis:
- Blood smear containing ring form or maltese cross
- Treatment:
- Atovaquone + Azithromycin

Transmission and general presentation of malaria
- Transmission:
- Amopheles mosquito
- Presentation:
- Fever, headache, anemia, splenomegaly
- Symptoms occur when RBCs rupture and release merozoites
- What are the 4 plasmodium species
- Describe fever cycles of each
- Which one has dormant form in liver
- Different species:
- P. Vivax/Ovale
- Fever cycle – 48 hours (tertian)
- Dormant form (hypnozoite) in liver
- P. malariae
- Fever cycle – 72 hour (quartan)
- P. falciparum
- Fever cycle – irregular fever pattern
- Parasitized RBCs occlude capillaries in brain (cerebral malaria), kidneys, lungs
- P. Vivax/Ovale
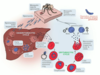
Describe the life cycle of plasmodium
- Malaria is transmitted by Anopholese mosquito, which carry sporozoites in saliva
- Mosquitoes bite human host and mature to trophozoites in liver
- Schizont divides into merozoites which burst from hepatocytes and infect RBCs
- Once inside the RBC, lifecycle continues: trophozoite -> schizont -> merozoite -> infect RBC
- Immature schizont has a ring form in the RBC
- After merozoite infects the RBC, it can also form gametocytes, which are sexual form of plasmodium
- Cycle continues when mosquitoes bite a human and take up RBCs containing gametocytes
Diagnosis of Plasmodium
- Blood stain with Giemsa stain to see parasites in RBCs (trophozoite ring)

Histology specific to P. falciparum
- P. Falciparum has banana-shaped gametocyte in blood smear

Malaria drug that has a lot of resistance
- Chloroquine
- For sensitive species
- Blocks plasmodium heme polymerase
What is the reason behind adding Primaquine to Chloroquine
- To kill dormant hynozoite in P. Vivax/Ovale
Which drugs treat chloroquine-resistant species
- Mefloquine
- For chloroquine-resistant species
- Prophylaxis for travelers
- Atovaquone +. Proguanil
- For chloroquine-resistant species
- Prophylaxis for travelers
- For life-threatening disease caused by P. Falciparum
Which drugs are used for life-threatening disease caused by P. falciparum
- Atovaquone +. Proguanil
- For chloroquine-resistant species
- Prophylaxis for travelers
- For life-threatening disease caused by P. Falciparum
- Quinidine
- For life-threatening disease caused by P. Falciparum
- Adverse effect = cinchonism
- Artesunate
- For life-threatening disease caused by P. Falciparum
Transmission and presentation of Leishmaniasis (both cutaneous and visceral)
- Transmission:
- Sandfly
- Vertebrae are the hosts
- Presentation:
- Cutaneous leishmaniasis
- Caused by Leishmania baziliensis
- Skin ulcers
- Visceral leishmaniasis (kala-azar)
- Caused by Leishmania donovani
- Spiking fevers, hepatosplenomegaly, pancytopenia, hyperpigmented lesions
- Cutaneous leishmaniasis
Diagnosis and treatment of Leishmaniasis
- Diagnosis:
- Macrophages containing amastigotes
- Treatment:
- Sodium stibogluconate (T-bone steak) = cutaneous
- Amphotericin = visceral

Transmission and presentation of Trichomonas
- Transmission:
- Sexual
- Presentation:
- Vaginitis – foul-smelling, greenish discharge; itching and burning; pH > 4.5
- Cervicitis – strawberry cervix
Diagnosis and treatment of Trichomonas
- Diagnosis:
- Trophozoites (motile) on wet mount
- Treatment:
- Metronidazole (treat patient and partner)

Describe transmission and characteristics of Enterobius vermicularis
- Sketchy = vermin lady crawling out of hole
- Transmission:
- Fecal-oral
- Characteristics:
- At night, females lay eggs in anus, people then scratch their butts
- Anal pruritus





