Anatomy of the Forearm Flashcards
(123 cards)
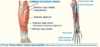
Skeleton - Forearm
- Radius bone - most lateral
- Proximal:
- Radial … - circular - lateral condyle of humerus articulates here
- Radial tuberosity - … … inserts here
- Distal:
- … process of radius
- Proximal:
- Ulna bone - medially
- Proximal:
- … - back of ulna near the elbow
- Radial … - circular head of radius articulates with ulna here
- … notch - medial condyle of humerus articulates ulna here
- … process
- Ulna tuberosity - … inserts here
- Distal:
- … process of ulna
- Proximal:
- Radius - most lateral
- Proximal:
- Radial head - circular - lateral condyle of humerus articulates here
- Radial tuberosity - biceps brachii inserts here
- Distal:
- Styloid process of radius
- Proximal:
- Ulna - medially
- Proximal:
- Olecranon - back of ulna near the elbow
- Radial notch - circular head of radius articulates with ulna here
- Trochlea notch - medial condyle of humerus articulates ulna here
- Coronoid process
- Ulna tuberosity - brachialis inserts here
- Distal:
- Styloid process of ulna
- Proximal:

Label the Forearm skeleton


Label the Forearm skeleton


Label the Forearm skeleton


Label the Forearm skeleton


Joints of the Forearm
- Two joints:
- Synovial hinge joint (… joint) flexion/extension
- Synovial pivot joint (… … joint) - supination/pronation
- Two joints:
- Synovial hinge joint (elbow joint) flexion/extension
- Synovial pivot joint (proximal radioulnar joint) - supination/pronation

Joints of the Forearm
- Two joints:
- Synovial … joint (elbow joint) flexion/extension
- Synovial … joint (proximal radioulnar joint) - supination/pronation
- Two joints:
- Synovial hinge joint (elbow joint) flexion/extension
- Synovial pivot joint (proximal radioulnar joint) - supination/pronation

Joints of the Forearm
- Two joints:
- Synovial hinge joint (elbow joint) …/… of forearm
- Synovial pivot joint (proximal radioulnar joint) - …/… of forearm
- Two joints:
- Synovial hinge joint (elbow joint) flexion/extension of forearm
- Synovial pivot joint (proximal radioulnar joint) supination/pronation of forearm

Joints of the Forearm
- Two joints:
- Synovial hinge joint (elbow joint) …/… of forearm
- Synovial pivot joint (proximal radioulnar joint) - …/… of forearm
- Two joints:
- Synovial hinge joint (elbow joint) flexion/extension of forearm
- Synovial pivot joint (proximal radioulnar joint) supination/pronation of forearm
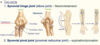
Elbow joint (Synovial hinge joint)
- It is the point of articulation of three bones: the … of the arm and the … and the … of the forearm.
- … - Biceps brachii, Brachialis, Brachioradialis muscles
Mnemonic: 3 B’s bend the elbow
Extension - … … muscle

- It is the point of articulation of three bones: the humerus of the arm and the radius and the ulna of the forearm.
-
Flexion - Biceps brachii, Brachialis, Brachioradialis muscles
Mnemonic: 3 B’s bend the elbow
Extension - Triceps brachii muscle
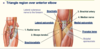
There are three bones that comprise the elbow joint, which are …
- the humerus
- the radius
- the ulna.
At the elbow joint, the proximal ends of the radius and ulna articulate with each other at the … … joint.
At the elbow joint, the proximal ends of the radius and ulna articulate with each other at the proximal radioulnar joint.
Proximal Radioulnar Joint
- The proximal radioulnar joint is located immediately distal to the … joint, and is enclosed with in the same articular capsule. It is formed by an articulation between the head of the radius and the radial notch of the ulna.
- There are two movements possible at this joint - … and …
- The proximal radioulnar joint is located immediately distal to the elbow joint, and is enclosed with in the same articular capsule. It is formed by an articulation between the head of the radius and the radial notch of the ulna.
- There are two movements possible at this joint: pronation and supination
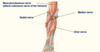
Ligaments of the Forearm
- Ligaments stabilise/strengthen joint
- … ligament wraps around rounded head of radius (attached to radial notch and ulna)
- Ulnar collateral ligrament - coming from … epicondyle
- Radial collateral ligament - coming from … epicondyle
- Ligaments stabilise/strengthen joint
- Annular ligament wraps around rounded head of radius (attached to radial notch and ulna)
- Ulnar collateral ligrament - coming from medial epicondyle
- Radial collateral ligament - coming from lateral epicondyle

Ligaments of the Forearm
- Label the diagram

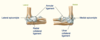
Ligaments of the Forearm
- Label the diagram


Ligaments of the Forearm
- Label the diagram


Ligaments of the Forearm
- Label the diagram


Forearm compartments
- Two compartments:
- Anterior/… compartment
- Posterior/… compartment
- Long … enter hand
- Two compartments:
- Anterior/Flexor compartment
- Posterior/Extensor compartment
- Long tendons enter hand
Anterior compartment of Forearm
- Mainly flexors
- Superficial muscles:
- 3 Flexors of wrist (…)
- 1 Pronator
- Intermediate muscles:
- 1 Flexor of digits 2-5 (…)
- Deep muscles:
- 1 Flexor of digits 2-5 (…)
- 1 Flexor of thumb (…)
- 1 Pronator
- Superficial muscles:
- Superficial and intermediate from common flexor origin (… epicondyle of humerus)
- Mainly flexors
- Superficial muscles:
- 3 Flexors of wrist (carpi)
- 1 Pronator
- Intermediate muscles:
- 1 Flexor of digits 2-5 (digitorum)
- Deep muscles:
- 1 Flexor of digits 2-5 (digitorum)
- 1 Flexor of thumb (pollicis)
- 1 Pronator
- Superficial muscles:
- Superficial and intermediate from common flexor origin (medial epicondyle of humerus)

Anterior compartment of Forearm
- Mainly flexors
- … muscles:
- 3 Flexors of wrist (carpi)
- 1 Pronator
- … muscles:
- 1 Flexor of digits 2-5 (digitorum)
- … muscles:
- 1 Flexor of digits 2-5 (digitorum)
- 1 Flexor of thumb (pollicis)
- 1 Pronator
- … muscles:
- … and … from common flexor origin (medial epicondyle of humerus)
- Mainly flexors
-
Superficial muscles:
- 3 Flexors of wrist (carpi)
- 1 Pronator
-
Intermediate muscles:
- 1 Flexor of digits 2-5 (digitorum)
-
Deep muscles:
- 1 Flexor of digits 2-5 (digitorum)
- 1 Flexor of thumb (pollicis)
- 1 Pronator
-
Superficial muscles:
- Superficial and intermediate from common flexor origin (medial epicondyle of humerus)

Anterior compartment of Forearm
- Mainly flexors
- Superficial muscles:
- … Flexors of wrist (carpi)
- … Pronator
- Intermediate muscles:
- … Flexor of digits 2-5 (digitorum)
- Deep muscles:
- … Flexor of digits 2-5 (digitorum)
- … Flexor of thumb (pollicis)
- … Pronator
- Superficial muscles:
- Superficial and intermediate from common flexor origin (… epicondyle of humerus)
- Mainly flexors
- Superficial muscles:
- 3 Flexors of wrist (carpi)
- 1 Pronator
- Intermediate muscles:
- 1 Flexor of digits 2-5 (digitorum)
- Deep muscles:
- 1 Flexor of digits 2-5 (digitorum)
- 1 Flexor of thumb (pollicis)
- 1 Pronator
- Superficial muscles:
- Superficial and intermediate from common flexor origin (medial epicondyle of humerus)

Anterior, Superficial layer of forearm
- Common flexor origin - … epicondyle of humerus
- Flexor … ulnaris - Flexor of wrist (origin - medial epicondyle, inserts into base of 5th metacarpal)
- … longus - Weak flexor of hand (origin - medial epicondyle, inserts onto palmar aponeurosis)
- Flexor … radialis - Flexor of wrist (origin - medial epicondyle, inserts into base of 2nd and 3rd metacarpal)
- … teres - (origin - Humeral head: medial supracondylar ridge of humerus, Ulnar head: Coronoid process of ulna, inserts into the radius)
- Common flexor origin - medial epicondyle of humerus
- Flexor carpi ulnaris - Flexor of wrist (origin - medial epicondyle, inserts into base of 5th metacarpal)
- Palmaris longus - Weak flexor of hand (origin - medial epicondyle, inserts onto palmar aponeurosis)
- Flexor carpi radialis - Flexor of wrist (origin - medial epicondyle, inserts into base of 2nd and 3rd metacarpal)
- Pronator teres - (origin - Humeral head: medial supracondylar ridge of humerus, Ulnar head: Coronoid process of ulna, inserts into the radius)

Anterior, Superficial layer of forearm
- Common flexor origin - medial epicondyle of humerus
- Flexor carpi ulnaris - Flexor of wrist (origin - medial epicondyle, inserts into base of 5th metacarpal)
- Palmaris longus - Weak flexor of hand (origin - medial epicondyle, inserts onto palmar aponeurosis)
- Flexor carpi radialis - Flexor of wrist (origin - medial epicondyle, inserts into base of 2nd and 3rd metacarpal)
- Pronator teres - (origin - Humeral head: medial supracondylar ridge of humerus, Ulnar head: Coronoid process of ulna, inserts into the radius)
- Common flexor origin - medial epicondyle of humerus
- Flexor carpi ulnaris - Flexor of wrist (origin - medial epicondyle, inserts into base of 5th metacarpal)
- Palmaris longus - Weak flexor of hand (origin - medial epicondyle, inserts onto palmar aponeurosis)
- Flexor carpi radialis - Flexor of wrist (origin - medial epicondyle, inserts into base of 2nd and 3rd metacarpal)
- Pronator teres - (origin - Humeral head: medial supracondylar ridge of humerus, Ulnar head: Coronoid process of ulna, inserts into the radius)