Visual System Flashcards
(16 cards)
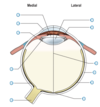
Arrangement of muscle fibres of the iris
Some are in a circular fashion, innervated by PNS which constrict the pupil, reducing the amount of light
Some in a radial fashion innervated by SNS which cause pupillary dilation
What is found behind the iris?
The ciliary body which contains the ciliary muscle and receives innervation from the PNS
Action of ciliary muscle
Contraction of the ciliary muscle, alters the shape and focussing power of the lens, a process known as accommodation.
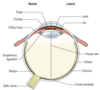
Division of the eye
The lens and suspensory ligament divide the lumen of the eyeball into an anterior and posterior part.
The anterior part contains an aqueous humour which is continuously secreted from the canal of Schelmm
Posterior part of the eye
Contains vitreous humour. The inner surface of the sclera is lined with choroid wich contains dark pigment and thus reduces reflection within the eye.
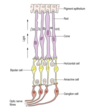
Structural arrangement of the retina
Contains a non neural and neural portion.
The non-neural part is represented by the pigment epithelium, a singler layer of light absorbing pigmented cells which lie adjacent to the choroid.
The photoreceptive cells lie deepest within the retina and interdigitate with the pigment epithelium.
Rods
Light
Cones
Colour
What is the first order cell of the central visual pathway?
The bipolar cell, which lies within the retina.
Formation of the optic nerve
Formed by the second order neurones or the ganglion cells.
infromation is transferred from bipolar cells then to ganglion cells with greater convergence for rods than cones
Horizontal cells and amacrine cells
Modulate transmission between photoreceptors and bipolar cells and between bipolar cells and ganglions respsectively.
Location of the optic chiasm
Immediately rostral to the tuber cinereum of the hypothalamu and between the termianting internal carotid arteries
Passage of the optic tracts
Diverge away from the chiasm and pass round the cerebral peduncle to terminate mainly in the LGN of the thalamus.
A relatively small number of fibres leave the optic nerve before reaching hte LGN to termiante in the pretectal area of the superior colliculus. These fibres are involved in mediation of the pupilalry light reflex.
Passage of fibres from the LGN
Third order thalamocortical neurones project through the retrolenticular part of the internal capsule, forming the optic radiation which terminates in the visual cortex of the occipital lobe.
Representation of the retina in the cortex
There is a precise point to point relationship between the retina and the visual cortex. Because of the importance of the macula in vision, it is represented disproportionately largely in relation to its size in the LGN and vsiual cortex with its region found most posteriorly in the region of the occipital pole


