Nick's Foundation block Flashcards
(210 cards)
What does haematoxylin bind to?
Acidic or anionic structures
What are the 3 types of granulocytes?
Basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils
What is an immature RBC called?
Reticulocyte
What is the average lifespan of a platelet cell?
8-10 days
What type of WBC is this?

Basophil
What shape is the nucleus of a monocyte?
Kidney /bean shaped or eccentric oval
What type of WBC is this?

Neutrophil
List the 4 main function of connective tissue
Structural support
Metabolic support
Immune defence
Tissue repair
Name 7 locations where simple columnar, non-ciliated epithelial cells are found
Stomach
Small intestine
Large intestine
Gall bladder
Bile ducts
Endocervix
Endometrium
Name 2 locations where simple columnar, ciliated epithelial cells are found
Bronchioles
Fallopian tube
What are the 7 causes of celll injury?
Hypoxia
Chemicals and drugs
Micro-organisms
Metabolic
Immune
Nutritional
Genetic
Describe 3 steps in fibrinoid necrosis
1 Deposited immune cells in blood vessels
2 Fibrin leakage
3 Necrosis
Define metastatic calcification
Abnormal calcium deposits due to hypercalcaemia.
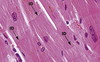
What type of tissue is this?

Smooth muscle
Name the 5 isotypes of Ig and what each is specialised for.
IgM - First responder. Activates classical pathway of complement cascade.
IgA - present in mucosa. Neutralises
IgG - Most common. Neutralises and opsonises. Antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC); flag for NK cells
IgE - Elevated in parasitic infections and allergy. Degranulation.
IgD - rarest. Expressed on B cells
Which germ layer is muscle derived from?
Mesoderm
What type of ttissue is this?

Skeletal muscle
What colour does eosin stain?
Pink/orange
Which WBC has a kidney-shaped nucleus?
Basophils OR Monocytes
Which WBC has a bilobed nucleus?
Eosinophils and basophils
Which three substances mediate vasodilation in inflammation?
Histamine, NO, prostaglandin PGE2
What is the function of glycoproteins of the basemenbt membrane?
They anchor integrins of epithelial cells to ECM of the underlying connective tissue
What is the structure of elastin?
Made of an elastin core surrounded by network of fibrilin myofibrils
Name these ligaments

A Supraspinous ligament
B Ligamentum flavum
C Posterior longitudinal ligament
D Anterior longitudinal ligament