Cardiovascular Flashcards
(156 cards)
In what form does Hb carries about 15% of its respiratory carbon dioxide?
carbaminohaemoglobin
What percentage of respiratory carbon dioxide does Hb carry as carbaminohaemoglobin?
15%
Name three factors that can shift the O2 saturation curve to the right
Increased DPG Increased temperature Decreased pH
What effect does altitude adaptation have on the O2 saturation curve?
Shifts it to the right
What is a typical EDV?
110 to 120ml (Guyton and Hall, 1996)
What is a typical cardiac output?
5-5.25 L/min
What effects does parasympathetic stimulation of the heart have?
Decreased heart rate
What is APTT
Activated partial thrombin time
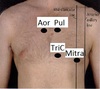
Identify these valve events


What are the 3 layers of a blood vessel?
Intima
Media
Adventitia
Which vessels contribute most to blood pressure?
Arterioles
Define embolus
Intravascular mass carried in the blood stream to a remote site. May be solid, liquid or gaseous
Define atherosclerosis
Accumulation of lipid and fibrous connective tissue (plaque) in the intima of medium and large arteries
Name 4 ways endothelium is implicated in atherosclerosis
- Endothelial damage increases permeability to LDL
- Damaged endothelium loses its normal anti-coagulant properties
- Endothelium recruits macrophages through expression of selectins, ICAM and VCAM
- Endothelial cells don’t produce as much prostacyclin or NO → impaired vasodilation
What is the ligamentum arteriosum a remnant of?
Ductous arteriosus
What condition is this?

Aortic regurgitation
What does concentric hypertrophy compensate for?
Increased afterload
What is the order of the cardio exam?
General inspection. Palmar creases. Capillary refill. Radial pulse. BP. Conjunctiva. Lips and tongue. JVP. Carotid pulse. Palpate apex beat. Auscultation. Lungs. Shin oedema. Dorsal pedis pulse. Posterior tibial pulse.
Define eccentric hypertrophy
Normal relative wall thickness
Increased LV mass
LV enlargement
Define concentric hypertrophy
Increased relative wall thickness
Increased LV mass
No LV enlargement
Define compliance
ability of any chamber to accept increased volume
What are the constitutive subunits of Hb in adults and foetuses?
Adults: 2 alpha and 2 beta Foetuses: 2 alpha and 2 gamma
What type of blood vessels are these?

Arterioles
What condition is this?

Mitral stenosis