Introduction and Overview Flashcards
(76 cards)
How many neurones are there in the human nervous system?
10^10
Numerical relationship between neurones and neuroglial cells
Neuroglial cells outnumber neurones by an order of magnitude
Ganglia=
Aggregation of nerve cell bodies
RMP of a neurone
~70mV
From which embryological layer is the nervous system derived?
Ectoderm gives rise to nervous system and skin
Neurulation
Process of formation of the embryonic nervous system
When does the neural plate form?
The dorsal midline ectoderm undergoes thickening to form the neural plate during the third week of embryonic development
Arrangement of the neural plate
The lateral margins become elevated to form the neural folds on either side of a longitudinal midline depression called the neural groove.
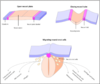
Formation of the neural tube
Neural folds become apposed and fuse. Some cells from the apices form the neural folds become separated to form the groups lying dorsolateral to the neural tube. These are known as neural crests.
The formation of neural tube is complete by the middle of the fourth week of embryonic development.
Fate of neural crest cells
Form the sensory ganglia of the spinal and cranial nerves and also the autonomic ganglia
Sulcus limitans
Longitudinal groove which appears on the inner surface of the lateral walls of the embronyic spinal cord and caudal part of the brain.
The dorsal and ventral cell groupings are thus delinated as the alar plate and basal plate

Alar plate->
Predominantly sensory
Basal plate
Predominantly motor
Arrangement of neuronal cell groups in alar plate from ventral to dorsal
General visceral afferent
Special visceral afferent
General somatic afferent
Special somatic afferent
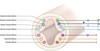
Arrangement of neuronal cell groups (efferent) in the basal plate from ventral to dorsal
Somatic efferent
Branchial efferent
General visceral efferent

Special somatic afferent
Associated with developing inner ear and ultimately receing auditory and vestibular input
General somatic afferent
Receiving general sensory input from the periphery
Special visceral afferent
Subserving the sense of taste
General visceral afferent
Receiving afferent input from the viscera
General visceral efferent
Preganglionic autonomic efferents
Branchial efferent
Containing motor neurones to muscles derived from branchial arches
Somatic efferent
Motor neurones to somatic muscles
What are the three primary brain vesicles?
Prosencephalon
Mesencephalon
Rhombencephalon

What are the two flexures of the developing CNS
Cephalix flexure
Cervical flexure












