Physics 2 Flashcards
(129 cards)
1
Q
Sound
- Differentiate b/t Infrasound and Ultrasound
- Give a real-life example of each
A
- Infrasound
- sound of a frequency TOO LOW to be perceived by the human ear.
- Ex: elephants can perceive infrasonic sounds that humans cannot
- Ultrasound
- sound of a frequency TOO HIGH to be perceived by the human ear.
- Ex: dogs can perceive ultrasonic sounds that humans cannot
1
Q
- Lenses & Mirrors
- Image Types
- Differentiate b/t Virtual and Real images wrt location of IMAGE & LIGHT SOURCE
- Image Types
A
Virtual Images
- there is NO ACTUAL LIGHT emanating from* or *reaching the image
- Ex: The image formed is behind a plane mirror
Real Images
-
THERE IS ACTUAL LIGHT at the image
- ex: Image formed on your retina

2
Q
Electricity
- Conductance
- Define wrt how they deal with ELECTRON FLOW:
- conductor
- resistor
- insulator
- semiconductor
- superconductor
- Define wrt how they deal with ELECTRON FLOW:
A
CONDUCTOR
- is a material that allows the flow of electrons through it relatively UNIMPEDED
RESISTOR
- is a material that tends to IMPEDE the flow of electrons.
- This being said, even the best conductors do exhibit some small degree of resistance to the flow of electrons
- superconductors being the possible exception
- and all resistors do conduct electrons to some small degree
- This being said, even the best conductors do exhibit some small degree of resistance to the flow of electrons
INSULATOR
- is a material with a very, very high resistivity.
- There is NO perfect ideal insulator that allows zero current flow under all conditions.
- However, materials like glass and Teflon allow negligible current flow up to extremely high voltages.
- There is NO perfect ideal insulator that allows zero current flow under all conditions.
SEMICONDUCTOR
- is a material thought to be right in the middle of an insulator and a conductor (in terms of conductivity vs. resistivity).
SUPERCONDUCTOR
- is a material that under very precise conditions is thought to exhibit zero resistance to electron flow
2
Q
- Deriving Electric Field equations
- Force
A
- For gravity near earth, F=mg
-
For a constant elec. field:
- **F=qE **
-
For a constant elec. field:
-
For “real” gravity, F=Gmm/r2
- For a point-charge elec. field:
- F=Kqq/r2 (Coulomb’s Law)
- For a point-charge elec. field:
3
Q
- Lenses & Mirrors
- The 4 Lens/Mirror Rules
- (for single-lens systems only!)*
1. Object distances, p, are always ___
2. Image distances, q, or focal point distances, f, are- ___ if they are on the SAME SIDE as the observer
- ___if they are on opposite sides
- The observer and object are on the:
- same side for a _____
- on opposite sides for a ____
- Explain “PRI/NVU”
A
- Object distances, p, are always (+)
- Image distances, q, or focal point distances, f, are
- (+) if they are on the SAME SIDE as the observer
- (-) if they are on opposite sides
- The observer and object are on the:
- same side for a mirror
- on opposite sides for a lens
-
PRI/NVU:
- “Positive, Real, Inverted”
- “Negative, Virtual, Upright”
-
ALWAYS STAY TOGETHER!!!!!!!!!
- if you know 1 trait, you know the other 2 by association
4
Q
- Electricity
- Charge
- Charge is QUANTIZED, according to?
- (what numerical value)
- Charge is QUANTIZED, according to?
- Charge
A
- e-= 1.6 x 10-19 C
5
Q
- Magnetism
- How do electric fields and magnetic fields relate to each other?
A
- Changing electric fields create magnetic fields
- any movement, velocity, rotation, etc. of a charged particle causes a change in the electric field created by that charge
- thus, creates a magnetic field
- any movement, velocity, rotation, etc. of a charged particle causes a change in the electric field created by that charge
- Changing magnetic fields create **electric fields **
6
Q
- Machines
- Levers
- Formula=?
- Levers
A
- Fm=mg (L1/L2)
- L1= lever arm for the MASS
- L2= lever arm for the APPLIED FORCE
6
Q
- Circuits
- Solving circuits using Ohm’s Law
- What if I can’t adding things together doesnt yield a Simple Circuit?
- Kirchoff’s Rules!
- Describe them (2)
- Kirchoff’s Rules!
- What if I can’t adding things together doesnt yield a Simple Circuit?
- Solving circuits using Ohm’s Law
A
- Apply Kirchoff’s rules
- 1st Rule:
- current INTO node=current OUT OF node
- 2nd Rule:
- In any cyclical circuit, V=0
- the sum of the voltage drops across each resistor equals the total voltage of the battery
- In any cyclical circuit, V=0
- 1st Rule:
6
Q
- Sound
- General Characteristics
- How is sound produced?
- What are its properties as a mechanical wave?
- General Characteristics
A
- Sound is always created by a vibrating medium
- these vibrations propagate through liquids or solids, and generate pressure waves that propagate through GASES (such as air)
- As a mechanical wave, sound CANNOT propagate in a vacuum
7
Q
- Waves
- The Doppler Effect
- Describe the “Doppler Shift”
- Give the 2 formulas
- The Doppler Effect
A
- The Doppler “Shift”
- perceived by observer
- dependent on the relative velocity b/t the SOURCE & OBSERVER
- Greater the relative velocity, greater the shift in frequency or wavelength
-
__Δf / fs= v / c
- fs= “source” frequency
-
Δλ/λs= v / c
- λs= “source” wavelength

8
Q
- Forms of Energy
- Kinetic Energy formula
A
- KE= ½mv2
9
Q
- Electric Fields
- Deriving Electric Field equations
- how do you get these kinds of equations?
- what do you need to remember to differentiate between?
- Deriving Electric Field equations
A
- Use conversions for equations you already know for GRAVITY
- Be sure to differentiate between:
-
CONSTANT Electric Fields
- are derived by comparison to gravity NEAR EARTH
-
POINT-CHARGE Fields
- are derived by comparison to “actual” gravity, or gravity IN SPACE
-
CONSTANT Electric Fields
9
Q
- Waves
- Wave speed
- Formula
- Name the “3 Cardinal Wave Rules”
- Wave speed
A
- Formula
- V=λf
- 3 CARDINAL WAVE RULES:
- Wave speed (velocity) is determined BY THE MEDIUM
- Frequency NEVER changes when a wave moves from medium to medium
- Wavelength DOES change when a wave moves from medium to medium

10
Q
- Lenses & Mirrors
- Give the 3 formulas we need to know:
- The one for mirrors
- Thin-Lens equation
- Magnification equation
- Wrt (+/-) signs, what does a negative M indicate?
- Give the 3 formulas we need to know:
A
- **f=½r **(for mirrors only!)
- 1/p+1/q=1/f (Thin Lens equation. Good for mirrors also)
- **M= -q /p = hq/hp **
- Negative M= inverted image
11
Q
- Waves
- Superposition of waves
-
The Beat Frequency
- Occurs when?
- what do waves need to have very similar to e/o?
- Give equation
- fbeat=?
- Occurs when?
-
The Beat Frequency
- Superposition of waves
A
- Occurs when 2 waves with close to the same FREQUENCY interfere with e/o

fbeat= |f1 - f2|
12
Q
- Optical Power
- Describe OP for Two-Lens Systems
- what are some examples of 2 lens systems?
- Give formulas for Magnification and Power
- Describe OP for Two-Lens Systems
A
- The image formed by the first lens BECOMES THE OBJECT for the second lens
- Ex: binoculars, telescopes, microscopes, etc.
- Magnification
- M=m1m2
- Power
- P=p1+p2
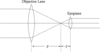
13
Q
- Sound
- Harmonics
- Why does a pipe open at BOTH ends give all harmonics, but a pipe open at one end and closed at the other only gives the odd harmonics?
- Harmonics
A
- For a pipe open at one end and closed at the other, the first harmonic features a node at one end and an antinode at the other.
- It is impossible to have a node at the open end of a pipe and impossible to have an antinode at the closed end of a pipe.
- These facts restrict the possible waveforms.
- The logical “next step,” if you will, to move to the next harmonic from the first one is to add a node—
- this is impossible, however, because it would require that there be nodes at both ends of the pipe.
- Thus, we skip this step and add one node and one antinode to get the third harmonic.

14
Q
- Electric Fields
- Deriving Elec Field equations
- PEelec
- Deriving Elec Field equations
A
- For gravity near earth, PEgrav=mgh (height measured against gravity)
- For a constant elec field:
- PEelec=qEd (distance measured against strength of elec. field)
- For a constant elec field:
- For “real” gravity, **PEgrav=-Gmm/r **
- for a point-charge elec field:
- **PEelec=-Kqq/r ** OR
- PEelec=Kqq/r
- for a point-charge elec field:
14
Q
Circuits
- Resistance
- How can “resistance” be conceptualized/compared to:
- ____in fluids or ____ between solids
- Give the Formula for resistance
- How is Resistance “Temperature Dependent?”
- The wires b/t any 2 elements in a circuit are assumed to be PERFECT _____S
- wherein resistance=___
- All resistance occurs where?
- How can “resistance” be conceptualized/compared to:
A
Resistance can be conceptualized as the equivalent of:
- DRAG in fluids or FRICTION between solids
R=ρL/A
- ρ=resistivity
- L=length
- A=cross-sectional area
Temperature Dependence
- Starting around room temp, an increase in temperature results in:
- a linear increase in resistivity
- Changing temp is the ONLY WAY you can change resistance in a circuit without replacing the resistor
The wires b/t any 2 elements in a circuit are assumed to be PERFECT CONDUCTORS!
- resistance=zero
- all resistance occurs at the resistors
14
Q
Waves
- Types of Waves
-
Electromagnetic (EM) Waves
- What kind of medium is req’d for these waves?
- EM waves are capable of propagating in WHAT?
- Can they transfer energy, momentum, or both?
- Are they transverse or longitudinal?
- Give examples of EM waves
-
Electromagnetic (EM) Waves
A
- NO medium required!
- Capable of propagating in a vacuum
- Can transfer BOTH energy & momentum
are TRANSVERSE ONLY
Ex: visible light, microwaves, radio waves
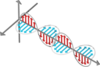
14
Q
- Wave Speed
- Wave velocity (v) in various mediums
- Describe velocity of a wave on a string
- Here, what are its elastic & intertial properties?
- How does increasing these properties affect V?
- Describe velocity of a wave on a string
- Wave velocity (v) in various mediums
A
- The elastic property (that provides the restoring force in a string)
- is the string’s TENSION
- Increased tension always increases velocity.
- The inertial property
- is mass per unit length, the “linear mass density”
- μ: v = √(T/μ).
- A thicker string (increased mass per length) always decreases velocity (provided the tension stays the same)
- is mass per unit length, the “linear mass density”
14
Q
- Waves
- Superposition of waves
- Differentiate b/t areas of constructive & descructive interference
- Superposition of waves
A
- Constructive Interference
- regions where the amplitudes of superimposed waves ADD TO each other
- INCREASES amplitude
- regions where the amplitudes of superimposed waves ADD TO each other
- Destructive Interference
- regions where the amplitudes of superimposed waves SUBTRACT FROM each other
- DECREASES amplitude
- regions where the amplitudes of superimposed waves SUBTRACT FROM each other

15
Q
- Machines
- What do machines do? What do they never do?
A
- They reduce the amount of forces necessary to perform a given amount of work
- They NEVER reduce or change the amount of work
16
* Electromagnetic Spectrum
* Describe Visible Light
* λ=?
* Describe RED light (3)
* Describe Violet light (3)
* Mnemonic=?
* ***390-700nm***
* ***RED*** *LIGHT*
1. ****lowest** energy
2. **lowest** frequency
3. **longest** λ
* ***VIOLET*** *LIGHT*
1. ****highest** energy
2. **highest** frequency
3. **shortest** λ
* Mnemonic:
* ROYGBIV

17
* Machines
* Ramps
* Formula
* What does a "5 meter long" ramp or a "5 meter ramp" ***imply?***
* **Fm=mg (h/d)**
* h=height of ramp
* d=distance along its hypotenuse
* Fm=force necessary to do the work *with* the machine
* "5 meter ramp" or "5 meters long"
* implies that the _***hypotenuse*** _of the ramp is 5m
18
* Circuits
* Ohm's Law
* Formula
* What is a common error when manipulating equations using Ohm's Law?
* Formula
* V=IR
* Common error:
* it ***CANNOT*** be said that if voltage **increases** and current remains **constant** that resistance will ***INCREASE***
* Resistance is a permanent quality of the resistor *itself*
* The only way to change resistance is to:
1. *physically replace* resistors with resistors that have different Ohm's ratings, or
2. change the temperature of the resistor
19
* The Law of Conservation of Energy
* *Energy in a/n ____ system is always \_\_\_\_*
* Describe this Law
* *Energy in an **ISOLATED** system is always **CONSERVED***
* Energies (KE, PE, Heat Energy, etc.) are frequently ***transferred*** back and forth, but ***NEVER LOST ***
20
* Electric Fields
* Comparing Elec. Field equations to Gravity
* What (in **gravity** equations) equates to what (in **elec. field** equations)?
_Example to start you off:_
**g** (stength of **grav**. field) = **E** (strength of **electric field**)
* **g** (stength of grav. field)
* =**E** (strength of electric field)
* **G** (constant)
* **K** (constant)
* **h** (distance)
* =**r or d**
* **m** (mass)
* =**q** (charge)
* **F** (force)
* =**F** (same in both)
* **gh** (PEgrav)
* =**V** (voltage, PEelectrical)

21
* Optical Power
* Formula (for single-lens systems)
* **P=1/f**
22
Electric Fields
* Electric **Dipoles**
* "a dipole is a _______ of positive & negative charges of ____ \_\_\_\_\_\_\_"
* What happens when a dipole is exposed to an **electric field**?
* What if the dipole **DOESNT** do the above thing when exposed to B?
* What does it **HAVE,** then?
*a dipole is a **separation** of positive & negative charges of **EQUAL magnitude***
When a dipole is exposed to an elec. field, it tends to ***align itself** with that field*
* ***a dipole that is _NOT aligned_ with the elec. field has PE***
* ******alignment with the field is a **lower energy state** than alignment ***AGAINST*** the field
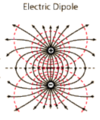
23
* Electricity
* Charge
* Explain "Conservation of Charge"
* The Universe always has a ***ZERO net charge***
* Charge is created by separation
* If you separate one electron from a neutral atom, you have created:
* one independent unit of **negative charge** (the electron)
* and _simultaneously_ created one independent unit of **positive ****charge** (the cation)
24
Electric Fields
* **Electric Field Lines**
* Always drawn with their \_\_\_\_s at the **POSITIVE** charge
* _____ LINES=**STRONGER** FIELD
* Field Lines best approximate "\_\_\_\_ flow"
* What is the *opposite* of this kind of flow?
* Always drawn with their ***tails*** at the ***positive*** charge
* Pointing *AWAY FROM*, or
* Pointing *TOWARDS* the ***negative*** charge
* ***CLOSER LINES=STRONGER FIELD***
* Field Lines best approximate *Current Flow*
* Current flows from **positive to negative** concentrations
**ELECTRON** Flow is the ***opposite*** (neg.⇒pos.)

24
* Waves
* Types of Waves
* compare Transverse vs. Longitudinal waves
* Transverse waves
* displace the medium ***perpendicular to*** their direction of travel
* ex: EM waves, waves on a string
* Longitudinal waves
* displace the medium ***parallel to*** their direction of travel
* ex: sound waves, p-wave earthquakes

24
* Wave Speed
* Wave Velocity in various mediums
* velocity of ***sound*** waves in a ***SOLID***
* ******what are the elastic & inertial properties?
* How do these sound waves differ than the ones going through a gas?
* Elastic property: "Bulk Modulus" (B)
* Inertial property: Density, ρ
* Although the *densities* of solids are typically ***thousands of times higher*** than the densities of gases...
* the elastic moduli are even increased ***by an even LARGER factor!!***
* This property causes solids to ***“spring back” extremely quickly*** following deformation.
* Sound (compression) waves in solids are therefore ***TYPICALLY _MUCH FASTER_ THAN SOUND WAVES IN GASES .***
25
* Power
* Formulas
* Think of power in ***THIS ORDER (4)***
* Units=?
1. **P=ΔE/t**
2. **P=W/t**
3. **P=Fscosθ**
4. **Pi=Fvcosθ**
* gives "**instantaneous** power"
* should only be used when asked for *specifically*
* **Units: **Watts**
* J/s
26
* Wave Characteristics
* Describe
* wavelength
* period
* velocity
* frequency
* intensity
* phase
* Wavelength (units = meters)
* distance between two adjacent:
* crests (a.k.a., peaks, maxima),
* troughs (a.k.a., valleys, minima).
* Period and frequency are ***ALWAYS _INVERSES_ OF EACH OTHER!!***
* Velocity
* ***how fast*** the wave moves _in space_ (in m/s).
* given by v = fλ.
* Amplitude
* the “distance” between:
* the equilibrium point and a crest, or between the equilibrium point and a trough.
* Intensity is
* a measure of power per unit area.
* Waves have power because they transport energy from one point to another in a given amount of time.
* Intensity is proportional to the ***square of the amplitude*** and the ***square of the frequency.***
* Phase
* is a relative measure of ***how closely two waves*** (typically with the same frequency) ***are oriented to one another in space***,
* typically expressed in *radians* or *degrees*.
* Two waves that are “in phase” should cross the x-axis **at the same point**, but _may have different amplitudes_
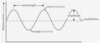
27
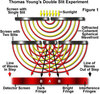
* Light
* Describe how Young's Double-Slit experiment was physically ***SET UP***
* ******What needed to happen for his experiment to work?
* Young shone a monochromatic light through a screen with a single slit in it.
* The purpose of this slit was to **create coherent wavefronts**
* Behind the first screen he placed a second screen ***with two narrow, parallel slits.***
* These created the *diffraction* pattern.
* Finally, behind the second screen he placed a *third* screen.
* Light traveled through the first two screens and formed alternating pattern of ***LIGHT*** and ***DARK*** bands on the third screen.
For the experiment to work, the light traveling through each of the 2 slits in the middle screen *must be coherent* and have the ***SAME FREQUENCY & POLARIZATION***
28
* Electric Fields
* Think of a "Field" as...?
* ***FIELD=*** *an invisible **influence** capable of **exerting a FORCE** on a:*
* *mass, or*
* *charge*
30
* Think of the *formulas* for ***WORK*** in this order (2)
* If ____ changed, think ***WORK! ***
1. W=Δ *Energy*
2. W=Fdcosθ
* If ***ENERGY*** changed, think ***WORK!***
31
* Lenses & Mirrors
* Near-Sighted vs Far-Sighted
* describe
* Where is the image in relation to the location of the retina?
* Near-sighted (myopia)
* able to focus clearly on ***CLOSE*** objects, but not on distant ones
* The image is ***IN FRONT OF*** the retina
* Far-sighted (hypertropia)
* able to focus clearly on ***DISTANT*** objects, but not on close ones
* The image is ***BEHIND*** the retina
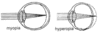
32
# * Light
* Dual nature
* Define particle & wave models for light
* What specific experiment/effect **supports** each model?
*How are these two models **reconciled**?*
**_The Wave Model of light_**
supposes that light is a **wave**
* **Young’s Double Slit Experiment** provides support for this model
* because only waves would show the **diffraction** and **interference** patterns necessary to create the characteristic **light** and **dark** bands
**_The Particle Model of light_**
supposes that light is a **particle**
* **The photoelectric effect** is the major support for this model.
* Says that electrons are ejected from a material when light of ***sufficiently high frequency*** is used—
* but ***NOT UNTIL*** a threshold frequency is reached.
*_The two are reconciled by:_*
***_QUANTUM MECHANICS!_***
photons are ***described by “wave functions”*** which sometimes act as
* macroscopic ***waves***, and sometimes as
* macroscopic ***particles***
33
* Waves
* In order for 2 waves to be "in phase" with each other:
* What **3 characteristics** must they share?
* Which of these 3 is **MOST IMPORTANT?**
* ****What do the 2 waves need to **share** in order to have this characteristic?
* In order to be **100% in phase**, two waves would have to have the same:
**1) Frequency**,
**2) Wavelength**
and *most importantly*
**3) TIMING OF MAXIMA/MINIMA**
* which could be done if they share the **same time/place of origin**)
34
* Light
* Energy of a Photon
* Formula
* **E=hf**
* h=Plack's constant (given)
35
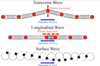
Waves
* Types of Waves
* What are **MECHANICAL** Waves?
* 2 traits:
* What do they **require** to propagate?
* Do they transfer **energy**, **momentum**, or **both**?
* Are they **Transverse** or **Longitudinal** or **Both**?

1. ***REQUIRE A MEDIUM*** to propagate
2. Transfer ***ENERGY ONLY!!!*** (not momentum)
Can be ***BOTH*** transverse & longitudinal
1. Transverse
* transverse mechanical waves require a fairly ***STIFF MEDIUM*** in order to propagate
* ∴ ***cannot*** propagate in **liquids** or **gases**
* ex: strings on a musical instrument
2. Longitudinal
* ex: sound waves
36
* Define Chemical Energy
* The energy contained ***within chemical bonds***
* Or the energy ***stored/released*** due to the separation and/or flow of ***ELECTRONS***
* i.e. a battery
37
* Electric Fields
* What are 2 additional ways to think of "voltage?"
1. ) Voltage =Potential Energy ***DIVIDED by _charge_ or _mass_***
2. ) Voltage= whatever "thing" you can ***MULTIPLY by mass or charge*** to get Potential Energy
* Examples:
* gh\*m=mgh=*PEgravitational*
* Ed\*q=*PEelectrical*=V\*q
38
Electromagnetic Spectrum
* List (in order) each class of the EM spectrum and their relative **ENERGIES** (10x)
* Hint:
* **R**emember **M**y **I**nterest **V**aries **U**nder
**X**ternal **G**roups
* **Radio** waves
* 103
* **Micro**waves
* 10-2
* **Infrared** waves
* 10-5
* **Visible** Light
* 10-6
* **Ultraviolet** light
* 10-8
* **X**-rays
* 10-10
* **Gamma** Rays
* 10-12

39
Waves
* Intensity
* The **Decibel (dB)** System
* Define
* How is it **similar** to & **differ** from the Richter scale (for earthquakes)
*is a rating system for the intensity of sound **within the range of human hearing***
Both it and the Richter scale use ***logarithmic scales***
* Difference:
_In short:_
***10x** increase on Richter Scale = **1 unit increase***
***10x** increase on dB scale=**10 unit increase***
10x increase in earthquake intensity=*1.0 unit increase on Richter scale*
***10x increase in sound intensity=1_0.0 unit increase on dB scale_***
* a sound 10x more intense is ***10dB higher***
* a sound 100x more intense is ***20 dB higher***
* a sound 1000x more intense is ***30 dB higher***
40
* Circuits
* Solving Circuits using Ohm's Law
* How to add in series/parallel:
* Resistors
* Capacitors
* Batteries
* Resistors
* in series:
* add directly
* in parallel:
* add the inverses
* take the inverse of *that* sum
* Capacitors ***(o******pposite of solving for resistors)***
* in series:
* add the inverses
* take the inverse of that sum
* In parallel:
* add directly
* Batteries
* in series:
* add directly
* in parallel:
* ***TOTAL voltage= ***the ***HIGHEST*** voltage of *any one of the batteries in **parallel***
40
* Waves
* Types of Waves
* List the ones we're supposed to know
* Transverse vs Longitudinal
* EM Waves
* Mechanical Waves
40
Sound
* Sound Resonance
* Explain how objects have "natural frequencies" and what a "harmonic" is
All objects have one or more ***natural frequencies*** *at which they will vibrate when disturbed.*
* Some objects produce a **random** array of different vibrational frequencies.
* Other objects (i.e., musical instruments) vibrate at ***non-random natural frequencies***
* ******which are integer multiples of a number (e.g. 200Hz, 400Hz, 600Hz, 800Hz).
* These orderly frequencies are called "***HARMONICS"***
41
* W=Δ Energy
* When you see the following **6 situations**, think ***WORK!*********
* Which of these 6 is the **most common** example of work you'll see?
* ******What's an important caveat to remember about energy transfer in a system?
1. Change in **VELOCITY**
* change in KE=work!
* ***most common example!***
2. Change in **HEIGHT**
* change in PEgrav = work
3. Change in **POSITION** (of **masses**/**planets**/etc.) **IN SPACE**
* change in PEgrav = work
4. **COMPRESSION** of a spring
* change in PEelastic = work
5. **FRICTION**
* change in internal energy=work
6. **AIR RESISTANCE**
* change in internal energy=work
***_CAVEAT_:***
Energy transfer in a system ***could** be due to **Heat Transfer** as well!!*
* **non**-conservative forces dissipate some heath energy
* this leaves ***LESS*** energy available to do work
* Use of word "heat" refers to *an **increase** in the* ***internal energy* of the molecules, NOT**"heat transfer" ('Q' from the first law of Thermodynamics).
42
Sound
* **Drawing** Harmonics:
* For a single vibrating guitar string of the same length*
* the 1st harmonic is only __ of a \_\_
* the 2nd harmonic is **exactly** __ \_\_
* the 3rd harmonic is __ \_\_
The harmonics shown below are all for a single vibrating guitar string of the ***same length***
* Notice:
* the 1st harmonic is only **½** of a **λ**
* the 2nd harmonic is **EXACTLY 1 λ**
* the 3rd harmonic is **1½** **λ**

43
Waves
* Define **"INTENSITY"**
* **Give Units**
* How does intensity relate to **waves**?
* What is intensity **_directly_ proportional** to in:
* **SOUND** *(aka* "mechanical"*)* waves
* **LIGHT** waves

Intensity= ***POWER per unit area***
*Units: Waves/m2*
* Waves often have power (often called "sound power")
* because they *transfer energy from one location to another w/in a specified time*
* (aka, energy flux)
_In *sound or **mechanical** waves,* Intensity is ***DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL TO:***_
* **AMPLITUDE 2**
* **FREQUENCY2 **
_******In **LIGHT** waves***,*** intensity is directly proportional to:_
* **AMPLITUDE2**
But ***NOT (!!)* FREQUENCY2**
44
* W=Fdcosθ
* Think of *_this_* definition of work 1st/2nd?
* Any time a ___ has been applied across a \_\_\_\_\_, WORK has been done
* Units=\_\_\_\_, which is **equivalent** to? (2)
Think of this definition ***second***
(First should be W= Δ in energy)
* Any time a ***force is applied across a displacement,*** _work_ has been done
_Units: **Joules, aka:**_
* N\*m
* kg\*m2 /s-2
45
# Intensity
Waves
* Intensity
* Why do sound waves create **spherical** shapes when traveling from their point of origin?
* **MAGNITUDE OF INTENSITY** \_\_\_\_\_es according to ___ of the growing sphere created by sound waves
* **Why**? (Has to do with how **Intensity** is measured; waves/**m2**)
* Many waves (such as sound) travel outward from their origin **in ALL directions SIMULTANEOUSLY***
* ...which creates a wave front in the*
* shape of a growing sphere*
Magnitude of Intensity ***DECREASES*** according to **AREA** of the growing sphere
* b/c **intensity** is measured *per **square meter***
_**IN**creasing **m2** leads to a **DE**crease in **Intensity**_ (ODI)
* **A=4πr2**

46
* Circuits
* Voltage
* Think of "voltage" as...?
* What's another "intuitive way" of thinking about voltage?
* 2 formulas
Voltage=the amount of PE a system is capable of storing per unit charge
**V=PEsys/q**
* Another way:
* Voltage=the amount of work necessary to **move** a charge ***against the electric field***
* moving a **longer** distance requires **more** work (voltage **increases** with distance)
Formulas:
* **V=Ed**
* **V=Kq/r**
47
Circuits
* Capacitors
* The Dialectric
* Describe what it is and what it does
* **INCREASING** Dialectric=\_\_\_\_\_ing **Capacitance**
* Which allows for...?
* The dialectric must *always* be a \_\_\_\_\_\_or
The "dialectric" is the
***substance BETWEEN the two plates***
* ***ALL** capacitors* have a dialectric, ***even if it is just air***
* Other dialectrics=gel, composites, etc.
* once inserted, some energy stored in the capacitor is used to align the polar molecules in the dialectric (ie, dipoles) with the field between the plates
* Increasing the strength of the dialectric ***increases the capacitance***
* ******allowing more charge and energy to be stored
***INCREASING dialectric=INCREASING capacitance***
* The dialectric must always be an ***INSULATOR.***

48
* Waves
* The Doppler Effect
* Remember these **3 key points**:
* "v" is _____ velocity
* "c" is the ____ of the \_\_\_
* Does the answer of the **equation** usually give us that answer we ***need***?
1. The variable ***v*** is ***RELATIVE*** velocity
* ***NOT*** the velocity of either object
2. The variable ***c*** is the ***speed of the wave***
* 3 x 108 m/s for light
* 340 m/s for sound
3. The answer is of the equation is***CHANGE IN λ***
* which is often ***NOT*** what they're asking for!!
***This*** value must be **added** or **subtracted** from the **initial** value in order to get the ***ACTUAL*** value due to the doppler effect
1. Add to the frequency (subtract from the λ) if the relative motion is ***towards*** each other
2. Add to the λ (subtract from the frequency) if the relative motion is ***away from*** each other
49
* Light
* Young's Double Slit experiment
* Equation
* Define diffraction
* **x=λL/ d**
* x=distance b/t fringes
* λ=wavelength of light used
* d=distance b/t the two slits
* L=distance b/t double-slit and final screen
* Diffraction
* is the tendency of light to ***spread out*** as it goes:
* ***around a corner, or***
* ***through a slit***
* *equally as important* as constructive & destructive interference in Young's experiment
* without it, Young's characteristic interference patterns wouldnt be formed

50
* Sound
* Harmonics
* Formulas (2)
* Differentiate b/t when to use each
* show their rearranged forms
* **L=nλ/ 2**
* For string or pipe with ***matching ends***
* Both nodes or both antinodes
* Gives all nodes
* n=1,2,3...
* Rearranged: **λ=2L/ n**
* **L=nλ/ 4**
* ****For *one node* and *one antinode*
* Pipe open at ***one end ONLY***
* Gives only the ***ODD harmonics! ***
* ******n=1,3,5...
* Rearranged:** λ=4L/ n**
51
* Circuits
* Current flows ____ wrt to electron flow?
* Current formula
* Current flows from __ to \_\_
* Electrons flow from __ to \_\_
* Current flows ***opposite*** to the direction of electron flow
* I=Δq/Δt
* Current flows from ***positive to negative***
* Electrons flow from ***negative to positive ***
52
* Snell's Law
* Total Internal Reflection
* What is the "Critical Angle?"
* What happens if it is exceeded?
* For waves passing from higher index mediums into lower index mediums, the critical angle ***is the angle of incidence for which the angle of refraction will be 90°.***
* If this angle is exceeded, ***refraction ceases*** and ***all waves are reflected back*** into the more dense medium (Total Internal Reflection)

53
* Torque & Lever Arms
* Fulcrums & Boards on Strings
* are simply ___ problems
* how do you solve?
* are simply ***equlibrium*** problems
* To Solve:
* set Tclockwise=Tcounterclockwise
* Include ***ALL ***torques
* including T created by mass of the board
* Force due to mass of the board will act as *center of mass*
* will always be the exact linear center of a uniform board
* Dont forget to set *torques* equal to e/o, ***NOT FORCES!!!***
* units: N\*m
* Forces or tensions located ***exactly at center*** of rotation do ***NOT CREATE A TORQUE!! (ignore)***
* ******since r=0
53
* The Work-Energy Theorem
* Describe
* Formula
* Best to just think of it as...?
* If a net force does work on a rigid object,** **the work done on that object ***is equal to the change in the KE*** of the object
* W= KEfinal - KEinitial
* ***Focus on ΔE***
* if you think of it this way, there is ***no need*** to use the Work-Energy Theorem
54
* Forms of Energy
* Gravitational PE formula
* PEg= -Gmm/r
55
* Magnetism
* Give 4 examples of things that involve moving charges, and thus create a magnetic field
1. Nuclei with an odd atomic # or mass #
* they exhibit nuclear spin
2. Electrons
* because they orbit and spin
3. Current
* because it ***IS*** moving electrons
4. Bar Magnets
* usually made of nickel, iron, or other alloy
* Normally, electrons in a metal are *approximately split* between spin states
* In bar magnets, though, they are ***partially aligned***, creating a ***net magnetic field***
57
Electric Fields
* **Equipotential** Lines
* How are they draw in comparison to **FIELD** **LINES?**
* What do Equipotential lines **represent**?
* Are drawn ***perpendicular to*** field lines
* Represent ***areas of equal voltage*** (i.e. electrical potential)

58
* Electricity
* Charge
* What is a ***BIG MISCONCEPTION*** about Charge?
* Thinking of positive charges as tiny little "things" with an inherent charge
* similar to electrons, except positive
* This is (essentially) a ***positron***
* ***Protons*** also fit this concept
* ***_FORGET ABOUT POSITRONS & PROTONS_*** when it comes to:
* ******circuits, electricity, current, etc.
* Positive charge is ***ALWAYS:*********
* ******a_ ***LACK OF ELECTRONS ***_(relative to being neutral)
59
* Circuits
* Ohm's Law across a resistor states that...?
* *Voltage drop* across _***THAT*** _resistor=*current* through ***_THAT _***resistor X *resistance* of ***_THAT _***resistor
60
* Sound
* Harmonics
* Characteristics (3)
* Frequency of any harmonic is equal to..?
* For oscillators with matching ends, the λ of the **2nd** harmonic equals..?
1. The frequency of the first harmonic is called the ***“fundamental frequency.”***
2. Each additional harmonic has its own unique *frequency* and *wavelength*.
3. Each harmonic always has one more node, and one more antinode, than the previous harmonic.
The frequency of **any** harmonic is equal to:
***n\*fundamental frequency***
* (e.g., if the first harmonic is exactly 200 Hz, the 2nd is 400 Hz, the 3rd is 600 Hz, etc.)
For oscillators with matching ends, ***the wavelength of the second harmonic equals:***
***the LENGTH of the string or pipe (λ= L)***
61
* Electric Fields
* Deriving Elec Field equations
* Voltage
* For gravity near earth, **V=gh **
* For a constant elec field:
* **V=Ed** (d measured against strength of elec field, E)
* For "real" gravity, **V=Gm/r**
* for a point-charge elec field:
* **V=Kq/r**
63
* Work
* The 1st Law of Thermodyamics
* Describe
* Formula
* Energy change ***is not ALWAYS due to work***
* some energy is lost to/dissipated as *heat*
* Work + Heat are the ***ONLY TWO WAYS*** energy can be transferred in/out of a system
* ΔE= W+Q
* Work=energy transfer *due to a **force***
* Heath=energy transfer *via **energy flow** from Hot⇒Cold*
64
* Waves
* Intensity
* Define "Attenuation"
* what 2 things cause it in *non-dispersive mediums* (like EM waves in a vacuum or ideal strings)
* the ***gradual loss of intensity*** as a wave passes *through a medium*
* *
* In non-dispersive mediums, this is ***due to scattering*** (i.e. reflection) ***of some waves*** and ***absorption of wave energy***

65
Sound
* Harmonics
* What are **Overtones**?
* How do they relate to harmonics?
* The terms “1st overtone,” “2nd overtone,” etc., are sometimes used.
* The 1st overtone is ***NOT the same*** as the 1st harmonic!!!!
* The first harmonic is called
* _the fundamental frequency,_
* the ***second*** harmonic is called
* the ***1st overtone***
* the ***third*** harmonic is called
* the ***2nd overtone***, and so forth.
67
* Magnetism
* Think of Magnetism as analogous to \_\_\_, with these (3) changes
* Magnetism=analogous to ***ELECTRICITY***, with these changes:
1. Replace (+) charges with ***NORTH ***poles
2. Replace (-) charges with ***SOUTH ***poles
3. Magnetic Field lines go from **North⇒South,** *instead* of Positive⇒Negative
68
* Define a system ***NOT*** in equilibrium
* How is solving these problems different than solving for equilibrium problems?
* any problem where the object in question has a ***_NON-ZERO_ ACCELERATION***
* *aka _Net Force_ is **NOT** zero*
* Solved in the same way as an equilibrium problem, but you ***add "ma"to the _losing side_***
* By adding ma to the weaker side we are making them **equal** again
70
* Circuits
* Switches
* Symbol=?
* Compare open vs. closed switches
* Symbol: a diagonal break in the line b/t circuit components
* Open switch
* ***NO ***electron flow
* Closed switch
* ***electrons flow***
71
* Torque & Lever Arms
* What are the 3 formulas we need to remember?
* in most cases, what should we simply use what equation?
* T=Fl
* T=mgl
* T=Frsinθ
* when force applied *_isnt_ perpendicular*
* *θ _isnt_ 90º*
* rsinθ=l, but ***only when θ=90º***
* You can usually just use ***T=Fl***
72
* Circuits
* Capacitors
* what do capacitors do?
* What is their symbol?
* Formulas
* Capacitance
* PE stored by a capacitor
* capacitors ***store energy and charge*** by holding electrons on plates separated by a very small distance
* Symbol: 2 vertical lines of equal length
* Formulas:
* Capacitance
* C=Q/V
* PE stored *by a capacitor*
* U=½CV2
* Solve C=Q/V for the missing variable, then plug it into the above equation
* U=½CV2 looks a lot like the KE formula!
73
* Define Heat Energy
* what are the 2 common forms you'll see on the MCAT?
* What is the term "Heat Energy" almost interchangeable with?
* Energy dissapated as heat
* on the MCAT, this usually is heat dissapated from a:
1. ***collision*** , or
2. ***curent-carrying wire***
* "Heat Energy" ≈ "Internal Energy"
74
* Circuits
* Capacitance
* Affect on capacitance: Increasing...
* Plate area
* Plate thickness
* distance b/t plates
* strength of the dialectric
* voltage
* _Increasing plate area_ ***increases*** capacitance because there is more room available on the inside surface of the plate to store electrons.
* Electrons do not line up on the sides or back of the plate, so _increasing plate thickness_ will have ***no effect*** on capacitance.
* _Increasing the distance between the plates_ increases voltage for a given Q on the plates, which ***decreases*** capacitance according to C = Q/V.
* _Increasing the strength of the dielectric_ ***increases*** capacitance because the dielectric impedes the buildup of the electric field between the plates and diverts some of the capacitor’s finite energy storage capacity to realign dipoles inside the dielectric.
* _Increased voltage_, increases the charge stored but ***does not increase capacitance,*** which is the charge stored per voltage.
75
* Sound
* Pitch
* Define
* What *kind* of term is "pitch?"
* what is pitch closely related to?
* Higher pitch=?
* Pitch is the ***"perception" of frequency*** by the human _ear_
* Closely related to frequency, but ***NOT IDENTICAL***
* Is a musical (not scientific) term
* Sounds with ***HIGHER PITCH*** have:
* *********higher frequencies***
* ******Sounds with ***LOWER PITCH*** have:
* ***lower frequencies***

76
* Deriving Electric Field equations
* Strength of the Electric Field
* For gravity *near earth, ***g=F/m** (from F=mg)
* for a constant elec field:
* **E=F/q** (or **E=V/d**)
* For "real" gravity, **g=Gm/r2 **
* for a point-charge elec field:
* **E=Kq/r2**
77
* Lenses & Mirrors
* What type of lens is found in:
* the human eye
* a magnifying glass
* The lens of the human eye ***is a converging lens***.
* It creates a **real (inverted)** image of the object onto the retina.
* A magnifying glass is ***also a converging lens***

78
* Waves
* The Doppler Effect
* Color Shifts
* How can the Doppler Effect shift *colors*?
* If the Dopper Effect causes an ***INCREASE*** in frequency (or ***DECREASE*** in λ):
* *White light* shifts ***BLUE***
* If the Dopper Effect causes an ***DECREASE*** in frequency (or ***INCREASE*** in λ):
* *White light* shifts ***RED***

79
* Light
* Visualizing photons as "light packets," predict **which way light will bend** at both boundaries in the scenarios below:


80
* Waves
* Superposition of Waves
* Standing Waves
* describe what creates nodes, anti-nodes, and properties of standing waves
* is a special case of simultaneous ***CONSTRUCTIVE _AND_ DESTRUCTIVE*** interference b/t 2 waves
* have ***identical*** frequencies moving through the *same medium* in ***opposite*** directions
* At points of maximum destructive interference, waves ***cancel entirely*** to create a "node"
* At points of maximum constructive interference, the waves ***ADD completely*** to form an "anti-node"
* Result:
* is a waveform in which the areas b/t the nodes appear to ***OSCILLATE up & down*** b/t crests and troughs
* A standing wave exhibits ***NO net transport of energy,*** and does not ***itself*** propagate
* basically, theres no translational mvmt of nodes or anti-nodes in *either* direction
* When a standard ***Traveling*** wave propagates, the minima & maxima move translationally in the direction of propagation

81
* Electric Fields
* What are the 2 types of electric fields?
* Name & describe
1. Point Charge Fields
* equate to "real" gravity, or **gravity in space**
* A point charge field is an electric field **created by a point charge**
* The strength of the electric field ***varies with the distance (r)*** from the point charge.
2. Constant Electric Fields
* equate to "assumed" gravity, or **gravity near earth**
* is *constant*
* its strength does ***NOT ***vary with distance
82
* Circuits
* What do you need to do before you can solve for a circuit using Ohm's Law (V=IR)?
* Create a simple circuit
84
* Circuits
* Resistors
* Symbol=?
* What always happens when current, I, flows through a resistor?
* What is "Internal Resistance?"
* What is current flow like through parallel resistors?
* Symbol=zig-zag line
* There is ***ALWAYS*** a ***voltage drop*** across a resistor when current flows through it
* Internal Resistance
* batteries experience internal resistance dur to the (inherent) *resistivity of their internal components*
* This results in a voltage drop, and therefore ***DECREASES ***(slightly) ***THE TERMINAL VOLTAGE OF THE BATTERY***
* Current flow through parallel resistors is always *inversely proportional *to ***resistance***
* if one resistor has 2X the resistance, it will receive ½ the current
86
* Machines
* Pulleys
* Formula=?
* What should you be cautious for?
* Fm= mg/ (# of vertical ropes ***_directly_ lifting*** the mass)
***CAUTION: ***
* Not ***_every_*** rope that is vertically oriented should be counted and entered into the above equation
* To be counted, a vertical section of rope must life the mass ***directly***
* ******either by being attached ***TO*** the mass, or
* ***by lifting a _pulley_*** that is attached to the mass
* To test, imagine grabbing ***ONLY THAT ROPE*** and pulling it upward. Would the mass lift?
87
* Electromagnetic Spectrum
* All of these waves (RMIVUXG) are \_\_\_?
* Longer wavelength=?
* Shorter wavelength=?
* ***All*** *of these waves are* ***LIGHT!***
* Longer wavelength
* **lower** frequency
* ***LESS ENERGY***
* Shorter wavelength
* **higher** frequency
* ***MORE ENERGY***
88
* Light
* How should be visualize "photons?"
* Why?
* ***AS PHYSICAL PACKETS OF LIGHT! ***
* ******Visualize one of these packages striking a flat boundary at an angle.
* It is easy to visualize that one corner of our little “light packet” is going to hit the surface first—before the other corner does.
* If the light is passing from a low index medium to a high index medium, that first corner is suddenly going to be forced to go slower than any other part of the packet that is still in the less dense medium, much like what happens when a car tire goes off the road and hits a soft shoulder.
* The “light packet” will tend to ***pivot around the corner that is “stuck” in the higher-index medium.***
* We can intuit exactly which way the light will bend.
90
* Forms of Energy
* Elastic PE
* PEelastic= ½kx2
91
* Lenses & Mirrors
* Lenses (single-lens systems)
* Compare Converging & Diverging lenses
* what do they each usually produce?
* what about when "p" (obj.) is *inside the* focal point?
* What should you assume about Far away objects? (like the moon)
* Converging (aka convex, positive)
* ***_USUALLY (!!)_*** produces a ***positive, real, inverted image***
* When "p" is inside the focal point, it produces a ***negative, virtual, upright image***
* Diverging (aka concave, negative)
* ***ALWAYS (!!)*** produces a ***negative, virtual, upright image***
* Far away objects
* assume the light hitting the lens ***are all PARALLEL***
* As object approaches the lens, the image will ***no longer*** be exactly at the focal point *f*

93
* Think of ***ENERGY*** as...?
* The capacity to do ***WORK***
95
* Machines
* Force necessary *_without_* a machine
* Formula=?
* What's the use of solving for this wrt machines?
* Fnecessary= mg
* Solving for force needed *without* a machine helps when comparing it to force needed *with* a machine
* Factors will differ by an exact ***ratio*** (e.g. 1:5)
96
* Forms of Energy
* PE stored in a capacitor (3)
* PEcapacitor= ½ QV
* PEcapacitor= ½ CV2
* PEcapacitor=½Q2/C
97
* Circuits
* Batteries
* Symbol=?
* Think of batteries as...?
* What do ALL batteries _cause_?
* Symbol: two vertical lines of UNequal length
* Longer line= (+) terminal
* shorter line= (-) terminal
* Batteries=***electron "pumps" that push electrons _onto the negative terminal_ of the battery***
* this creates a *separation of charge*, and therefore a ***potential difference*** b/t terminals
* this drives electron flow *around the circuit t*o the positive terminal
* All batteries cause ***A SEPARATION OF CHARGE***
* (which in turn creates a voltage)
98
* Circuits
* Household AC current
* Define:
* "Root mean square current" (RMS)
* what is it, how to calculate, etc.
* The “root mean square” (RMS) method of calculating both voltage and current are necessary for alternating current applications because the current and voltage over time are sinusoidal.
* This creates a ***problem ,*** because the average of a sine wave centered _at the origin_ is ***zero***.
* If you randomly sampled the voltage in your household wiring it could literally have a voltage of 120V *one* instant and a voltage of -120V the *next* instant.
* That would ***average*** to zero, even though the alternating current does deliver a continuously useful source of power (It can dissipate energy during both cycles).
* Power companies therefore use the RMS method to calculate the ***average power*** ***delivered to your home***
* RMS is just a mathematical calculation and it can be applied to voltage, current, to sine waves, or even to other waveforms such as square waves.
* To find RMS, you take readings at various time intervals, ***square*** all of those readings, take the ***average of those squares*** (i.e., the mean of the squares) and then take the ***square root of that average***.
99
* Electrical Power
* Household Electrical Power
* Name & Describe the 2 types
1. Alternating Current (AC)
* Both the polarity of the voltage and the direction of the current ***periodically reverse.***
* A graph of current versus time for an AC current creates a sine wave
2. Direct Current (DC)
* Direct flow of current through a circuit from positive to negative
* (or in terms of electron flow, from negative to positive).
* DC current is the kind of power used in automobiles because it comes directly from the battery.
* In fact, if something uses a battery you would be perfectly safe on the MCAT to assume that ***it must be an example of DC current.***

100
* Magnetism
* Formula
* Units
* F=qvBsinθ
* θ=angle between v and B
* Units (of B):
* N\*s/C\*m OR
* Kg/A\*s2
101
* Electrical Power
* Formula
* **P=IV**
* Just memorize this one
* Solve V=IR for the missing variable, then plug it in to get the other two

102
* Waves
* Intensity
* The Decibel System
* Intensity in dB equation=?
* **Intensity (dB)= 10\* log ( I / I0 )**
* I=intensity of the sound wave in (W/m2)
* I0= threshold of human hearing
* I0=1 x 10-12 W/m2
* will always be given
104
* Define "Internal Energy"
* what relation do **non-conservative force**s (such as? Give 2 examples) have with internal energy?
*_The energy of:_*
* the **internal vibrations***
* and **random motions of molecules** and/or atoms*
* within a system*
* Non-conservative forces (such as **friction** or **drag**) acting on a moving object results in the _transfer_ of:
***KE⇒ INTERNAL ENERGY***
105
* Systems NOT in equilibrium
* 2D Forces
* The system we have outlined simplifies everything into **up/down** or **left/right** forces.
* You may well have a force that acts in two-dimensions, say at an angle of 30° to the horizontal.
* In such cases simply enter into your table the ***formula that predicts the component of that force*** that acts up, down, left or right.
106
* Sound
* Harmonics
* Draw diagrams for the first 3 harmonics of:
1. a pipe ***open at one end*** (antinode) and ***closed at the other end*** (node)
2. pipe open ***at both ends***

107
* Mechanical Energy
* Give the formula
* What happens to mechanical energy in the ***absence*** of *non-conservative* forces?
* ***ME=KE+PE***
* ******In the absence of no-conservative forces, Mechanical Energy is ***CONSERVED***
* ******aka "Total Energy" is conserved
108
* Wave Speed
* Wave velocity in various mediums
* wave speed (v) is typically equal to the ____ of the medium, divided by \_\_\_\_
* Show *this* in equation format ^^
* Describe it a bit
* Wave speed is typically equal to *the **square root** of an **ELASTIC** property* of the medium divided *by an **INTERTIAL** property*
* ***v =*** *√****(elastic/inertial) ***
* The elastic property is often called a ***“modulus”.***
* The inertial property is a ***type of density. ***
111
* Equilibrium
* Give 5 examples of equilibrium
1. Terminal velocity (Fair=mg)
2. constant velocity
3. Objects at rest
4. Balanced fulcrums
* or boards hanging from strings
5. Objects floating in a liquid
112
* Snell's Law
* Index of Refraction
* Formula (for I.O.R.)
* Give Formula for Snell's Law
* What does a ray of light being refracted at an interface where **n2\>n**1 look like?
* Index of Refraction
* **n=c/v**
* Snell's Law
* **n1sinθ1=n2sinθ2**

113
Systems **NOT** in equilibrium
* Equilibrium on an Inclined Plane
* all forces acting down the plane are ____ \_\_\_\_\_
* all forces acting up the plane __ \_\_\_\_\_
* The force **down** the plane **due to gravity** is always F = \_\_\_\_\_
* The force of **friction** is always ______ to the plane \_\_\_\_\_the direction of motion.
* There will NEVER be ______ **perpendicular** to the plane, so you can ignore these forces.
* all forces acting down the plane are “**down** forces”
* all forces acting up the plane “**up** forces.”
* The force down the plane due to gravity is always **F = mgsinθ**.
* The force of friction is always **parallel** to the plane **opposite** the direction of motion.
* There will ***_NEVER_*** be **acceleration** perpendicular to the plane
* so you can **ignore these forces**.

114
* Forms of Energy
* Electrical PE (3)
* PEelec= Kqq/r
* PEelec= qEd
* PEelec= qV
115
* Lenses & Mirrors
* Mirrors
* For plane mirrors ***ONLY***, the image *q* and object *p* will always be...?
* ***EQUAL DISTANCES*** on either side of the mirror

116
* Wave Speed
* Wave velocity in various mediums
* Velocity of ***sound ***waves in a ***GAS***
* what are the elastic & intertial properties?
* How does increasing these affect V?
* The elastic property is called the “bulk modulus” **(B)**
* ***directly proportional*** to ***BOTH ***
* ******density _and_
* temperature
* ∴ for gases, the velocity ends up having this "temperature dependence:"
* **v ~ √(T)**
* The inertial property is normal density, ρ
* **v = √(B/ρ)**
117
* Electricity
* Charge
* What "is" a (-) and (+) charge?
* Negative (-) Charge=***electrons***
* Positive (+) Charge= relatively ***FEWER*** electrons
118
* Snell's Law
* Total Internal Reflection
* Describe
* What must happen for it to occur?
* Formula
* For light crossing a boundary from a slower to a faster medium (like from glass or water into air), if the angle of refraction would be 90° or more, the incident light ***does not enter the second medium at all!!***
* ******100% of the light is reflected off the boundary and ***back into the first medium***.
* For total internal reflection to occur, the light must be passing from a **higher index** medium to a **lower index** medium.
* Formula
* n1sinθ1=n2sin_90º_ ***SO...***
* **sinθ1=n2/n1**

119
What do **TRANSVERSE** Mechanical waves **require** to propagate?
* ∴ they **cannot** propagate in \_\_\_\_s or \_\_\_\_s
* What's an **example** of a transverse mechanical wave?
Transverse mechanical waves require a fairly **STIFF MEDIUM** in order to propagate
* ∴ cannot propagate in **liquids** or **gases**
ex: **strings** on a musical instrument
120
When solving for **Batteries** in **PARALLEL:**
How do you find the **TOTAL VOLTAGE?**
*HINT: It's easy!*

**_Batteries in parallel:_**
**TOTAL** voltage=
the **HIGHEST** voltage of **any** one of the batteries in parallel
121
**Current, I,** flows from ____ to _____ concentrations
* What's the **OPPOSITE** of Current Flow?
**CURRENT** FLOW goes from **(+)⇒(-)**
**ELECTRON** FLOW is the opposite **(-)⇒(+)**
122
Sound
* Sound Resonance
**Harmonics** (aka "Natural" Frequency)
* Explain how one object **vibrating** near another object can cause them both to be in "**RESONANCE"**, and how "harmonics" factors into all of this
* What do 2 objects being in resonance **CAUSE?**
* ****What **in** **particular** that is happening to cause this effect?
*When one object is vibrating near another object it can cause the neighboring object*
***to begin vibrating at that SAME frequency***
If the **exact** frequency at which the second object is caused to vibrate **happens** to be one of its "natural frequencies" (i.e., **harmonics**):
_the two objects are said to be "**in resonance"**_
* ...and via **CONSTRUCTIVE** **interference** can produce a much **LOUDER** sound!
If the first object causes a vibration in the second object that is **NOT** a match to one of its natural frequencies, resonance does **NOT** occur
123
\_\_\_\_\_ing _______ is the **ONLY WAY** you can **change RESISTANCE** in a circuit
Changing **TEMPERATURE** is the **ONLY WAY** you can change resistance in a circuit!
124
The Doppler Effect
* The answer of the **equation** will give us is **CHANGE IN \_\_?**
_THIS IS **NOT** THE ANSWER THEY'LL BE ASKING FOR!!!_
* How do you get the **ACTUAL** value due to the **doppler** effect?
* *HINT: It depends if the relative motion is **towards/away from** each other...*
**Δf/fs = v/c**
**Δλ/λs = v/c**
The answer is of the equation is **CHANGE IN λ**
* which is often **NOT** what they're asking for!!
***This** value must be*
***added** or **subtracted** from the **initial** value*
* in order to get the **ACTUAL** value*
* due to the **doppler** effect*
_If the relative motion is **TOWARDS** each other:_
* Add to the **FREQUENCY**
* (subtract from the λ)
_If the relative motion is **AWAY FROM** each other:_
* Add to the **λ**
* (subtract from the frequency)
125
* A parallel plate capacitor charged to **4 x 10-13C** is allowed to discharge for several seconds until it bears a charge of **2.4 x 10-13C***
* How many electrons flowed off of the capacitor during the discharge?*
***1.0 x 106C***
**4E-13 - 2.4E-13=1.6E-13**
*Divide by **1.6E-19** to get 1**E6C***
This question requires that you remember **the charge on an electron is -1.6 x 10-19C**
* Subtract the **final** charge from the **initial** charge and **divide** **by the charge on one electron**
* to get 1.0 x 106C
Remember that electron charge is **quantized** according to -1.6 x 10-19C
* In other words, you cannot have a **fraction** or **decimal** of an electron
* In practice, the charge of an electron is so small that generally it is not possible to count individual electrons with precision
*
126
* A **20 Coulomb** charged particle is dropped into a parallel plate capacitor with very large and distant plates and experiences a **force of 250 N***
* The distance between the plates is **2.0 meters***
* What is the **voltage** across the capacitor?*
**25V**
## Footnote
***E=F/q** **OR** **E=V/d***
_To answer this question you must remember that the **strength of a field** (**"E"**) is defined by:_
* the **force** it can exert on a given **charge**,
* expressed in:
* **Newtons /Coulomb** or
* **Volts /meter**
* *(Why? Remember that **V = Ed**, solve for E)*
**Calculate E** using **N/C**
* set that number **equal to V/m**
* then **solve for V**
127
# Sound
The **frequency** of **ANY** harmonic is equal to?
\_\_ x ___ \_\_\_\_
**n\*fundamental frequency**
## Footnote
"Fundamental Frequency"= **FIRST** harmonic object resonates at
(e.g., if the first harmonic is exactly 200 Hz, the 2nd is 400 Hz, the 3rd is 600 Hz, etc.)
128
* The **first** harmonic is called
* the _____ \_\_\_\_\_\_\_
* the **second** harmonic is called
* the\_\_\_ \_\_\_\_\_
* the **third** harmonic is called
* the\_\_\_ \_\_\_\_\_
* The **first** harmonic is called
* the **fundamental frequency**,
* the **second** harmonic is called
* the **1st overtone**
* the **third** harmonic is called
* the **2nd overtone**, and so forth


