An Overview of Immunology Flashcards
(84 cards)
What is an antigen?
Anything the immune system responds to
Antigens are usually …
protein
Antigens are not necessarily ‘…’
‘bad’
The main role of the immune system is to protect from …
infection
What is an antigen receptor?
Recognises the antigen -> fundamental basis of immunity, basis of division into innate and adaptive
The innate immune system fundamentally recognizes antigens using ….
Germline-encoded pattern-recognition receptors
The adaptive immune system is activated in the presence of pathogens - … cells and … cells recognise antigens through …-specific … and … cell receptors
The adaptive immune system is activated in the presence of pathogens - T cells and B cells recognise antigens through antigen-specific T and B cell receptors
… mechanisms are an action to respond to the antigen (innate and adaptive have a lot of shared mechanisms - distinction is in the way they recognise the antigen rather than what happens next)
effector mechanisms
The cells of the immune system originate in the … …
The cells of the immune system originate in the bone marrow
Pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells thus differentiate into bone marrow as … or … stem cells.
Pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells thus differentiate into bone marrow as myeloid or lymphoid stem cells.

Pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells thus differentiate into bone marrow as lymphoid or myeloid stem cells (common lymphoid progenitor or common myeloid progenitor). These then give rise to the two lineages of immunological cell. We have lymphocyte lineage (… cells) and myeloid lineage (cells such as …)
Pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells thus differentiate into bone marrow as lymphoid or myeloid stem cells (common lymphoid progenitor or common myeloid progenitor). These then give rise to the two lineages of immunological cell. We have lymphocyte lineage (T,B, NK cells) and myeloid lineage (cells such as neutrophils, eosinphil, basophil, monocyte, mast cell)

Pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells thus differentiate into bone marrow as … or … stem cells.
Pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells thus differentiate into bone marrow as myeloid or lymphoid stem cells.

Pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells thus differentiate into bone marrow as lymphoid or myeloid stem cells (common lymphoid progenitor or common myeloid progenitor). These then give rise to the two lineages of immunological cell. We have lymphocyte lineage (… cells) and myeloid lineage (cells such as …)
Pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells thus differentiate into bone marrow as lymphoid or myeloid stem cells (common lymphoid progenitor or common myeloid progenitor). These then give rise to the two lineages of immunological cell. We have lymphocyte lineage (T,B, NK cells) and myeloid lineage (cells such as neutrophils, eosinphil, basophil, monocyte, mast cell)

What is the function of a neutrophil?

Phagocytosis
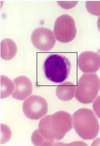
What cell is this? (White blood cell)
Neutrophil
What cell is this? (White blood cell)
Neutrophil
What is the function of an eosinophil? (is not fully understood - may be important in what infections?)

? Helminth (parasitic) infection, allergies also
What cell is this? (White blood cell)
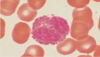
Eosinophil
What cell is this? (White blood cell)

Monocyte (Circulating) Called Macrophage (in the tissue)
What is the function of a monocyte? (called macrophage in tissue)

Phagocytosis, Antigen presentation
What is the function of a dendritic cell?

Antigen presentation
What cell is this?

Dendritic cell
What cell is this? (White blood cell)

Basophil - tissue-resident counterpart = mast cell
What is the function of a basophil? (tissue-resident counterpart = mast cell)
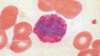
?Helminth (parasitic infection) also in allergy - release histamine