Thalamus Flashcards
(63 cards)
Components of the forebrain
Telencephalon
Diencephalon
Composition of the diencephalon from rostral to caudal
Epithalamus
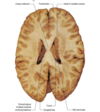
Thalamus
Subthalamus
Hypothalamus
What is found immediately caudal to the optic chiasm?
Small midline elevation, the tuber cinereum.
From its apex extends the infundibulum or pituatry stalk which attaches to the pituitary gland
What is found caudal to the tuber cinereum
A pair of rounded eminences, the mamillary bodies.
These contain the mamillary nuclei of the hypothalamus.


What forms the lateral wall of the third ventricle?
The diencephalon.
The dorsal part formed by the thalamus and the ventral, the hypothalamus.
Epithalamus
Relatively small part of the diencephalon located in its most caudal and dorsal region, immediately rostral to the superior colliculus of the midbrain.
It consists principally of the pineal gland and the habenula (habenular nuclei)
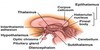
Pineal gland
Implicated in control of sleep/waking.
Synthesises the hormone melatonin
Habenular nuclei
Have connections with the limbic system









Subthalamus
Lies beneath the thalamus and dorsolateral to the hypothalamus with its ventrolateral aspect against the internal capsule
What are the two notable cell groups of the subthalamus
Subthalamic nucelus
Zona incerta
Subthalamic nucleus
Located in the ventrolateral part of the subthalamus, immediately medial tom the internal capsule.
It has a shape of a biconvex lens in coronal section.
It has prominent conections with the globus pallidus and the substantia nigra and is important in the control of movement.
Zona incerta
Rostral extension of the brainstem reticular formation.
Relationship of ascending sensory pathways to the subthalamus
Several important fibre systems traverse the subthalamus en route to the thalamus. These include the medial lemniscus, spinothalamic and trigeminothalamic tracts, cerebellothalamic fibres from the dentate nucleus and pallidothalamic fibres from the internal segment of Globus pallidus.
The latter group of fibres envelop the zona incerta as the lenticular fasciculis and thalamic fasciculus
What demarcates the hypothalamus from the thalamus
A faint groove, the hypothalamic sulcus
Massa intermdia
The interthalamic adhesion across the third ventricle.
Stria medullaris
A fascicle of nerve fibres which has limbic connections that courses along the dorsomedial margin of the thalamus. Along this line, the ependymal lining of the third ventricle spans the narrow lumen to form the vnetricular roof.
To where does the anterior pole of the thalamus extend?
As far as the intervetricular foramen, through which the third and lateral ventricles are in continuity.
What is found lateral to the thalamus?
Posterior limb of the internal capsule