Lecture 16 Flashcards
(41 cards)
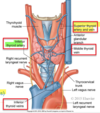
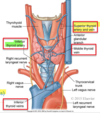
What are the BONES of the neck region?
- Temporal bone
- Mandible
- Hyoid
- Clavicle
- Sternum
- Cervical vertebrae posteriorly

What are the processes in the temporal bone?
mastoid process and styloid process
______ is the only bone in body that is not attached to any other bone; serves as an attachment point for ligaments and muscles
Hyoid bone

Hyoid bone sits ___________ to the larynx
superior
Larynx sits __________ to the pharynx. Larynx leads to the _________ and pharynx leads to the _____________.
anterior, trachea, esophagus
What are the 3 large unpaired cartilages of the larynx? What are they made out of?
Thyroid, cricoid, epiglottis hyaline cartilage

What are the ligaments within the larynx? What do they connect?
thyrohyoid - thyroid to bone
cricothyroid - connect cricoid cartilage to thyroid cartilage

What are the 3 small, paired cartilages in the larynx? function of these cartilages and their associated muscles?
Arytenoid, corniculate, cuneiform
controls vocal cords and allow voice production (control pitch)
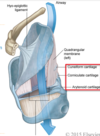
Larynx is supplied by ________ and ___________
Superior laryngeal artery and inferior laryngeal artery

Superior laryngeal artery branches off of the ____________ while inferior laryngeal artery branches off of the _____________
External carotid
Thyrocervical trunk of subclavian
Muscles of the pharynx that form it’s walls and allow for swallowing?
Constrictor muscles (superior, middle, inferior) Longitudinal muscles

What are the anterior muscles of the neck?
Hint: There are 8 total!
Digastric, mylohyoid, omohyoid, geniohyoid, stylohyoid, thyrohyoid, sternothyroid, and sternohyoid

What are the suprahyoid muscles?
Stylohyoid, digastric, mylohyoid, geniohyoid
“students distract my gecko”

List the infrahyoid muscles.
Also known as the “strap” muscles Sternohyoid, omohyoid, thyrohyoid, sternothryoid.
“ISOTS”

Which one of the muscles below are NOT innervated by ansa cervicalis?
a) Sternohyoid
b) Omohyoid
c) Thyrohyoid
d) Sternothyroid
C - innervated by ventral rami of C1
List the branches of the right and left subclavian, which supply the root of the neck.
Internal thoracic artery, vertebral arteries, smaller branches of the thyrocervical and costocervical trunks

The vertebral arteries that originate from the root of the neck will travel up towards the _______ and travel through the ____ ____ of the vertebrae.
brain, transverse foramina
The _____ carotid supplies the neck and the face, while the _____ carotid supplies the brain, via the _____ ____ ____.
external, internal, circle of willis
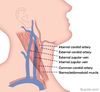
What are the major branches of the external carotid artery? Hint: There are 5!
Lingual, facial, maxillary, superficial, and superior thyroid arteries
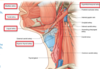
A 19 year old male suffered severe facial lacerations to the face after being flung from the passenger seat through the windshield in a car accident. What major artery of the external carotid would likely be compromised?
Maxillary artery - this supplies the bulk of the face!
What landmarks in the neck are used to palpate the carotid pulse?
Fingers should be positioned between the larynx and anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle at the level of cricoid cartilage
T/F? Only the internal and external jugular veins will drain into the subclavian vein. The anterior jugular vein will drain into the external carotid.
FALSE - all veins will drain to the subclavian
What major artery and nerve will the internal jugular vein travel with?
common carotid and the vagus nerve
The superficial cervical and deep cervical nodes are found near what major arteries? Which bone will separate the superficial from deep cervical nodes?
superficial - external jugular
deep - internal jugular
Infrahyoid