Haematology 5 - Haemolytic anaemias Flashcards
(36 cards)
Recall some causes of intravascular vs extravascular haemolytic anaemias
Intravascular:
- Malaria (black water fever)
- G6PDD
- MAHA (due to HUS/TTP/PNH)
- ABO haemolysis
Extravascular:
- Autoimmune
- hereditary spherocytosis
Which infection are patients with haemolytic anaemias more susceptibile to?
Parvovirus B19
What is hepatic siderosis indicative of?
haemolytic anaemia

What laboratory results can you expect in haemolytic anaemia?
anaemia, reticulocytosis, polychromasia
↑ BR, ↑ LDH, ↓ haptoglobins, haemoglobinuria, haemosiderinuria
What is the inheritance pattern of hereditary spherocytosis?
Autosomal dominant
Recall the pathophysiology of hereditary spherocytosis
Spectrin or ankyrin deficiency → problems in RBC cytoskeleton
Extravascular haemolysis
How can hereditary spherocytosis be diagnosed?
osmotic fragility test: ↑ sensitivity to lysis in hypotonic saline
Di-binding test (eosin-5-maleimide / EMA)→ ↓ binding
pathology slide = lack of central pallor
What is the difference in clinical features of hereditary elliptocytosis in a heterozygote vs a homozygote?
Heterozygote: no polychromasia
Homozygote: Severe haemolytic anaemia (pyropoikilocytosis)

Recall the pathophysiology of hereditary elliptocytosis
spectrin mutation
In which parts of the world is G6PDD most common?
Where malaria is endemic
What is the inheritance pattern of G6PDD?
X linked recessive
What is the normal physiological role of G6PD?
catalyses 1st step in pentose phosphate pathway (to generate NADPH)
What is the main symptom of G6PDD in neonates?
Neonatal jaundice (otherwise asymptomatic)
Recall 3 triggers for a crisis in G6PDD
Acute haemolysis - triggered by:
haemoglobunirua
Anti-malarials (Primaquine)
Antibiotics (sulphonamides, ciprofloxacin, nitrofurantoin)
Other (Dapsone, Vitamin K)
Fava beans and mothballs
Infections
Recall features of G6PD deficiency on blood film
Bite cells, hemi-ghosts, nucleated RBCs, Heinz bodies (methyl violet stain)

What is the typical appearance of erythrocytes in Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency?
echinocytes (hedgehog) and spherocytes on slide
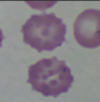
What is the typical appearance of erythrocytes in Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency?
basophilic inclusions on slide

What is the first investigation to do in haemolytic anaemia?
DAT/ Coombs test
Positive = autoimmune haemolysis
What does a positive urinary haemosiderin test show?
Intravascular haemolysis
What is the osmotic fragility test used to detect?
Hereditary spherocytosis
What is homozygous hereditary elliptocytosis also known as?
Pyropoikilocytosis
What do Heinz bodies indicate?
denatured haemoglobin - G6PDD
Differentiate the class of immunoglobin involved in warm vs cold AIHA
Warm: IgG
Cold: IgM
Recall the causes of warm vs cold AIHA
warm - mainly primary idiopathic, lymphoma, CLL, SLE, methyldopa
cold - primary idiopathic, lymphoma, infections: EBV, mycoplasma


