Innate Immune Defences & Inflammation 2: The Induced Response Flashcards
(183 cards)
Cells of the innate & adaptive immune system
- The discovery of innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) is blurring the traditional boundaries between innate and adaptive immune systems. Invariant natural killer T cells, some B cells at epithelial barriers (B1 cells) and gamma delta T cells have innate qualities whereas NK cells may adapt after their first encounter with a pathogen due to innate immune memory. T and B cells also have innate immune receptors such as TLRs.
- The discovery of innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) is blurring the traditional boundaries between innate and adaptive immune systems. Invariant natural killer T cells, some B cells at epithelial barriers (B1 cells) and gamma delta T cells have innate qualities whereas NK cells may adapt after their first encounter with a pathogen due to innate immune memory. T and B cells also have innate immune receptors such as TLRs.

Innate immune cells
- What cells are involved? What do they do?
- Neutrophils - Phagocytosis, Antimicrobial peptides, Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species
- Macrophages - Phagocytosis, Antimicrobial peptides, Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, Inflammatory mediators, antigen presentation, cytokines, complement proteins
- Dendritic cells - Antigen presentation, Costimulatory signals, Reactive oxygen species, Interferon, Cytokines
- Natural Killer cells - Lysis of viral-infected cells, Interferon, Macrophage activation, Granzyme, Perforin

What are the functions of a neutrophil?
- Phagocytosis, Antimicrobial peptides, Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species

What are the functions of a macrophage?
- Phagocytosis, Antimicrobial peptides, Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, Inflammatory mediators, antigen presentation, cytokines, complement proteins

What are the functions of dendritic cells?
- Antigen presentation, Costimulatory signals, Reactive oxygen species, Interferon, Cytokines (Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (DCs) are of lymphoid origin, Myeloid DCs are of myeloid origin - plasmacytoid DCs produce large amounts of type 1 IFN whereas for myeloid DCs the main role is antigen presentation)

What are the functions of natural killer cells?
- Lysis of viral-infected cells, Interferon, Macrophage activation, Granzyme, Perforin (Perforin is pore forming permitting entry of granzyme into cells where it induces apoptosis)

… is pore forming permitting entry of granzyme into cells where it induces apoptosis.
Perforin is pore forming permitting entry of granzyme into cells where it induces apoptosis.
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (DCs) are of … origin
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (DCs) are of lymphoid origin
Myeloid DCs are of … origin
Myeloid DCs are of myeloid origin
… DCs produce large amounts of type 1 IFN whereas for … DCs the main role is antigen presentation
plasmacytoid DCs produce large amounts of type 1 IFN whereas for myeloid DCs the main role is antigen presentation
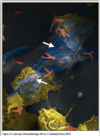
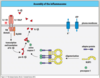
Phagocyte recruitment
- … produced by macrophages dilate local blood vessels and increase endothelial adhesion molecule expression.
- … attract monocytes and neutrophils to the infection
- Cell adhesion molecules (ICAM-1 and VCAM-1) are upregulated on the endothelium which bind to integrins (family of adhesion molecules) on the leukocytes
- Cytokines produced by macrophages dilate local blood vessels and increase endothelial adhesion molecule expression.
- Chemokines attract monocytes and neutrophils to the infection
- Cell adhesion molecules (ICAM-1 and VCAM-1) are upregulated on the endothelium which bind to integrins (family of adhesion molecules) on the leukocytes

Phagocyte recruitment
- Cytokines produced by macrophages … local blood vessels and … endothelial adhesion molecule expression.
- Chemokines attract monocytes and … to the infection
- Cell adhesion molecules (ICAM-1 and VCAM-1) are upregulated on the endothelium which bind to integrins (family of adhesion molecules) on the leukocytes
- Cytokines produced by macrophages dilate local blood vessels and increase endothelial adhesion molecule expression.
- Chemokines attract monocytes and neutrophils to the infection
- Cell adhesion molecules (ICAM-1 and VCAM-1) are upregulated on the endothelium which bind to integrins (family of adhesion molecules) on the leukocytes

Phagocyte recruitment
- Cytokines produced by macrophages dilate local blood vessels and increase endothelial adhesion molecule expression.
- Chemokines attract monocytes and neutrophils to the infection
- Cell … molecules (ICAM-1 and VCAM-1) are upregulated on the endothelium which bind to integrins (family of … molecules) on the leukocytes
- Cytokines produced by macrophages dilate local blood vessels and increase endothelial adhesion molecule expression.
- Chemokines attract monocytes and neutrophils to the infection
- Cell adhesion molecules (ICAM-1 and VCAM-1) are upregulated on the endothelium which bind to integrins (family of adhesion molecules) on the leukocytes

Phagocyte recruitment
- Cytokines produced by macrophages dilate local blood vessels and increase endothelial adhesion molecule expression.
- Chemokines attract monocytes and neutrophils to the infection
- Cell adhesion molecules (…-1 and …-1) are upregulated on the endothelium which bind to integrins (family of adhesion molecules) on the leukocytes
- Cytokines produced by macrophages dilate local blood vessels and increase endothelial adhesion molecule expression.
- Chemokines attract monocytes and neutrophils to the infection
- Cell adhesion molecules (ICAM-1 and VCAM-1) are upregulated on the endothelium which bind to integrins (family of adhesion molecules) on the leukocytes

Phagocytosis is performed by …, … cells and …
Phagocytosis is performed by neutrophils, dendritic cells and macrophages
Neutrophils, Dendritic Cells and Macrophages all perform…
phagocytosis
Phagocytosis is the … and … of … particles
Phagocytosis is the capture and digestion of foreign particles
Phagocytosis is the … and … of … particles
Phagocytosis is the capture and digestion of foreign particles
What is phagocytosis?
Phagocytosis is the capture and digestion of foreign particles
… are proteins of the innate and adaptive immune system that facilitate phagocytosis and cell lysis by “marking” antigen.
Opsonins are proteins of the innate and adaptive immune system that facilitate phagocytosis and cell lysis by “marking” antigen.
Complement components (C3b) and Collectins (Mannose-binding lectin) and antibodies are all good examples of …
opsonins (opsonins are proteins of the innate and adaptive immune system that facilitate phagocytosis and cell lysis by “marking” antigen.)

Opsonins engage with … receptors (complement receptors, fc receptors, Mannose receptor, Scavenger receptors)
Opsonins engage with phagocytic receptors (complement receptors, fc receptors, Mannose receptor, Scavenger receptors)
… receptors recognize bacteria, viruses and apoptotic cells
Scavenger receptors recognize bacteria, viruses and apoptotic cells
The complement receptor CR1 binds to … (complement component)
The complement receptor CR1 binds to C3b (complement component)