Introduction to Surgery of the Foot and Ankle Flashcards
(96 cards)
Basics of Foot & Ankle Pathology
- 3 Sections- …, … and …
- Pathology in any one of these areas has a reciprocating effect in the rest of the foot
- The foot is like a tripod
- 3 Sections- hindfoot, midfoot and forefoot
- Pathology in any one of these areas has a reciprocating effect in the rest of the foot
- The foot is like a tripod

Basics of Foot & Ankle Pathology
- 3 Sections- hindfoot, midfoot and forefoot
- Pathology in any one of these areas has a reciprocating effect in the rest of the foot
- The foot is like a …
- 3 Sections- hindfoot, midfoot and forefoot
- Pathology in any one of these areas has a reciprocating effect in the rest of the foot
- The foot is like a tripod

Why is the foot so important?
- To ensure that we have a smooth … cycle
- If foot anatomy is abnormal foot … is compromised
- To ensure that we have a smooth gait cycle
- If foot anatomy is abnormal foot function is compromised
Basics of Foot and Ankle
- Have a natural … valgus
- Further valgus your … and … will compensate
- If you go into varus it will also compensate
- Have a natural hindfoot valgus
- Further valgus your midfoot and forefoot will compensate
- If you go into varus it will also compensate

Basics of Foot and Ankle
- Have a natural hindfoot …
- Further … your midfoot and forefoot will compensate
- If you go into … it will also compensate
- Have a natural hindfoot valgus
- Further valgus your midfoot and forefoot will compensate
- If you go into varus it will also compensate

How do we achieve this surgically? (natural hindfoot valgus)
- Tendons
- Debridement
- Tenodesis
- Tendon …
- … repair
- Ligaments
- … repair
- Tendon transfer
- Bone
- …tomy
- …stectomy
- Tendons
- Debridement
- Tenodesis
- Tendon transfer
- Direct repair
- Ligaments
- Indirect repair
- Tendon transfer
- Bone
- Osteotomy
- Exostectomy
How do we achieve this surgically? (natural hindfoot valgus)
- Tendons
- …ment
- …
- … transfer
- Direct repair
- Ligaments
- Indirect repair
- Tendon transfer
- Bone
- Osteotomy
- Exostectomy
- Tendons
- Debridement
- Tenodesis
- Tendon transfer
- Direct repair
- Ligaments
- Indirect repair
- Tendon transfer
- Bone
- Osteotomy
- Exostectomy
Aims of treating Foot and Ankle Pathology
- Is always to achieve a foot which is :
- …
- Plantigrade
- … normal
- Functionally normal
- Is always to achieve a foot which is :
- Painless
- Plantigrade
- Structurally normal
- Functionally normal
Aims of treating Foot and Ankle Pathology
- Is always to achieve a foot which is :
- Painless
- …
- Structurally normal
- … normal
- Is always to achieve a foot which is :
- Painless
- Plantigrade
- Structurally normal
- Functionally normal
Achilles Tendon
- Also known as the … cord
- The gastrocnemius, soleus and plantaris muscle unites to form a band of fibrous tissue which becomes the Achilles tendon which attaches to the … tuberosity
- … and … tendon
- Approximately 15 cm in length
- … of the foot
- Also known as the heel cord
- The gastrocnemius, soleus and plantaris muscle unites to form a band of fibrous tissue which becomes the Achilles tendon which attaches to the calcaneal tuberosity
- Largest and strongest tendon
- Approximately 15 cm in length
- Plantarflexor of the foot

Achilles Tendon
- Also known as the heel cord
- The …, soleus and … muscle unites to form a band of fibrous tissue which becomes the Achilles tendon which attaches to the calcaneal tuberosity
- Largest and strongest tendon
- Approximately … cm in length
- Plantarflexor of the foot
- Also known as the heel cord
- The gastrocnemius, soleus and plantaris muscle unites to form a band of fibrous tissue which becomes the Achilles tendon which attaches to the calcaneal tuberosity
- Largest and strongest tendon
- Approximately 15 cm in length
- Plantarflexor of the foot

Achilles tendon is approximately … cm in length
Achilles tendon is approximately 15 cm in length

Label the diagram


Why is the achilles tendon vulnerable to pathology?
- Unlike other tendons it has no … …
- It is surrounded by a … (connective tissue sheath to ensure gliding )
- It has a poor blood supply
- i. Posterior tibial artery ( proximal and distal section)
- ii. Peroneal artery ( supplies midsection)
- Blood vascularity weakest at the bone –tendon interface
- Blood supply weakest at 2 to 6 cm form the calcaneal attachment
- Unlike other tendons it has no tendon sheath
- It is surrounded by a paratenon ( connective tissue sheath to ensure gliding )
- It has a poor blood supply
- i. Posterior tibial artery ( proximal and distal section)
- ii. Peroneal artery ( supplies midsection)
- Blood vascularity weakest at the bone –tendon interface
- Blood supply weakest at 2 to 6 cm form the calcaneal attachment
Why is the achilles tendon vulnerable to pathology?
- Unlike other tendons it has no tendon sheath
- It is surrounded by a paratenon ( connective tissue sheath to ensure …)
- It has a poor … …
- i. Posterior … artery (proximal and distal section)
- ii. … artery ( supplies midsection)
- Blood vascularity weakest at the bone –tendon interface
- Blood supply weakest at 2 to 6 cm form the calcaneal attachment
- Unlike other tendons it has no tendon sheath
- It is surrounded by a paratenon ( connective tissue sheath to ensure gliding )
- It has a poor blood supply
- i. Posterior tibial artery ( proximal and distal section)
- ii. Peroneal artery ( supplies midsection)
- Blood vascularity weakest at the bone –tendon interface
- Blood supply weakest at 2 to 6 cm form the calcaneal attachment
Why is the achilles tendon vulnerable to pathology?
- Unlike other tendons it has no tendon sheath
- It is surrounded by a paratenon ( connective tissue sheath to ensure gliding )
- It has a poor blood supply
- i. Posterior tibial artery ( proximal and distal section)
- ii. Peroneal artery ( supplies midsection)
- Blood vascularity weakest at the … –… interface
- Blood supply weakest at 2 to 6 cm from the … attachment
- Unlike other tendons it has no tendon sheath
- It is surrounded by a paratenon ( connective tissue sheath to ensure gliding )
- It has a poor blood supply
- i. Posterior tibial artery ( proximal and distal section)
- ii. Peroneal artery ( supplies midsection)
- Blood vascularity weakest at the bone –tendon interface
- Blood supply weakest at 2 to 6 cm form the calcaneal attachment
- Achilles tendon - Blood vascularity weakest at the … –tendon interface
- Blood supply weakest at .. to … cm form the calcaneal attachment
- Achilles tendon - Blood vascularity weakest at the bone –tendon interface
- Blood supply weakest at 2 to 6 cm form the calcaneal attachment
Achilles rupture
- Occurs after a sudden forced … to the foot
- Violent … in a planatar flexed foot
- Usually ruptures 4 to 6 cm above the calcaneal insertion in the hypovascular region
- Occurs after a sudden forced plantarflexion to the foot
- Violent dorsiflexion in a plantar flexed foot
- Usually ruptures 4 to 6 cm above the calcaneal insertion in the hypovascular region

Achilles rupture
- Occurs after a sudden forced … to the foot
- Violent dorsiflexion in a … foot
- Usually ruptures 4 to 6 cm above the … insertion in the hypovascular region
- Occurs after a sudden forced plantarflexion to the foot
- Violent dorsiflexion in a plantar flexed foot
- Usually ruptures 4 to 6 cm above the calcaneal insertion in the hypovascular region

Achilles Rupture - Treatment
- Most common - In Functional …
- Surgery
- … to … repair
- VY advancement
- Failure to heal- Tendon …
- Tendon used is the one closest in proximity – FLEXOR HALLUCIS LONGUS
- In Functional bracing
- Surgery
- End to end repair
- VY advancement
- Failure to heal- Tendon transfer
- Tendon used is the one closest in proximity – FLEXOR HALLUCIS LONGUS

Achilles Rupture - Treatment
- Most common - In Functional bracing
- Surgery
- End to end repair
- … advancement
- Failure to heal- … transfer
- Tendon used is the one closest in proximity – FLEXOR … …
- In Functional bracing
- Surgery
- End to end repair
- VY advancement
- Failure to heal- Tendon transfer
- Tendon used is the one closest in proximity – FLEXOR HALLUCIS LONGUS
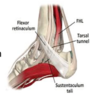
What is tendon transfer?
This procedure repositions the flexor hallucis longus tendon, (commonly called the “FHL” tendon) to reinforce a diseased Achilles tendon.
When is tendon transfer used?
This procedure repositions the flexor hallucis longus tendon, (commonly called the “FHL” tendon) to reinforce a diseased Achilles tendon.
Surgical approach to the Achilles
- Patient is … (Requires intubation) or in lazy … position
- Landmarks: The malleoli and the Achilles tendon- which is easily …
- Incision: Longitudinal – slightly medially based ( but can go laterally as well)
- Structure to avoid : … nerve laterally
- Avoid going medial to Flexor hallucis longus (FHL) ( easily identifiable as has muscle fibres at this level ) - NEUROVASCULAR BUNDLE MEDIALLY
- Patient is prone (Requires intubation) or in lazy lateral position
- Landmarks: The malleoli and the Achilles tendon- which is easily palpable
- Incision: Longitudinal – slightly medially based ( but can go laterally as well)
- Structure to avoid : Sural nerve laterally
- Avoid going medial to Flexor hallucis longus (FHL) ( easily identifiable as has muscle fibres at this level ) - NEUROVASCULAR BUNDLE MEDIALLY
































