Introduction to the Hypothalamic-Pituitary Axis Flashcards
(80 cards)
Autocrine signalling is a form of cell signalling in which a cell secretes a hormone or chemical messenger that binds to autocrine receptors on …
that same cell, leading to changes in the cell

Paracrine signalling is a form of cell-to-cell communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in …
nearby cells, altering the behaviour of those cells.

Endocrine action is where the hormone is …
distributed in blood and binds to distant target cells.
… action: the hormone is distributed in blood and binds to distant target cells.
… action: the hormone acts locally by diffusing from its source to target cells in the neighborhood.
… action: the hormone acts on the same cell that produced it.
… action: neuronal cells that secrete chemicals which enter the bloodstream and flow to a distant site and act on target cell receptors.
Endocrine action: the hormone is distributed in blood and binds to distant target cells.
Paracrine action: the hormone acts locally by diffusing from its source to target cells in the neighborhood.
Autocrine action: the hormone acts on the same cell that produced it.
Neuroendocrine action: neuronal cells that secrete chemicals which enter the bloodstream and flow to a distant site and act on target cell receptors.

Where does the pituitary lie?
in the brain, just behind the eyes

The pituitary has two parts, the … pituitary and the … pituitary
anterior pituitary
posterior pituitary

Anatomy of the pituitary:
The pituitary gland is a pea-sized oval structure, suspended from the underside of the brain by the pituitary … (known as the infundibulum). It sits within a small depression in the … bone, known as the sella turcica (‘’Turkish saddle’’).
It consists of how many parts? Where are they derived from?
It has it’s own pituitary … which protects it inside the skull
stalk
sphenoid bone
2 parts - posterior derived from hypothalamus and anterior derived from roof of pharynx, called Rathke’s pouch
pituitary fossa

Pituitary gland blood supply:
- It has a … sinusoidal circulation
- circulation is lined by …
- … … is above the pituiatry = linked to pituitary tumours
- portal sinusoidal circulation
- circulation lined by sinusoids
- optic chiasm is above the pituitary
What is shown in this image?

Pituitary gland anatomy
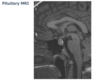
What is shown in this image?

Bottom - pituitary tumour pressing on the optic chiasm
Anatomy of pituitary image

What is shown in the image?

Drawings by Leonardo de Vinci - showing relationship between the third ventricle and hypothalamus
The hypothalamus
- Integrates functions that maintain chemical and temperature …
- Functions with the … system
- Controls the release of … from the anterior and posterior pituitary
- Integrates functions that maintain chemical and temperature homeostasis
- Functions with the limbic system
- Controls the release of hormones from the anterior and posterior pituitary
Hypothalamic releasing hormones
- The median … secretes small peptides and …
- These hormones control the secretion of gonadotropes, somatotropes, lactotropes, corticotropes and thyrotropes
- Discovery of the hypothalamic releasing hormones and the blood supply connecting the hypothalamus and pituitary led to the Nobel Prize physiology/medicine in … for Andrew Schally and Roger Guillemin.
- The median eminence secretes small peptides and dopamine
- These hormones control the secretion of gonadotropes, somatotropes, lactotropes, corticotropes and thyrotropes
- Discovery of the hypothalamic releasing hormones and the blood supply connecting the hypothalamus and pituitary led to the Nobel Prize physiology/medicine in 1977 for Andrew Schally and Roger Guillemin.
Gonadotropes cells are endocrine cells in the anterior pituitary that produce the gonadotropins, such as the … hormone and … hormone
- Follicle stimulating hormone - FSH
- Luteinizing hormone - LH
Somatotrophs are the cells in the anterior pituitary that release … … hormone (also called somatotropin). They constitute about …-…% of the anterior pituitary cells.
- pituitary growth hormone
- 30-40% of anterior pituitary cells
A lactotropic cell is a cell in the anterior pituitary which produces … in response to hormonal signals including dopamine which is … and thyrotropin-releasing hormone which is stimulatory.
- produces prolactin
- dopamine is inhibitory
- thyrotropin-releasing hormone is stimulatory
- … is made in the corticotroph cells of the anterior pituitary gland, where it is released in bursts into the bloodstream and transported around the body.
- ACTH
Thyrotropes (also called thyrotrophs) are endocrine cells in the anterior pituitary which produce … …. hormone in response to … … hormone. Thyrotropes consist around …% of the anterior pituitary lobe cells
Thyrotropes (also called thyrotrophs) are endocrine cells in the anterior pituitary which produce thyroid stimulating hormone in response to thyrotropin releasing hormone. Thyrotropes consist around 5% of the anterior pituitary lobe cells
Who discovered the hypothalamic releasing hormones?
Andrew Schally and Roger Guillemin - led to Nobel prize in 1977
Hypothalamic releasing hormones
- GnRH (… releasing hormone)
- … AA, isolated in 1971
- Stimulates secretion of … and …
- GnRH (Gonadotropin releasing hormone)
- 10 AA, isolated in 1971
- Stimulates secretion of FSH and LH
Hypothalamic releasing hormones
- SS, known as (…)
- Inhibits … hormone secretion
- SS (Somatostatin)
- Inhibits growth hormone secretion
Hypothalamic releasing hormones
- Dopamine
- Inhibits … secretion
- Dopamine
- Inhibits prolactin secretion
Hypothalamic releasing hormones
- … releasing factor (CRF)
- … AA, isolated in 1981
- stimulates secretion of …
- Corticotropin releasing factor (CRF)
- 41 AA, isolated in 1981
- stimulates secretion of ACTH