Lecture 14 Flashcards
(61 cards)
What bones make up the shoulder girdle and the upper extremity, respectively?
Shoulder girdle - scapula and clavicle
Upper extremity - humerus, radius and ulna, carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges
Where do both ends of the clavicle attach to?
Medial attachment - sternum
Lateral - acromion process of the scapula
The ____ of the humerus attaches at the glenoid cavity to form a _____ joint. The lateral projection is called the ____ tubercle, while the medial projection is the ____ tubercle.
head, ball and socket, greater, lesser
The tendon of the long head of the biceps muscle runs in this groove; found in between the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus.
Intertubercular sulcus/groove
A 5 year old child is admitted to the ER for a fracture in his arm. The X-ray shows a fracture in his humerus. What part of the humerus is likely fractured?
Surgical neck
The rounded protuberance at the distal end of the humerus is called a ______. This forms an articulation with another bone.
Condyle
T/F? The coronoid process is found on the anterior side of the humerus, and the olecranon process is located posteriorly.
TRUE
List the condyles found within the humerus, and whether they are medial or lateral.
Capitulum - lateral; for radial articulation
Trochlea - medial; for ulnar articulation
Epicondyles - lateral and medial
Name the joints of the shoulder. Which is capable of flexion, extension, adduction, and abduction (most flexible)?
Glenohumoral, sternoclavicular, and acromioclavicular.
The glenohumoral is the most flexible
Because the cup of the glenoid cavity has more of a flattened shape, what provides for a better fit for the head of humerus?
Glenoid labrum
Where are the sternoclavicular and acromioclavicular joints found?
Sternoclavicular - between manubrium of the sternum and the medial end of the clavicle
Acromioclavicular - between acromion of the scapula and the lateral end of the clavicle
The radius of the forearm will articulate with the _____ in the humerus
Capitulum
Radial Tuberosity
Bumpout point of the radius where the bicep will attach here
T/F? The radius and the ulna can both do flexion, extension, and a pivoting motion.
FALSE - the ulna and the radius can do both flexion and extension, however only the radius can pivot. The ulna is “locked” into place due to its articulation fashion.
Describe whether the ulna and radius are smaller are larger at both the proximal and distal ends.
Proximal - radius is smaller, ulna is larger
Distal - radius is larger and the ulna is smaller
The ______ _____ is a pen-like projection located at the distal end of both the ___ and ____ and will form the ___ joint.
Styloid process, ulna and radius, wrist joint
The _____ ______ separates the ulna and the radius; this helps stabilize and separate the forearm into compartments.
Interosseous sheath
T/F? Pronation and supination occur at both the wrist and the elbow.
FALSE - pronation and supination both occur at the ELBOW ONLY.
What allows for pronation and supination at the elbow? Hint: it has to do with one of the bones in the forearm!
The radius is not locked into place across the humerus; during pronation, the radius will cross the ulna.
What are the 3 joints of the elbow?
1) trochlear notch of the ulna and trochlea of the humerus
2) Head of the radius and capitulum of humerus
3) Head of the radius and the radial notch of the ulna.
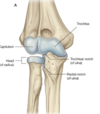
List the carpal bones. Out of these bones, which is a sesmoid bone? Which bone will form the joint between the carpal and the metacarpal of the thumb? What type of joint does it form?
Scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform (bottom) trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate (top)
The pisiform.
Trapezium, saddle joint (only type in the body)

Anular Ligament
A ligament that goes around the radial head to hold it in place; enables pivoting motion without moving out of its socket.
What is the tissue layer that covers the arch created by the carpal bones?
Flexor retinacullum
Define the carpals, metacarpals, and the metacarpophalalangeal joints, and the interphalangeal joints.
- Carpals - little bones in the wrist
- Metacarpals - bones in between the carpals and phalanges
- MCP - joints between the metacarpals and the proximal phalanges
- Interphalangeal joints - found between the phalanges