Lecture 17 Flashcards
(56 cards)
What are the cranial bones?
Which is the internal, bony component of the nasal cavity?
Which cranial bones are internal?
Frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, sphenoid, ethmoid
ethmoid
Sphenoid and ethmoid.
The supraorbital notch and zygomatic process are found on which cranial bone?
a) sphenoid
b) ethmoid
c) frontal
d) occipital
C
List the components of the temporal bone. Which component of the temporal bone contains the styloid, mastoid, and zygomatic processes?
Squamous and petrous parts, external acoustic meatus, styloid, mastoid, and zygomatic processes.
Petrous part

This is where the brain stem becomes the spinal cord. What cranial bone is this structure found in?
Foramen magnum
Occipital
The occipital bone contains the ___ ___ and the ___ ___. The condyles of the occipital bone will articulate with what joint?
foramen magnum and the occipital condyles.
occipital condyles will articulate with the atlas (C1) to allow us to say yes
List the components of the sphenoid bone.
Which part hangs down, towards the oral cavity?
Which forms part of the back of the oral cavity?
Greater and lesser wings, sella turcica, and pterygoid processes
Pterygoid process
Sella turcica

Which cranial bone connects with almost every other bone in the head?
Sphenoid
Name the components of the ethmoid bone.
Hint: There are 6!
cribriform plate, crista galli, perpendicular plate, superior and middle nasal conchae, ethmoid air cells/sinuses
Which component of the ethmoid bone increases surface area for cleaning, warming, and humidifying the air we breathe?
Which component of the ethmoid bone is found on either side of the cresta galli?
Which also contains small holes for the olfactory nerve?
Nasal conchae - superior and inferior
Cribriform plate
Cribriform plate
T/F? The perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone forms the top half of the cartilage of the nose.
FALSE - perpendicular plate forms the the top half of the BONY septum
The ___ suture is found in between the frontal and parietal bones. The ____ suture is found in between the parietal bones. The ___ suture is were the sagittal suture meets the coronal.
Which suture forms the soft spot in babies?
Coronal, sagittal, bregma
bregma

Which suture lies between the temporal and parietal bones?
Which suture lies between parietal and occipital bones?
Define lambda.
squamous
lamboidal
lambda - where sagittal suture meets the lambdoidal suture; another soft spot in babies - not as prominent as bregma
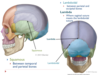
List the facial bones. Which come in two’s?
Maxilla, palatine, zygomatic, mandible, lacrimal, nasal, vomer, and inferior nasal conchae.
All come in two’s, EXCEPT the mandible and vomer bones

The zygomatic bone will articulate with which other bones?
a) frontal, occipital, temporal
b) frontal, temporal, maxilla
c) maxilla, temporal, parietal
d) maxilla, mastoid, mandible
B
The nasal facial bone articulates with which bone?
a) frontal and temporal
b) parietal and temporal
c) occipital and parietal
d) frontal and maxillary
D
What bone makes up the lower, more inferior part of the nasal septum?
vomer
What structures make up the borders for the maxilla?
Zygomatic - lateral
infraorbital - medial
Palatine - inferior
List the components of the mandible.
What is the function of the coronoid process?
Mental foramen, body of mandible, rams of mandible, angle of mandible, coronoid process, condylar process (forms TMJ joint)
The coronoid process serves as a site for muscle attachment in mastication.
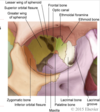
List the bones of the orbit.
Hint: There are 7!
frontal, sphenoid, zygomatic, lacrimal, maxillary, ethmoid, palatine
Which muscle is used to raise eyebrows?
frontalis
What are the muscles of facial expression that the cranial nerve — specifically facial nerve CNVII innervates?
Frontalis, orbicularis oculi, zygomaticus major, orbicularis oris, buccinator
Which of these muscles is used to smile?
A. Zygomaticus major
B. Orbicularis oris
C. Frontalis
D. Orbicularis oculi
A
Which facial muscle allows for you to prevent biting the cheek while eating?
Buccinator - it also compresses distended cheeks
Temporalis and Masseter muscles are innervated by what?
What is the function of these muscles?
cranial nerve (trigeminal nerve CNV) They both raise mandible and allow for mastication to occur






