Structure and Function of the Spinal Cord Flashcards
(64 cards)
Anatomy of the spinal cord:
- Spinal cord extends from … to …
- Spinal cord narrows at … to form conus medullaris
- Terminal filum (pia extension) attaches to coccyx
- Space below … … vertebrae - lumbar cistern - will find cauda equina - dorsal and ventral roots of lumbar and sacral spinal nerves
- Spinal cord extends from atlas to L1
- Spinal cord narrows at L1 to form conus medullaris
- Terminal filum (pia extension) attaches to coccyx
- Space below first lumbar vertebrae - lumbar cistern - will find cauda equina - dorsal and ventral roots of lumbar and sacral spinal nerves

Anatomy of the spinal cord:
- Spinal cord extends from atlas to L1
- Spinal cord narrows at L1 to form … …
- Terminal filum (pia extension) attaches to …
- Space below first lumbar vertebrae - lumbar cistern - will find … … - dorsal and ventral roots of lumbar and sacral spinal nerves
- Spinal cord extends from atlas to L1
- Spinal cord narrows at L1 to form conus medullaris
- Terminal filum (pia extension) attaches to coccyx
- Space below first lumbar vertebrae - lumbar cistern - will find cauda equina - dorsal and ventral roots of lumbar and sacral spinal nerves

Anatomy of the spinal cord (2)
- Sits protected within … column (in … canal)
- Surrounded by the …
- Sits protected within vertebral column (in vertebral canal)
- Surrounded by the meninges

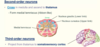
Label the meninges


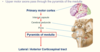
Spinal cord is divided into four regions:

Spinal cord - 4 regions:

… enlargement - innervation to upper limb and … enlargement - innervation to lower limb
Cervical enlargement - innervation to upper limb and lumbosacral enlargement - innervation to lower limb
Lumbar cistern contains what?
contains the cauda equina
Spinal Nerves
- Spinal nerves connect the periphery to the spinal cord
- …. pairs, each formed by a dorsal root (… fibres) and ventral root (…. fibres)
- Spinal nerves connect the periphery to the spinal cord
- 31 pairs, each formed by a dorsal root (afferent fibres) and ventral root (efferent fibres)

Spinal Nerves
- Spinal nerves connect the periphery to the spinal cord
- 31 pairs, each formed by a … root (afferent fibres) and … root (efferent fibres)
- Spinal nerves connect the periphery to the spinal cord
- 31 pairs, each formed by a dorsal root (afferent fibres) and ventral root (efferent fibres)

Internal Anatomy (Spinal cord)
- Inner core, … matter
- Neuronal cell bodies
- H shaped
- Ventral, lateral and dorsal horns(division of H shape)
- Outer, … matter
- … axons
- White columns/tracts/funiculi
- Note the expanded grey matter at levels that supply the limbs
- Inner core, grey matter
- Neuronal cell bodies
- H shaped
- Ventral, lateral and dorsal horns(division of H shape)
- Outer, white matter
- Myelinated axons
- White columns/tracts/funiculi
- Note the expanded grey matter at levels that supply the limbs

Internal Anatomy (Spinal cord)
- … core, grey matter
- Neuronal cell bodies
- … shaped
- Ventral, lateral and dorsal horns (division of … shape)
- …, white matter
- Myelinated …
- White columns/tracts/funiculi
- Note the expanded grey matter at levels that supply the limbs
- Inner core, grey matter
- Neuronal cell bodies
- H shaped
- Ventral, lateral and dorsal horns(division of H shape)
- Outer, white matter
- Myelinated axons
- White columns/tracts/funiculi
- Note the expanded grey matter at levels that supply the limbs

Grey matter organisation
- … horn - neurons receiving sensory input
- … horn - preganglionic sympathetic neurons (autonomic)
- … horn - motor neurons
- Dorsal horn - neurons receiving sensory input
- Lateral horn - preganglionic sympathetic neurons (autonomic)
- Ventral horn - motor neurons

Grey matter organisation
- Dorsal horn - neurons receiving … input
- Lateral horn - preganglionic … neurons (autonomic)
- Ventral horn - … neurons
- Dorsal horn - neurons receiving sensory input
- Lateral horn - preganglionic sympathetic neurons (autonomic)
- Ventral horn - motor neurons

White matter organisation (1)
- Contains tracts
- Long … tracts carry afferent (Sensory) impulses to centres within the brain
- Long … tracts carry efferent (Motor) impulses from centres within brain
- Tracts to/from cerebral hemispheres - … (i.e. left cerebral hemisphere controls right side of body)
- Contains tracts
- Long ascending tracts carry afferent (Sensory) impulses to centres within the brain
- Long descending tracts carry efferent (Motor) impulses from centres within brain
- Tracts to/from cerebral hemispheres - crossed (i.e. left cerebral hemisphere controls right side of body)

White matter organisation (1)
- Contains tracts
- Long ascending tracts carry … (Sensory) impulses to centres within the brain
- Long descending tracts carry … (Motor) impulses from centres within brain
- Tracts to/from … hemispheres - crossed (i.e. … cerebral hemisphere controls …. side of body)
- Contains tracts
- Long ascending tracts carry afferent (Sensory) impulses to centres within the brain
- Long descending tracts carry efferent (Motor) impulses from centres within brain
- Tracts to/from cerebral hemispheres - crossed (i.e. left cerebral hemisphere controls right side of body)

White matter organisation (2)
- … column contains ascending tracts
- … column contains descending and ascending tracts
- … column contains mainly descending tracts
- Dorsal column contains ascending tracts
- Lateral column contains descending and ascending tracts
- Ventral column contains mainly descending tracts

White matter organisation (2)
- Dorsal column contains … tracts
- Lateral column contains … and … tracts
- Ventral column contains mainly … tracts
- Dorsal column contains ascending tracts
- Lateral column contains descending and ascending tracts
- Ventral column contains mainly descending tracts

Ascending (sensory) tracts
- Two types of sensory information carried in these tracts
- …
- Information originating from inside the body (from muscles, joints, tendons)
- …
- Information originating from outside the body (pain, temperature, touch)
- Two types of sensory information carried in these tracts
- Proprioceptive
- Information originating from inside the body (from muscles, joints, tendons)
- Exteroceptive
- Information originating from outside the body (pain, temperature, touch)
Ascending (sensory) tracts
- Two types of sensory information carried in these tracts
- Proprioceptive
- Information originating from … the body (from …, joints, …)
- Exteroceptive
- Information originating from … the body (pain, …, …)
- Two types of sensory information carried in these tracts
- Proprioceptive
- Information originating from inside the body (from muscles, joints, tendons)
- Exteroceptive
- Information originating from outside the body (pain, temperature, touch)
Ascending tracts - anatomy
- Often three neurons in circuit:
- First order (primary sensory) neuron
- Enters spinal cord via … root
- Second order neuron
- Ascends spinal cord or …
- Third order neuron
- Projects to the … …
- First order (primary sensory) neuron
- Often three neurons in circuit:
- First order (primary sensory) neuron
- Enters spinal cord via dorsal root
- Second order neuron
- Ascends spinal cord or brainstem
- Third order neuron
- Projects to the cerebral cortex
- First order (primary sensory) neuron

Ascending tracts - anatomy
- Often three neurons in circuit:
- … order (primary sensory) neuron
- Enters spinal cord via … root
- … order neuron
- Ascends spinal cord or …
- … order neuron
- Projects to the … …
- … order (primary sensory) neuron
- Often three neurons in circuit:
- First order (primary sensory) neuron
- Enters spinal cord via dorsal root
- Second order neuron
- Ascends spinal cord or brainstem
- Third order neuron
- Projects to the cerebral cortex
- First order (primary sensory) neuron

Dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway
- … touch (from cutaneous mechanoreceptors)
- … (from muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs, joints)
- Provides brain with … information
- Fine touch (from cutaneous mechanoreceptors)
- Proprioception (from muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs, joints)
- Provides brain with positional information

Dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway
- Fine touch (from cutaneous …)
- Proprioception (from muscle …, … tendon organs, …)
- Provides brain with positional information
- Fine touch (from cutaneous mechanoreceptors)
- Proprioception (from muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs, joints)
- Provides brain with positional information