Lecture 15 Flashcards
(57 cards)
What is the difference between extrinsic and intrinsic muscles in the hand?
Extrinsic muscles do not originate in the hand
Intrinsic muscles originate in the hand
What does musculocutaneous nerve innervate?
It innervates the brachialis, coracobrachialis, and biceps brachii muscles in the anterior arm; also travels to innervate skin over the forearm
What is the difference between the brachialis and biceps brachii muscles?
Biceps brachii has 2 origins and allows actions of flexing and supination of the forearm; good for when load is carried
Brachialis has 1 origin and allows for flexion of forearm (elbow)
What’s special about Triceps brachii?
It has 3 origins It’s also in the posterior arm which is called the elbow extensor compartment
Describe the path radial nerve travels
Radial nerve branches off the posterior cord.
Travels through the triangular interval, goes behind humerus and travels on posterior side of humerus near spiral groove

What travels with the radial nerve?
The deep brachial branch/profunda brachii
What is the cubital fossa? What are its borders?
A depression on front of the elbow.
Borders are the brachioradialis muscle, pronator teres muscle, epicondyles of humerus

What are the contents of the cubital fossa?
Tendon of biceps muscle, median nerve, and brachial artery
What travels over the bicipital aponeurosis? What passes under the brachiradialis muscle? What passes posterior to medial epicondyle?
The median cubital vein which connects the cephalon and basilica veins
Radial nerve
Ulnar nerve
What is radial deviation and ulnar deviation?
Radial deviation = ABduction
Ulnar deviation = ADduction

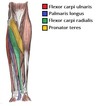
What muscles originate from the medial humerus?
All superficial muscles in the anterior compartment: flexor capri ulnaris, palmaris longis, flexor carpi radialis, and pronator teres

What is the one superficial muscle from anterior compartment that is NOT innervated by median nerve?
The flexor Capri ulnaris - it’s innervated by ulnar nerve
flexor digitorum superficialis muscle’s tendon flexes digits at what joint?
The metacarpal-phalangeal joint and PIP
The tendon of flexor digitorum profundus flexes what joint? Where does the tendon travel?
Distal phalangeal joint — also PIP, MCP, and the wrist joint
The tendon goes through split tendon of the flexor digitorum superficialis tendon
Superficial Muscles of the posterior compartment of forearm (HINT: there are 7) What innervates these?
Extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis
Extensor carpi ulnaris
Extensor digitorum
Digiti minimi
Anconeus
Brachioradialis
Innervated by Radial nerve

What are the DEEP muscles of the posterior compartment of forearm? What nerve innervates these?
Abductor pollicis longus
Extensor pollicis longus and brevis
Extensor indicis
Supinator
Innervated Radial nerve

The anterior compartment of the arm functions to:
The posterior compartment of the arm functions to:
Anterior - flex elbow, flex arm, forearm supination Posterior - extend elbow
The anterior and posterior compartments of the forearm functions to:
Anterior - flex wrist and fingers, pronation
Posterior - extend wrist and fingers, supination
What are the muscles of the anterior arm? These muscles are innervated by which nerve?
Coracobrachialis, brachialis, biceps brachii
Innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve
Name the origins of the biceps brachii muscles. Where do both heads originate from?
the short origin is at the coracoid process and the long origin is at the superglenoid tubercle
What is the muscle of the posterior arm and what is it innervated by? List its origin for each head.
Triceps brachii - innervated by the radial nerve
Long - scapula
Lateral and medial - humerus
The ____ nerve innervates the triceps brachii and travels through the ____ _____, in the _____ groove of the humerus. It then travels with an artery called the ___________ , which supplies the posterior part of the upper limb.
Radial, triangular interval, spiral, profunda brachii
A 7 year old patient is seen over concerns of a possible in her upper arm. Examination reveals that she has fractured the mid shaft of her humerus. What nerve would be of most concern if damaged?
Radial nerve
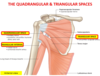
The space in between the teres major and minor is called the ______ space. Which nerve and artery both travel through here?
quadtrangular space
axillary nerve and posterior circumflex artery