Anatomy of the Leg and Foot Flashcards
(112 cards)
Function of the Foot
- 3 functions - what are they?
- Stability/standing (support body weight)
- Locomotion/propulsion (acts as lever)
- Shock absorption
Function of the Foot
- Stability/standing (support … …)
- …/propulsion (acts as …)
- … absorption
- Stability/standing (support body weight)
- Locomotion/propulsion (acts as lever)
- Shock absorption
Bones of the leg


Bones of the leg


Bones of the leg


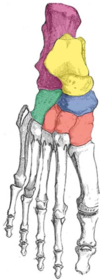
Bones of the foot


Bones of the foot


Bones of the foot
- Label the tarsal bones of the foot.

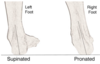
Supination of foot vs Pronation of foot
- Supination (feet … – …/… of front of foot)
- Pronation (feet … – …/… of front of foot)
- When standing on irregular surfaces
- Supination (feet together – inversion/adduction of front of foot)
- Pronation (feet apart – eversion/abduction of front of foot)
- When standing on irregular surfaces

If you stand with your feet parallel and face forward, and rotate your body and look over your left shoulder - your … foot would be supinated and your … foot would be pronated
If you stand with your feet parallel and face forward, and rotate your body and look over your left shoulder - your left foot would be supinated and your right foot would be pronated
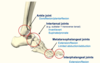
Joints of the foot


Joints of the foot


Joints of the foot
- Ankle joint (dorsiflexion and plantarflexion)
- Intertarsal joints (e.g. … - inversion/eversion and … tarsal - supination and pronation)
- Metatarsophalangeal joints (extension/flexion and limited abduction/adduction)
- Interphalangeal joints (extension/flexion)
- Ankle joint (dorsiflexion and plantarflexion)
- Intertarsal joints (e.g. Subtalar - inversion/eversion and Transverse tarsal - supination and pronation)
- Metatarsophalangeal joints (extension/flexion and limited abduction/adduction)
- Interphalangeal joints (extension/flexion)
Joints of the foot
- Ankle joint (dorsiflexion and plantarflexion)
- Intertarsal joints (e.g. Subtalar - inversion/eversion and transverse tarsal - … and …)
- Metatarsophalangeal joints (extension/flexion and limited …/…)
- Interphalangeal joints (extension/flexion)
- Ankle joint (dorsiflexion and plantarflexion)
- Intertarsal joints (e.g. Subtalar - inversion/eversion and Transverse tarsal - supination and pronation)
- Metatarsophalangeal joints (extension/flexion and limited abduction/adduction)
- Interphalangeal joints (extension/flexion)

Ankle Joint is the articulation between the … and …/…
Ankle Joint is the articulation between the talus and tibia/fibula

The ankle joint is what type of joint?
synovial hinge joint

The ankle joint allows what movements?
dorsiflexion (extension of foot - lift up) and plantarflexion (flexion of foot - downwards)

Label the diagram


The ankle joint is stabilised by what ligaments?
-
Collateral ligaments
- Lateral ligament - lateral malleolus to talus/calcaneus (3 parts total)
- Medial/deltoid ligament - medial malleolus to talus/calcaneus/navicular (3 parts total)

Ankle joint - collateral ligaments
- Lateral ligament - lateral malleolus to talus/calcaneus (… parts total)
- Medial/deltoid ligament - medial malleolus to talus/calcaneus/navicular (… parts total)
- Lateral ligament - lateral malleolus to talus/calcaneus (3 parts total)
- Medial/deltoid ligament - medial malleolus to talus/calcaneus/navicular (3 parts total)

Ankle joint ligaments
- There are two main sets of ligaments, which originate from each malleolus.
- Medial Ligament
- The medial ligament (or deltoid ligament) is attached to the medial malleolus - 3 parts (to talus/calcaneus)
- Lateral Ligament
- The lateral ligament originates from the lateral malleolus - 3 parts (to talus/calcaneus/navicular)
- Medial Ligament

Clinical: Injury to ,,, ligament due to excessive inversion of foot (usually anterior talofibular ligament)
Clinical: Injury to lateral ligament due to excessive inversion of foot (usually anterior talofibular ligament) - red line on RHS

Subtalar joint
- Between … and calcaneus
- Allows inversion/eversion during locomotion
- Between talus and calcaneus
- Allows inversion/eversion during locomotion

The subtalar joint is responsible for what movements of the foot?
Allows inversion/eversion during locomotion