Nerve and Blood Supply to the Upper Limb Flashcards
(134 cards)
The surgical neck of the humerus is at risk of …, and if this happens, it can cause trauma to which arteries?
The surgical neck of the humerus is at risk of fracture, and if this happens, it can cause trauma to the anterior/posterior circumflex humeral arteries

Brachial artery
- The brachial artery is a continuation of the axillary artery past the lower border of the … major.
- It is the main supply of blood for the arm.
- Supplies … muscles (biceps brachii, coracobrachialis, brachialis muscle in … compartments)
- Immediately distal to the teres major, the brachial artery gives rise to the … brachii (deep artery), which travels with the radial nerve in the spiral/radial groove of the humerus and supplies structures in the … aspect of the upper arm (…, e.g. triceps brachii).
- It terminates by contributing to an … network around the elbow joint.
- The brachial artery proper descends down the arm. As it moves through the … fossa, underneath the bicipital aponeurosis, the brachial artery terminates by bifurcating into the … and … arteries.
- The brachial artery is a continuation of the axillary artery past the lower border of the teres major.
- It is the main supply of blood for the arm.
- Supplies flexor muscles (biceps brachii, coracobrachialis, brachialis muscle in anterior compartments)
- Immediately distal to the teres major, the brachial artery gives rise to the profunda brachii (deep artery), which travels with the radial nerve in the spiral/radial groove of the humerus and supplies structures in the posterior aspect of the upper arm (extensors, e.g. triceps brachii).
- It terminates by contributing to an anastomotic network around the elbow joint.
- The brachial artery proper descends down the arm. As it moves through the cubital fossa, underneath the bicipital aponeurosis, the brachial artery terminates by bifurcating into the radial and ulnar arteries.

Motor Functions of the Median Nerve
- Innervates the … and … muscles in the … compartment of the forearm (except the flexor carpi ulnaris and medial 2 bellies of the flexor digitorum profundus, innervated by the ulnar nerve). Also supplies innervation to the thenar muscles and lateral two lumbricals in the hand (lateral hand)
- Innervates the flexor and pronator muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm (except the flexor carpi ulnaris and medial 2 bellies of the flexor digitorum profundus, innervated by the ulnar nerve). Also supplies innervation to the thenar muscles and lateral two lumbricals in the hand (lateral hand)
Motor innervation - (Brachial Plexus roots)
- Motor axons within each root innervate a different functional group of muscles (myotomes)
- C5 Motor root innervate Arm abductor (the …)
- C6 innervate Forearm flexors (the …)
- C7 innervate Forearm extensors (the …) and Wrist flexors/extensors
- C8 innervate … flexors/extensors
- T1 innervate … hand muscles
- Motor axons within each root innervate a different functional group of muscles (myotomes)
- C5 Motor root innervate Arm abductor (Deltoid)
- C6 innervate Forearm flexors (Biceps)
- C7 innervate Forearm extensors (Triceps) and Wrist flexors/extensors
- C8 innervate Digit flexors/extensors
- T1 innervate Intrinsic hand muscles

Lateral cord of the Brachial Plexus
- Terminates as … nerve and lateral part of … nerve
- Terminates as musculocutaneous nerve and lateral part of median nerve

Cutaneous innervation by terminal branches
- Map looks different to … map
- Terminal branches contain axons from … spinal nerve
- Map looks different to dermatome map
- Terminal branches contain axons from multiple spinal nerve

What artery supplies the upper limb?
Subclavian artery supplies the upper limb

The axillary artery ends at the lower border of … major
teres major

The map shows the cutaenous innervation by terminal branches - match the colour to a nerve
- Grey =
- Pink =
- Green =
- Purple = (from the … cord)
- Blue =
- Yellow =

- Grey = axillary
- Pink = radial
- Green = musculocutaneous
- Purple = medial cutaneous (from the medial cord)
- Blue = ulnar
- Yellow = median

Muculocutaenous nerve
- The musculocutaneous nerve is the terminal branch of the … cord of the brachial plexus and emerges at the inferior border of pectoralis minor muscle
- It pierces the … muscle near its point of insertion on the humerus. It gives a branch to this muscle.
- The musculocutaneous nerve then passes down the flexor compartment of the upper arm, superficial to … but deep to the … … muscle.
- It innervates both these muscles and gives articular branches to the humerus and the elbow.
- The nerve continues into the forearm as the lateral … nerve and provides sensory innervation to the lateral aspect of the forearm.
- The musculocutaneous nerve is the terminal branch of the lateral cord of the brachial plexus (C5, C6 and C7) and emerges at the inferior border of pectoralis minor muscle
- It pierces the coracobrachialis muscle near its point of insertion on the humerus. It gives a branch to this muscle.
- The musculocutaneous nerve then passes down the flexor compartment of the upper arm, superficial to brachialis but deep to the biceps brachii muscle.
- It innervates both these muscles and gives articular branches to the humerus and the elbow.
- The nerve continues into the forearm as the lateral cutaneous nerve and provides sensory innervation to the lateral aspect of the forearm.

Sensory Functions of the Axillary Nerve
- Gives rise to the upper lateral cutaneous nerve of arm, which innervates the skin over the lower deltoid (‘regimental … area’).
- Gives rise to the upper lateral cutaneous nerve of arm, which innervates the skin over the lower deltoid (‘regimental badge area’).
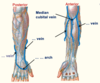
Cephalic and basilic veins drain into what vein?
Cephalic and basilic veins drain into axillary vein
C… Motor Axon innervates Arm abductor (Deltoid)
C5 Motor Axon innervate Arm abductor (Deltoid)

The brachial artery gives rise to the … brachii
The brachial artery gives rise to the profunda brachii
Medial Cord of the Brachial Plexus
- The medial cord is formed by:
- The anterior division of the … trunk.
- The medial cord is formed by:
- The anterior division of the inferior trunk.
The axillary artery can be divided into three parts based on its position relative to the … … muscle
The axillary artery can be divided into three parts based on its position relative to the pectoralis minor muscle

These are the 5 … branches

These are the 5 terminal branches
The median nerve is derived from the … and … … of the brachial plexus
The median nerve is derived from the medial and lateral cords of the brachial plexus

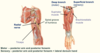
Axillary Nerve
- Axillary nerve goes through the … space (teres minor above, teres major below, long head of tricep, shaft of humerus)
- Also passing through this space with the axillary nerve is the posterior … humeral artery which weaves around surgical neck
- Supplies … muscle and the teres … muscle as it’s passing through
- Also supples region of skin on lateral aspect of arm - military … area of arm
- Axillary nerve goes through the quadrangular space (teres minor above, teres major below, long head of tricep, shaft of humerus)
- Also passing through this space with the axillary nerve is the posterior circumflex humeral artery - weaves around surgical neck
- Supplies deltoid muscle and the teres minor muscle as it’s passing through
- Also supples region of skin on lateral aspect of arm - military badge area of arm

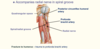
Cephalic Vein
- Like the basilic vein, the cephalic vein also arises from the … venous network of the hand. It ascends the antero-… aspect of the upper limb, passing anteriorly at the elbow.
- At the shoulder, the cephalic vein travels between the deltoid and pectoralis major muscles (known as the deltopectoral groove), and enters the axilla region via the clavipectoral triangle. Within the axilla, the cephalic vein empties into … vein.
- The cephalic and basilic veins are connected at the elbow by the median cubital vein.
- The cephalic vein also arises from the dorsal venous network of the hand. It ascends the antero-lateral aspect of the upper limb, passing anteriorly at the elbow.
- At the shoulder, the cephalic vein travels between the deltoid and pectoralis major muscles (known as the deltopectoral groove), and enters the axilla region via the clavipectoral triangle. Within the axilla, the cephalic vein empties into axillary vein.
- The cephalic and basilic veins are connected at the elbow by the median cubital vein.

Median nerve
- Runs down the arm with the … artery
- Doesn’t innervate anything in the upper arm
- Passes into forearm through the … fossa
- Nerve roots: C6 – T1 (also contains fibres from C5 in some individuals).
- Motor functions: Innervates … forearm and lateral hand
- Sensory functions: Innervates … palm hand and what digits?
- Runs down the arm with the brachial artery
- Doesn’t innervate anything in the upper arm
- Passes into forearm through the cubital fossa ->
- Nerve roots: C6 – T1 (also contains fibres from C5 in some individuals).
- Motor functions: Innervates anterior forearm and lateral hand
- Sensory functions: Innervates lateral palm hand (near thumb), D1,D2,D3 and half of D4
The map shows the cutaenous innervation by terminal branches - match the colour to a nerve
- Grey =
- Pink =
- Green =
- Purple = (from the … cord)
- Blue =
- Yellow =

- Grey = axillary
- Pink = radial
- Green = musculocutaneous
- Purple = medial cutaneous (from the medial cord)
- Blue = ulnar
- Yellow = median

Medial Cord of the Brachial Plexus
- Terminates as … part of median nerve and the … nerve
- Terminates as medial part of median nerve and the ulnar nerve

Lymphatic drainage of the Upper Limb
- Relatively … lymph nodes in upper limb
- Some lymph nodes around elbow beside basilic vein - … nodes
- Some lymph nodes sit beside cephalic vein in the … groove - … node
- Lymph drains to … nodes
- Relatively few lymph nodes in upper limb
- Some lymph nodes around elbow beside basilic vein - cubital nodes
- Some lymph nodes sit beside cephalic vein in the deltopectoral groove - deltopectoral node
- Lymph drains to axillary nodes - sit around our axillary vein