Multi-system Autoimmune Disease Flashcards
(113 cards)
… are forms of arthritis that usually strike the bones in your spine and nearby joints.
Spondyloarthropathies are forms of arthritis that usually strike the bones in your spine and nearby joints.
Spondyloarthropathies types
- … spondylitis
- Psoriatic Arthropathy
- … Arthropathy
- Intestinal Arthropathy
- … Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Hallmark ocular involvement is UVEITIS
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Psoriatic Arthropathy
- Reactive Arthropathy
- Intestinal Arthropathy
-
Juvenile Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Hallmark ocular involvement is UVEITIS

Spondyloarthropathies types
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- … Arthropathy
- Reactive Arthropathy
- … Arthropathy
- Juvenile Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Hallmark ocular involvement is …
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Psoriatic Arthropathy
- Reactive Arthropathy
- Intestinal Arthropathy
- Juvenile Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Hallmark ocular involvement is UVEITIS

Spondyloarthropathies types
- … spondylitis
- … Arthropathy
- … Arthropathy
- Intestinal Arthropathy
- Juvenile Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Hallmark … involvement is UVEITIS
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Psoriatic Arthropathy
- Reactive Arthropathy
- Intestinal Arthropathy
- Juvenile Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Hallmark ocular involvement is UVEITIS
CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF SPONDYLOARTHROPATHIES
- Pattern of peripheral arthritis: predominantly … limb, asymmetric
- E..
- Tendency to radiographic sacroiliitis
- Absence of rheumatoid factor / anti CCP
- Extra-articular features characteristic of the group (such as anterior uveitis)
- Significant … aggregation
- Association with HLA-…
- Pattern of peripheral arthritis: predominantly lower limb, asymmetric
- Enthesitis
- Tendency to radiographic sacroiliitis
- Absence of rheumatoid factor / anti CCP
- Extra-articular features characteristic of the group (such as anterior uveitis)
- Significant familial aggregation
- Association with HLA-B27
CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF SPONDYLOARTHROPATHIES
- Pattern of peripheral arthritis: predominantly lower limb, …
- Enthesitis
- Tendency to radiographic …
- Absence of … factor / anti …
- Extra-articular features characteristic of the group (such as anterior …)
- Significant familial aggregation
- Association with …-B27
- Pattern of peripheral arthritis: predominantly lower limb, asymmetric
- Enthesitis
- Tendency to radiographic sacroiliitis
- Absence of rheumatoid factor / anti CCP
- Extra-articular features characteristic of the group (such as anterior uveitis)
- Significant familial aggregation
- Association with HLA-B27
… is inflammation of the …, the sites where tendons or ligaments insert into the bone
Enthesitis is inflammation of the entheses, the sites where tendons or ligaments insert into the bone
Ankylosing Spondylitis - Disease Probability
- Chronic back pain - ‘inflammatory’ (requires the presence of at least four of the following)
- Age at onset less than … years
- … onset
- Improvement with …
- No improvement with …
- … pain with improvement upon getting up
- Enthesitis
- family history
- Uveitis
- Asymmetic arthritis
- Response to NSAIDs
- Chronic back pain - ‘inflammatory’ (requires the presence of at least four of the following)
- Age at onset less than 40 years
- Insidious onset
- Improvement with exercise
- No improvement with rest
- Night pain with improvement upon getting up
- Enthesitis
- family history
- Uveitis
- Asymmetic arthritis
- Response to NSAIDs

Ankylosing Spondylitis - Disease Probability
- Chronic back pain - ‘inflammatory’ (requires the presence of at least four of the following)
- Age at onset less than 40 years
- … onset
- Improvement with exercise
- No improvement with rest
- Night pain with improvement upon getting up
- E…
- … history
- Uveitis
- … arthritis
- Response to …
- Chronic back pain - ‘inflammatory’ (requires the presence of at least four of the following)
- Age at onset less than 40 years
- Insidious onset
- Improvement with exercise
- No improvement with rest
- Night pain with improvement upon getting up
- Enthesitis
- family history
- Uveitis
- Asymmetic arthritis
- Response to NSAIDs
Ankylosing Spondylitis - Disease Probability
- Chronic back pain - ‘inflammatory’ (requires the presence of at least … of the following)
- Age at onset less than 40 years
- Insidious onset
- Improvement with exercise
- No improvement with rest
- Night pain with improvement upon getting up
- E…
- family history
- U…
- Asymmetic arthritis
- Response to …
- Chronic back pain - ‘inflammatory’ (requires the presence of at least four of the following)
- Age at onset less than 40 years
- Insidious onset
- Improvement with exercise
- No improvement with rest
- Night pain with improvement upon getting up
- Enthesitis
- family history
- Uveitis
- Asymmetic arthritis
- Response to NSAIDs

Ankylosing Spondylitis - Disease Probability
- Chronic back pain - ‘inflammatory’ (requires the presence of at least four of the following)
- Age at onset less than … years
- Insidious onset
- Improvement with …
- No improvement with …
- Night pain with … upon getting up
- Enthesitis
- family history
- Uveitis
- Asymmetic arthritis
- Response to NSAIDs
- Chronic back pain - ‘inflammatory’ (requires the presence of at least four of the following)
- Age at onset less than 40 years
- Insidious onset
- Improvement with exercise
- No improvement with rest
- Night pain with improvement upon getting up
- Enthesitis
- family history
- Uveitis
- Asymmetic arthritis
- Response to NSAIDs

Imaging for Ankylosing Spondylitis diagnosis
Sacroiliac joint X-ray, if normal or equivocal, then CT or MRI, or HLA-B27 test
In patients with over … months back pain, with/without peripheral manifestations and age at onset 1 SpA feature or HLA-… + plus >2 other SpA features
In patients with over 3 months back pain, with/without peripheral manifestations and age at onset <45 years - Sacroiliitis on imaging plus >1 SpA feature or HLA-B27 + plus >2 other SpA features

Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Greek ‘ankylos‘- bent/crooked (fused) - ‘spondylos‘-a spinal vertebra
- Characteristically affects … adults
- Peak onset between …-… yrs
- Male:female - approximately 3:1*
- Greek ‘ankylos‘- bent/crooked (fused) - ‘spondylos‘-a spinal vertebra
- Characteristically affects young adults
- Peak onset between 20-30 yrs
- Male:female - approximately 3:1*

Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Greek ‘ankylos‘- bent/crooked (fused) - ‘spondylos‘-a spinal vertebra
- Characteristically affects young adults
- Peak onset between 20-30 yrs
- Male:female - approximately ..-..*
- Greek ‘ankylos‘- bent/crooked (fused) - ‘spondylos‘-a spinal vertebra
- Characteristically affects young adults
- Peak onset between 20-30 yrs
- Male:female - approximately 3:1*

Examining tenderness over sacroiliac joint

… test is classically used to determine if there is a decrease in lumbar spine range of motion (flexion), most commonly as a result of ankylosing spondylitis.
Schober’s test is classically used to determine if there is a decrease in lumbar spine range of motion (flexion), most commonly as a result of ankylosing spondylitis.
For both versions of the test, an increase of less than 5cm is a positive test and may indicate ankylosing spondylitis (AS).

Positive Schober’s Test
Less than 5cm increase in length with forward flexion: Decreased lumbar spine range of motion, ankylosing spondylitis

The … to Wall Distance is a routine clinical test for thoracic kyphosis that has been in use for many years
The Occiput to Wall Distance is a routine clinical test for thoracic kyphosis that has been in use for many years

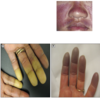
Ankylosis of spine
on right

Ankylosed sacroiliac joints

Ankylosing Spondylitis - Clinical features
- Low back pain - Often the first symptom (in ~ …%).
- … pain - indicative of SI involvement. Often poorly localised and may be referred to the posterior thigh.
- Limited spinal …
- Hip and Shoulder pain- … arthritis
- Peripheral arthritis -Acute monoarthritis or oligoarthritis Mostly non-erosive and non-destructive.
- Enthesitis.
- Constitutional features- fatigue and malaise. Disturbed sleep, caused by back or joint pain at night, may contribute to fatigue
- Low back pain - Often the first symptom (in ~ 75%).
- Buttock pain - indicative of SI involvement. Often poorly localised and may be referred to the posterior thigh.
- Limited spinal mobility
- Hip and Shoulder pain- girdle arthritis
- Peripheral arthritis -Acute monoarthritis or oligoarthritis Mostly non-erosive and non-destructive.
- Enthesitis.
- Constitutional features- fatigue and malaise. Disturbed sleep, caused by back or joint pain at night, may contribute to fatigue
Ankylosing Spondylitis - Clinical features
- … … pain - Often the first symptom (in ~ 75%).
- Buttock pain - indicative of SI involvement. Often poorly localised and may be referred to the posterior …
- Limited spinal mobility
- … and … pain- girdle arthritis
- Peripheral arthritis -Acute monoarthritis or oligoarthritis Mostly non-erosive and non-destructive.
- Enthesitis.
- Constitutional features- fatigue and malaise. Disturbed sleep, caused by back or joint pain at night, may contribute to fatigue
- Low back pain - Often the first symptom (in ~ 75%).
- Buttock pain - indicative of SI involvement. Often poorly localised and may be referred to the posterior thigh.
- Limited spinal mobility
- Hip and Shoulder pain- girdle arthritis
- Peripheral arthritis -Acute monoarthritis or oligoarthritis Mostly non-erosive and non-destructive.
- Enthesitis.
- Constitutional features- fatigue and malaise. Disturbed sleep, caused by back or joint pain at night, may contribute to fatigue
Ankylosing Spondylitis - Clinical features
- Low back pain - Often the first symptom (in ~ 75%).
- Buttock pain - indicative of SI involvement. Often poorly localised and may be referred to the posterior thigh.
- Limited … mobility
- Hip and Shoulder pain- girdle arthritis
- Peripheral arthritis -Acute monoarthritis or oligoarthritis Mostly non-erosive and non-destructive.
- E…
- Constitutional features- … and …. Disturbed …, caused by back or joint pain at …, may contribute to …
- Low back pain - Often the first symptom (in ~ 75%).
- Buttock pain - indicative of SI involvement. Often poorly localised and may be referred to the posterior thigh.
- Limited spinal mobility
- Hip and Shoulder pain- girdle arthritis
- Peripheral arthritis -Acute monoarthritis or oligoarthritis Mostly non-erosive and non-destructive.
- Enthesitis.
- Constitutional features- fatigue and malaise. Disturbed sleep, caused by back or joint pain at night, may contribute to fatigue