Ventricular System Flashcards
(32 cards)

Location of the fourth ventricle
On the dorsal surface of the brainstem beneath the cerebellum
Shape of the fourth ventricle
Rhomboid
What is found on each side of the fourth ventricle
Lateral recess which extends towards the lateral margin of the brainstem and is continuity through a small lateral aperture with the subarachnoid space of the CPA (Foramen of Luschka)
Foramen Luschka
Lateral communication between fourth ventricle in arachnoid space of CPA.
Structure of the roof of the fourth ventricle?
For the most part, the roof is made up of the cerebellum.
However, the roof of the caudal part consitsts of pia and ependyma, a central defect in which constitutes the median aperture or foramen Magendie, which provides communication between the ventricle and the cisterna magna of the subarachnoid space.
The rostral part of the roof of the fourth is partly formed by the superior cerebellar peduncles on either side, with the space between them bridged by the thin superior medullary velum
Foramen of Magendie
Median aperture of fourth ventricle at its caudal end which allows communication with the cisterna magna
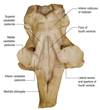

Foramen of Magendie
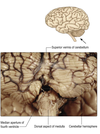
Rostral extent of the fourth ventrcile
Extends as far as the pontomesencephalic junction, where it becomes continuous with the cerebral aqueduct.
Location of cerebral aqeuduct
Passes throughout the length of the midbrain, beneath the inferior and superior colliculi (tectum)
Walls of the third ventricle
Thalamus and hypothalamus
Intermediate mass/commsiure
Adhesion between the medial surfaces of the two thalami across the third ventircle
Roof of the third ventricle
Pia-ependyma which spans between the two nerve fibre bundles, striae medullaris thalami which are situated along the dorsomedial bordder of the thalamus.
Location of the foramen Monro
Between the column of the fornix and the anterior pole of the thalamus
Def: anterior horn
Part of the lateral ventricle lying anyerior to the interventricular foramne.
Lateral wall of the anterior horn of the lateral ventricle
Head of the caudate nucleus
Medial wall of lateral ventricle
Septum pallucidum
Floor of the body of the lateral ventricle
Thalamus
Tail of the caudate nucleus.
What is found in the floor of the inferior horn
Hippocampus
What is found in the roof of the temporal horn of the lateral venrricle
Attenuated tail of caudate nucleus
Location of the choroid plexus
Lateral, third, fourth ventricles.
Formation of the choroid plexus
Formed by the invagination of the vascular pia mater into the ventricular lumen, where it becomes highly convoluted, producing a sponge like appearance.
Entry of the choroid plexus to the third and fourth ventricles
Through their roofs.