Cranial nerves and cranial nerve nuclei Flashcards
(101 cards)


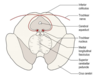
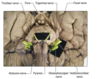
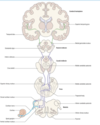
What are the afferent nuclei of the cranial nerves?
Trigeminal
Vestibular
Cochlear
Nucleus solitarius (visceral afferents)
How can the efferent nuclei of the cranial nerves be divided?
On the basis of their embryological derivation, they can be divided into three groups, each lying in a discontinuous longitudinal column
What are the three embryological columns of the efferent cranial nerves?

Somatic efferent cell column
Nuclei of the parasympathetic cell column
Nuclei of the branchimotor cell column
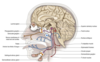
Somatic efferent cell column
Lies near to the midline and consists of the nuclei of the III, IV, VI and XII nerves.
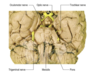
Oculomotor nucleus
Lies in the ventral apex of the periaqueductal grey matter of the midbrain at the level of the superior colliculus.
Its efferent fibres run in the oculomotor nerve to innervate LPS and all of the extraocular muscles except SO and LR
Trochlear nucleus
Midbrain at the ventral border of teh periaquedcutal grey matter, but at the level of the inferior colliculus.
Fibres leave in the trochlear nerve to innervate SO
Abducens nuclei
Located in the caudal pons, beneath the floor of the fourth ventricle.
Innervates LR
Hypoglossal nucleus
In the medulla
Innervates the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue
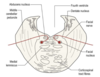
Which are the nuclei of the branchimotor cell column
Innervates striated muscles derived from the branchial arches
Trigeminal motor nucleus
Facial motor nucleus
Nucleus ambiguus
Trigeminal motor nucleus
In the tegmentum of the mid-pons.
Supplies fibres to the trigeminal nerve which innervate the muscles of mastication, tensor tympani, tensor veli palatini, mylohyoid and anterior belly of digastric muscle
Facial motor nucelus
In the caudal pontine tegmentum.
Innervates the muscles of facial expression and stapedius
Nucleus ambiguus
Within the medulla
Sends motor fibres in the GPA, vagus and cranial part of the accessory nerve to innervate the muscles of the pharynx and larynx
Nuclei of the parasympathetic column
Edinger-Westphal
Superior and inferior salivatory nuclei
Dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus
Edinger Westphal
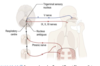
Most rostral cell group which lies in the midbrain periaqueductal grey matter adjacent to the oculomotor nucelus.
Its axons leave in the oculomotor nerve and pass into the cilairy ganglion from which postgnaglionic fibres innervate the sphincter pupillae and ciliary muscles within the eye
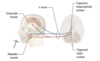
Superior and inferior salivatory nulei
Lie in the pontine tegmentum
Superior salivatory nucleus
Supplies preganglionic fibres to the facial nerve that terminate in the pterygopalatine and submandibular ganglia.
Postganglionic fibres innervate the lacrimal gland nasal and oral mucous membranes.
Those from the submandibular innervate the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands
Inerior salivatory nuclei
Sends preganglionic fibres into GPA which termiante in the otic ganglion, which in turn sends postganglionic axons to the parotid gland
Dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus
Medulla
Rostral portion lies immediately beneath the floor of the fourth ventricle, lateral to hypoglossal.
Fibres leave in the vagus nerve and are widely distributed to thoracic and abdominal viscera
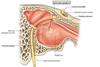
Contents of the oculomotor nerve
Somatoic motor axons that innervate the extraocular muscles.
Also contains preganglionic parasympathetic neruoens that control the smooth muscle of the eye via the ciliary ganglion
Passage of oculomotor neurones in the brainstem.
Oculomotor nucleus and Edinger Westphal.
Course ventrally through the midbrain tegmentum, with many of them traversing the red nucleus to exit on the medial aspect of the crus cerebri within the interpeduncular fossa

At what site does the oculomotor nerve leave the midbrain?
On the medial aspect of the crus cerebri within the interpeduncular fossa, passing between PCA and SCA
Oculomotor course after leaving the brainstem
Runs anteriorly, lying in the wall of the cavernous sinus, before gaining access to the orbit through the superior orbital fissure.
Somatic motor function of oculomotor
Elevates, depresses and adducts the eyeball.
Elevates upper eyelid.