Lecture 13 Flashcards
(25 cards)
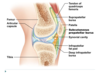
What are the 6 features of a synovial joint?
1) Articular cartilage
2) synovial cavity
3) synovial fluid
4) joint capsule (fibrous and synovial layers)
5) reinforcing ligaments
6) nerves and blood vessels
The following terms are other features of synovial joints. Define each. Fatty pads, articular discs, bursae, tendon sheaths
Fatty pads - cushioning between fibrous and synovial membrane layers or bone
Articular discs (menisci) - fibrocartilage that separates articular surfaces to improve the “fit” of bone ends
Bursae - sacs that are lined with synovial membrane; reduce friction
Tendon Sheaths - Elongated bursa that wrap around tendons that are subjected to friction
What are the 6 types of synovial joints?
plane, hinge, pivot, condylar, saddle, ball and socket
Which type of joint has the most mobility, but the least stability?
Ball and socket
Identify the type of joint that accommodates a larger movement and are more involved in micro movements. Where are they found?
Plane joint
Intercarpal, inter tarsal, joints between vertebral articular surfaces
Define the type of movement that the pivot joint executes and where they are found.
Movement - supination, pronation, and rotation
Pivot joints are found in proximal radioulnar and the atlantoaxial
The condylar joint is found in the knuckles and the wrists. Describe their shape and their movements.
Condylar joints move on oval articular surfaces.
Biaxial movement - flexion, extension, adduction, and abduction
Which joint allows for flexion, extension, adduction, and abduction?
a) condylar
b) pivot
c) ball and socket
d) saddle e) A, C, and D
E
Describe the shape and movements of the saddle joint. Where are they found?
Shape - articular surfaces are both convex and concave
Movement - biaxial movement: adduction, abduction, extension, and flexion
Found in the caropometacarpal joints of the thumbs
Biaxial Movement
Movement on a joint on both a medial/lateral axis and a anterior/posterior axis
The _____ joint is only found in the _____; functions to allow for opposition.
saddle, thumb (where it attaches at the wrist)
The _____ joint has a multiaxial movement and is found in the shoulder and hip joints.
ball and socket
The nerve to the quadratus femoris supplies the ____ and the ____, while the nerve to obturator internus supplies the ____ and the ______
Quadratus femoris nerve - quadratus femoris and the inferior gemellus
Obturator internus nerve - obturator internus and the superior gemellus
The sciatic nerve branch supplies SENSORY innervation to which structures?
Skin over the lateral leg and foot, sole and dorsal surface of the foot
T/F? The superior gluteal nerve branch supplies motor innervation to the gluteus Maximus, medius, and minimus.
FALSE - superior gluteal supplies the gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and the tensor fascia lata
Which branch supplies sensory innervation to the parietal peritoneum in the iliac fossa, or the skin over the anterolateral thigh?
Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh
What make up the superficial group of larger muscles that function to abduct and extend the hip?
Gluteus maximus, medius, minimus, and tensor fascia latae

What makes up the deep group of small muscles that function to externally rotate the femur?
Piriformis, obturator internus, superior and inferior gemellus, quadratus femoris
What muscle lies in between the “twin” muscles - the inferior and superior gemellus?
obturator internus
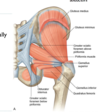
All nerves in the gluteal region travel through the ______ sciatic foramen. Identify which nerves travel above or below the piriformis muscle.
All travel through the greater sciatic foramen.
Below - nerve to quadratus femorus, obturator internus, cutaneous nerve of the thigh, sciatic, and inferior gluteal
Above - superior gluteal

T/F? The pudendal nerve provides sensory innervation to only the deep gluteal muscles.
FALSE - pudendal nerve originates from the lumbosacral plexus but it does not carry any innervation to the gluteal region.
Which nerve pierces the sacrotuberous ligament? What does it innervate?
Perforating cutaneous nerve; innervates the skin over medial gluteus Maximus
The inferior gluteal artery originates from the ____ trunk of the internal iliac, and the superior gluteal artery comes from the ____ trunk. Do they exit above or below the pirirformis?
anterior, posterior
The inferior exits below the piriformis and the superior exits above
The superior gluteal artery will divide in the gluteal region into which branches? Where do they travel?
superficial and deep
superficial - passes onto deep surface of gluteus maximus
deep - passes between gluteus medius and minimus


