Microbiology 12 - Wound, bone and joint infections Flashcards
(34 cards)
What are the major pathogens causing surgical site infections?
Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA and MRSA)
Escherichia coli
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
At what point is SSI risk increased?
surgical site contaminated with >10^5 microorganisms / gram of tissue
What are the 3 levels of wound infection?
Superficial incisional (skin and subcutaneous tissue) Deep incisional (fasical and muscle layers) Organ/ space infection
What is the likely organism for SSI if there is a Gram +ve, haemolytic coccus visualised?
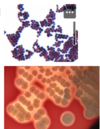
MRSA
What is the treatment for MRSA SSI?
IV linezolid
Recall 2 important risk factors for wound/ bone/ joint infection
Diabetes
Obesity (adipose tissue is poorly-vascularised)
age
Rheumatoid arthritis (stoop DMARDs before operation)
Smoking (nicotine delays wound healing and → PVD = poor vascularisation)
How does shaving affect risk of SSI?
Shaving ↑ risk (micro-abrasions multiply bacteria)
What can be done during orthpaedic procedures to reduce risk of infection?
Laminar flow
What is the MOST POWERFUL risk factor for SSI following cardiothoracic surgery?
Staph aureus nasal carriage
Nasal decontamination should be offered if they are found to be carrying S. aureus
How does body temperature affect the risk of surgical site infections?
hypothermia → vasoconstriction → ↓O2 → impaired neutrophil function
Which patient group is particularly at risk of septic arthritis?
- Rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, crystal arthritis
- Joint prosthesis
- IVDU
- Diabetes, chronic renal disease, chronic liver disease
- Immunosuppression (e.g. steroids)
- Trauma – intra-articular injection, penetrating injury
Where in the joint do organisms adhere to in septic arthritis?
Synovial membrane
Bacterial proliferation in synovial fluid → inflammatory response → joint damage
Joint damage → exposure of host derived protein (e.g. fibronectin) to which bacteria can adhere
What are some bacterial factors which may increase the risk of septic arthritis?
S aureus
- fibronectin-binding protein that recognise selected host proteins
- cytotoxin PVL → fulminant infection
Kingella kingae synovial adherence is via bacterial pili
What are some host factors which may increase the risk of septic arthritis?
- Leucocyte derived proteases and cytokines → cartilage and bone damage
- Raised intra-articular pressure impedes capillary blood flow → cartilage and bone ischaemia/necrosis
- Genetic deletion of macrophage-derived cytokines → reduce host-response in S. aureus sepsis
- Absence IL-10 increases severity of staphylococcus joint disease
Recall some causative organisms for septic arthritis
Staphylococcus aureus 46%
Streptococci: pyogenes, pneumoniae, agalactiae
Gram-negative organisms: Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria gonorrhoea, Salmonella
Coagulase-negative staphylococci 4%
rare: Lyme disease, Brucellosis, Mycobacteria, Fungi Rare
What are the symptoms of septic arthritis?
Red, painful and swollen joint with *restricted movement*
Monoarticular in 90%
Knee is involved in 50%
What investigations for septic arthritis should be done before starting antibiotics?
- Blood cultures
- Synovial fluid aspiration (synovial count >50,000 WBC/mL is used to suggest septic arthritis) - USS guided
When is MRI indicated for septic arthritis patients and what would it show?
When osteomyelitis is suspected
joint effusion, articular cartilage destruction, abscess, contiguous osteomyelitis
How is septic arthritis managed?
IV cephalosporin or flucoxacillin, up to 6 weeks (outpatient setting)
may need to +vancomycin (if high risk MRSA)
OPAT (outpatient parenteral Abx team)
Drainage - arthoscopic washout
What are the symptoms of spinal osteomyelitis/epidural abscess?
Back pain and fever
Neuro impairment
Where is Spinal osteomyelitis / epidural abscess most commonly localised?
Lumbar (43.1%)
Cervical (10.6%)
Cervico-thoracic (0.4%)
Recall the pathophysiology of spinal osteomyelitis/epidural abscess
Acute haematogenous spread (bacteraemia)
Exogenous (after disc surgery, implant associated)
what are the most common causative organisms for spinal osteomyelitis/epidural abscess?
- Staphylococcus aureus (48.3%)
- Streptococcus
- Gram-negative rods
- Coagulase-negative staphylococcus
How is vertebral osteomyelitis treated?
At least 6w of antibiotics



