Basal Principles of Memory Flashcards
(27 cards)
Early distinctions of Memory
- William James (1890) drew a distinction between primary and secondary memory
- Primary Memory
- Portion of … space of time
- Linked to conscious experience
- Retrieval is …
- Secondary Memory
- Genuine …
- Unconscious - permanent
- Retrieval is …
- William James (1890) drew a distinction between primary and secondary memory
-
Primary Memory
- Portion of present space of time
- Linked to conscious experience
- Retrieval is effortless
-
Secondary Memory
- Genuine past
- Unconscious - permanent
- Retrieval is effort
Early distinctions of Memory
- William James (1890) drew a distinction between … and … memory
- .. Memory
- Portion of present space of time
- Linked to conscious experience
- Retrieval is effortless
- … Memory
- Genuine past
- Unconscious - permanent
- Retrieval is effort
- William James (1890) drew a distinction between primary and secondary memory
-
Primary Memory
- Portion of present space of time
- Linked to conscious experience
- Retrieval is effortless
-
Secondary Memory
- Genuine past
- Unconscious - permanent
- Retrieval is effort
Atkinson & Shiffrin’s (1968) Modal model of memory


Atkinson & Shiffrin’s (1968) Modal model of memory


Sensory memory
- Sensations persist after the stimulus has …
- Subject to very rapid …
- Stores exist for … (iconic) and … (echoic) sensory information
- What is the capacity of these stores?
- … experiments
- Sensations persist after the stimulus has disappeared
- Subject to very rapid decay
- Stores exist for visual (iconic) and auditory (echoic) sensory information
-
What is the capacity of these stores?
- Sperling’s experiments

Sperling’s experiments

Working memory
- What is the short-term store for?
- Some kind of “work space” to solve …
- … and … argued that working memory must comprise different components
- What is the short-term store for?
- Some kind of “work space” to solve problems
- Baddeley and Hitch argued that working memory must comprise different components
Baddeley (1986)
- Dual task:
- B is preceded by A — BA True/False
- A is not followed by B — BA True/False
- Performed while remembering strings of …
- Results:
- Reasoning time increases in with digit load (consistent with unitary STS)
- BUT, increase in reasoning time is modest
- … rate does not increase at all
- Dual task:
- B is preceded by A — BA True/False
- A is not followed by B — BA True/False
- Performed while remembering strings of digits
- Results:
- Reasoning time increases in with digit load (consistent with unitary STS)
- BUT, increase in reasoning time is modest
- Error rate does not increase at all

Baddeley & Hitch’s (1974) working memory model

Multicomponent model of working memory: (Baddeley and Hitch)
- 3 different components:
- Visuo-… sketch pad
- Central … - coordinated by this
- … loop - sound
-
3 different components:
- Visuo-spatial sketch pad
- Central executive - coordinated by this
- Phonological loop - sound

Multicomponent model of working memory: (Baddeley and Hitch)
- 3 different components:
- Visuo-spatial … pad
- … executive - coordinated by this
- Phonological loop - …
-
3 different components:
- Visuo-spatial sketch pad
- Central executive - coordinated by this
- Phonological loop - sound

Evidence for the phonological loop
- … … effect: Baddeley (1966)
- Presented lists of 5 words to write down in order
- List A: mad, cap, cat, map, cad - sound similar
- List B: pen, cow, bar, day, sup - same length, sound dissimilar
- List C: long, tall, wide, large, great - sound different, same meaning (semantically similar)
- List D: foul, strong, hot, old, deep - sound dissimilar and semantically dissimilar
- A - bad at recall B, C, D - quite good recall
- … … effect - coding used in the …-term memory store is based around the … of the word
- Word length effect:
- Baddeley et al., (1975)
- Presented lists of 5 words to write down in order
- List A: some, harm, bond, yield, hate - sound dissimilar but length of words change (single syllable)
- List B: 2 syllable
- List C: 3 syllable
- List D: 4 syllable
- List E: association, considerable, representative, individual, immediately
- Results: Correct recall related to number of syllables - Strong correlation between reading speed and correct recall
- … directly related to …
- Same effect found if number of syllables is the same but the lists are quicker to say:
- Bishop, wicket
- Friday, harpoon
- Phonological similarity effect: Baddeley (1966)
- Presented lists of 5 words to write down in order
- List A: mad, cap, cat, map, cad - sound similar
- List B: pen, cow, bar, day, sup - same length, sound dissimilar
- List C: long, tall, wide, large, great - sound different, same meaning (semantically similar)
- List D: foul, strong, hot, old, deep - sound dissimilar and semantically dissimilar
- A - bad at recall B, C, D - quite good recall
- Phonological similarity effect - coding used in the short-term memory store is based around the sound of the word
- Word length effect:
- Baddeley et al., (1975)
- Presented lists of 5 words to write down in order
- List A: some, harm, bond, yield, hate - sound dissimilar but length of words change (single syllable)
- List B: 2 syllable
- List C: 3 syllable
- List D: 4 syllable
- List E: association, considerable, representative, individual, immediately
- Results: Correct recall related to number of syllables - Strong correlation between reading speed and correct recall
- Performance directly related to syllable
- Same effect found if number of syllables is the same but the lists are quicker to say:
- Bishop, wicket
- Friday, harpoon
A selective impairment to the phonological loop
- Several patients have been described who have severely reduced verbal spans (for all types of unconnected items)
- Intact word …
- no problem with speech …
- Several patients have been described who have severely reduced verbal spans (for all types of unconnected items)
- Intact word perception
- no problem with speech production
Phonological loop - summary
- Acts like a … recorder for a limited time
- The contents are actively … by an articulatory process (sub-vocal speech)
- Disruption of this articulatory process (e.g. saying, “the… the… the…”) results in poor … in the phonological loop
- Acts like a tape recorder for a limited time
- The contents are actively refreshed by an articulatory process (sub-vocal speech)
- Disruption of this articulatory process (e.g. saying, “the… the… the…”) results in poor retention in the phonological loop
Phonological loop - summary
- Acts like a tape recorder for a … time
- The contents are actively refreshed by an … process (sub-vocal speech)
- Disruption of this … process (e.g. saying, “the… the… the…”) results in … retention in the phonological loop
- Acts like a tape recorder for a limited time
- The contents are actively refreshed by an articulatory process (sub-vocal speech)
- Disruption of this articulatory process (e.g. saying, “the… the… the…”) results in poor retention in the phonological loop
Other components of the model - Baddeley and Hitch
- … buffer added - area of research
- Episodic buffer added - area of research

The visuospatial Sketchpad
- Necessary for holding online a sequence of visually guided …
- Also necessary for “… in the mind’s eye”
- Necessary for holding online a sequence of visually guided actions
- Also necessary for “seeing in the mind’s eye”

Evidence for the visuospatial sketchpad
- De Renzi & Nichelli (1975) showed some patients with brain damage had impaired digit spans some had impaired … spans
- “Double …”; evidence for independent processes
- Subsequent research has shown that the visuospatial sketchpad can itself be divided (Logie, 1995)
- Visual cache – passively stores visual information about form and colour
- Inner scribe – stores spatial and movement information and can rehearse the contents of the visual cache
- Viewing … pictures interfered with the visual task, whereas tracing the outline of a series of pegs on a board interfered with the spatial task
- De Renzi & Nichelli (1975) showed some patients with brain damage had impaired digit spans some had impaired spatial spans
- “Double dissociation”; evidence for independent processes
- Subsequent research has shown that the visuospatial sketchpad can itself be divided (Logie, 1995)
- Visual cache – passively stores visual information about form and colour
- Inner scribe – stores spatial and movement information and can rehearse the contents of the visual cache
- Viewing abstract pictures interfered with the visual task, whereas tracing the outline of a series of pegs on a board interfered with the spatial task

Evidence for the visuospatial sketchpad
- De Renzi & Nichelli (1975) showed some patients with brain … had impaired digit spans some had impaired spatial spans
- “Double dissociation”; evidence for independent processes
- Subsequent research has shown that the visuospatial sketchpad can itself be divided (Logie, 1995)
- Visual cache – passively stores visual information about form and colour
- Inner scribe – stores spatial and movement information and can rehearse the contents of the visual cache
- Viewing abstract pictures interfered with the … task, whereas tracing the outline of a series of pegs on a board interfered with the … task
- De Renzi & Nichelli (1975) showed some patients with brain damage had impaired digit spans some had impaired spatial spans
- “Double dissociation”; evidence for independent processes
- Subsequent research has shown that the visuospatial sketchpad can itself be divided (Logie, 1995)
- Visual cache – passively stores visual information about form and colour
- Inner scribe – stores spatial and movement information and can rehearse the contents of the visual cache
- Viewing abstract pictures interfered with the visual task, whereas tracing the outline of a series of pegs on a board interfered with the spatial task

Encoding:
- repeated exposure is … …
- Eg ask - Which is the correct American cent coin?
- People really … at giving this
- repeated exposure is not enough
- Which is the correct American cent coin?
- People really bad at giving this
Encoding: levels of processing
- Craik & Lockhart (1972) introduced the concept of “levels of processing”
- Craik & Lockhart (1972) introduced the concept of “levels of processing”

Encoding: levels of processing
- Craik & Lockhart (1972) introduced the concept of “levels of processing”

- Craik & Lockhart (1972) introduced the concept of “levels of processing”

Encoding: levels of processing
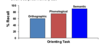
- Participants asked to made judgments about words
- Is word in upper or lower case? (Orthographic)
- Does the word rhyme with hat? (Phonological)
- Does the word fit the sentence “The cat sat on the ….. ? (Semantic)
- Given a surprise memory test - Which one did they recall more, which in middle, which recalled least?
- Participants asked to made judgments about words
- Is word in upper or lower case?
- Does the word rhyme with hat?
- Does the word fit the sentence “The cat sat on the ….. ?
- Given a surprise memory test
- Which one did they recall more - Semantic, which in middle - Phonological, which recalled least - Orthographic
Encoding: levels of processing
- The approach has proved hugely influential
- Downplays the importance of encoding as an … process - it is processing per se that leads to durable memories
- Deep encoding or elaboration is one of the best ways to learn … material
- BUT the reasoning is … - is memory strong because encoding was “Deep” or do we infer that strong memories must have been “deeply encoded”?
- The approach has proved hugely influential
- Downplays the importance of encoding as an independent process - it is processing per se that leads to durable memories
- Deep encoding or elaboration is one of the best ways to learn new material
- BUT the reasoning is circular - is memory strong because encoding was “Deep” or do we infer that strong memories must have been “deeply encoded”?