Chemical Pathology 14 - Acute and Chronic Renal failure 1 & 2 Flashcards
(59 cards)
What is the best measure of kidney function?
GFR
What is a normal GFR?
120mls/ min
Define clearance and how to measure it
volume of plasma that can be completely cleared of a marker substance per unit time
if marker a)not bound to proteins, b)not freely filtered by glomerulus, c)not secreted or reabsorbed by tubular cells then gfr = clearnce
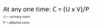
What is the gold-standard measure of GFR?
Inulin clearance
but required steady state infusion so reserved for research
What are some exogenous measure of GFR?
51Cr-EDTA and 99Tc-DTPA
How can plasma creatinine be used to estimate GFR?
Clearance = P(U x V) P = plasma concentration U = urinary concentration V = plasma volume
What are some endogenous markers of GFR?
blood urea
creatinine
cystatin C
What would invalidate a creatinine-based measurement of GFR?
non linear creatinine:GFR relationship (↓GFR → creatinine less acurate at predicting precise GFR)
rate of creatinine generation affected by many factors
- Muscularity (proportional to mass) - main factor
- Age
- Sex (higher in men)
- Ethnicity (higher in Afro-Caribbean)
Why does plasma urea have a limited clinical value for measuring renal function?
variable resorption
dependent on nutritional state, hepatic function, GI bleeding
Describe the movement of creatinine from blood to urine
Freely filtered
Actively transported into urine by tubular cells
What equation can be used to refine your interpretation of creatinine clearance?
Cockcroft Gault Equation
- age + weight + gender
- May overestimate GFR (esp <30mL/min)
Estimated GFR adjusted equation / MDRD
- age + sex + creatinine + ethnicity
CKD-Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI)
- age + sex + creatinine + ethnicity(modelled slightly differently)

What is the equation for estimated creatinine clearance with the Cockroft Gault adjustment?
((1.23 x (140- age) x weight))/ serum creatinine
Adjust by 0.85 if female
What is cystatin C, and why is it particularly useful?
constitutively produced by all nucleated cells at a constant rate and is freely filtered
Almost completely reabsorbed and catabolised by tubular cells
Alternative to creatinine clearance
Largely unaffected by muscle mass/ gender/ age
In what condition does cystatin C not give a reliable result for GFR estimation?
Hypo/ hyperthyroidism
How can proteinuria be quantified?
Spot urine measurement
What can a 24-hour urine collection be used for?
- Creatinine clearance estimation
- Examination for stone-forming elements
- Proteinuria quantification (but this can also be done on spot urine testing)
- Electrolyte estimation (but this can also be done on spot urine testing)
CAn you reliably exclude bacteraemia if leucocyte esterase and nitrie is negative?
Yes - leucocyte esterase
No - nitrites
What is the preferred method for assessing urine protein creatinine ratio?
spot urine measurement > 24 collection
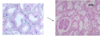
What does this urine microscopy show?

calcium oxalate crystals
What does this urine microscopy show?

RBCs - malignancy/infection
What does this urine microscopy show?
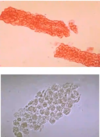
casts - fuzzy burritos (glomeraular dysfunction)
What does this urine microscopy show?
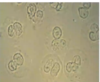
WBCs - multi nucleate cells
What does this urine microscopy show?

bacteria
What is the first choice of imaging in a suspected renal stone?
CT KUB
2nd - USS KUB (AKI/hydronephrosis)